Yixiong Meng
On the Practice of Deep Hierarchical Ensemble Network for Ad Conversion Rate Prediction
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:The predictions of click through rate (CTR) and conversion rate (CVR) play a crucial role in the success of ad-recommendation systems. A Deep Hierarchical Ensemble Network (DHEN) has been proposed to integrate multiple feature crossing modules and has achieved great success in CTR prediction. However, its performance for CVR prediction is unclear in the conversion ads setting, where an ad bids for the probability of a user's off-site actions on a third party website or app, including purchase, add to cart, sign up, etc. A few challenges in DHEN: 1) What feature-crossing modules (MLP, DCN, Transformer, to name a few) should be included in DHEN? 2) How deep and wide should DHEN be to achieve the best trade-off between efficiency and efficacy? 3) What hyper-parameters to choose in each feature-crossing module? Orthogonal to the model architecture, the input personalization features also significantly impact model performance with a high degree of freedom. In this paper, we attack this problem and present our contributions biased to the applied data science side, including: First, we propose a multitask learning framework with DHEN as the single backbone model architecture to predict all CVR tasks, with a detailed study on how to make DHEN work effectively in practice; Second, we build both on-site real-time user behavior sequences and off-site conversion event sequences for CVR prediction purposes, and conduct ablation study on its importance; Last but not least, we propose a self-supervised auxiliary loss to predict future actions in the input sequence, to help resolve the label sparseness issue in CVR prediction. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to previous single feature crossing modules with pre-trained user personalization features.
Graph-based Multi-View Fusion and Local Adaptation: Mitigating Within-Household Confusability for Speaker Identification
Jul 08, 2022


Abstract:Speaker identification (SID) in the household scenario (e.g., for smart speakers) is an important but challenging problem due to limited number of labeled (enrollment) utterances, confusable voices, and demographic imbalances. Conventional speaker recognition systems generalize from a large random sample of speakers, causing the recognition to underperform for households drawn from specific cohorts or otherwise exhibiting high confusability. In this work, we propose a graph-based semi-supervised learning approach to improve household-level SID accuracy and robustness with locally adapted graph normalization and multi-signal fusion with multi-view graphs. Unlike other work on household SID, fairness, and signal fusion, this work focuses on speaker label inference (scoring) and provides a simple solution to realize household-specific adaptation and multi-signal fusion without tuning the embeddings or training a fusion network. Experiments on the VoxCeleb dataset demonstrate that our approach consistently improves the performance across households with different customer cohorts and degrees of confusability.
Building Synthetic Speaker Profiles in Text-to-Speech Systems
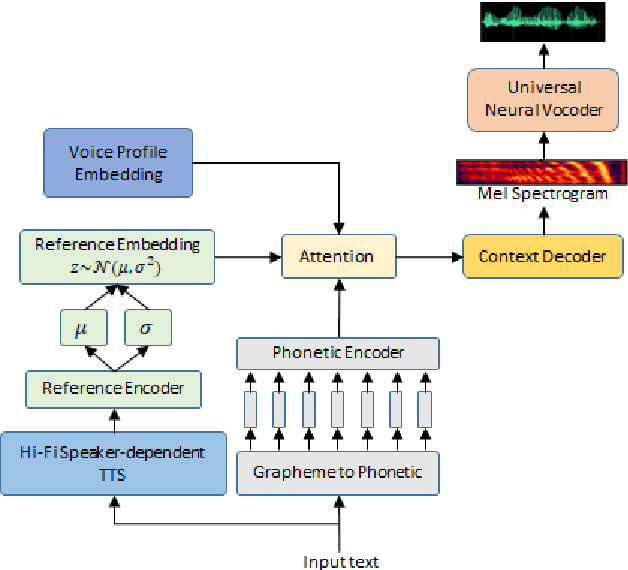
Feb 07, 2022Abstract:The diversity of speaker profiles in multi-speaker TTS systems is a crucial aspect of its performance, as it measures how many different speaker profiles TTS systems could possibly synthesize. However, this important aspect is often overlooked when building multi-speaker TTS systems and there is no established framework to evaluate this diversity. The reason behind is that most multi-speaker TTS systems are limited to generate speech signals with the same speaker profiles as its training data. They often use discrete speaker embedding vectors which have a one-to-one correspondence with individual speakers. This correspondence limits TTS systems and hinders their capability of generating unseen speaker profiles that did not appear during training. In this paper, we aim to build multi-speaker TTS systems that have a greater variety of speaker profiles and can generate new synthetic speaker profiles that are different from training data. To this end, we propose to use generative models with a triplet loss and a specific shuffle mechanism. In our experiments, the effectiveness and advantages of the proposed method have been demonstrated in terms of both the distinctiveness and intelligibility of synthesized speech signals.
SynthASR: Unlocking Synthetic Data for Speech Recognition
Jun 14, 2021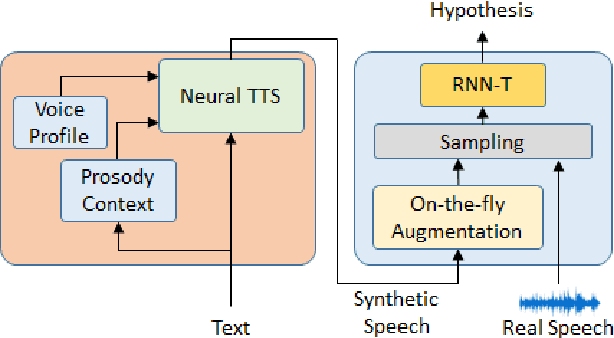
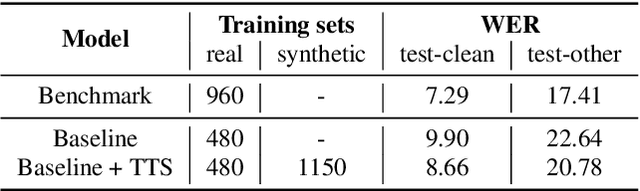
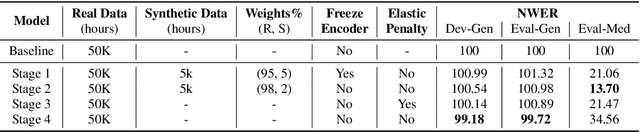
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) models have recently demonstrated superior performance over the traditional hybrid ASR models. Training an E2E ASR model requires a large amount of data which is not only expensive but may also raise dependency on production data. At the same time, synthetic speech generated by the state-of-the-art text-to-speech (TTS) engines has advanced to near-human naturalness. In this work, we propose to utilize synthetic speech for ASR training (SynthASR) in applications where data is sparse or hard to get for ASR model training. In addition, we apply continual learning with a novel multi-stage training strategy to address catastrophic forgetting, achieved by a mix of weighted multi-style training, data augmentation, encoder freezing, and parameter regularization. In our experiments conducted on in-house datasets for a new application of recognizing medication names, training ASR RNN-T models with synthetic audio via the proposed multi-stage training improved the recognition performance on new application by more than 65% relative, without degradation on existing general applications. Our observations show that SynthASR holds great promise in training the state-of-the-art large-scale E2E ASR models for new applications while reducing the costs and dependency on production data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge