Koushik Sen
Let the Barbarians In: How AI Can Accelerate Systems Performance Research
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) is beginning to transform the research process by automating the discovery of new solutions. This shift depends on the availability of reliable verifiers, which AI-driven approaches require to validate candidate solutions. Research focused on improving systems performance is especially well-suited to this paradigm because system performance problems naturally admit such verifiers: candidates can be implemented in real systems or simulators and evaluated against predefined workloads. We term this iterative cycle of generation, evaluation, and refinement AI-Driven Research for Systems (ADRS). Using several open-source ADRS instances (i.e., OpenEvolve, GEPA, and ShinkaEvolve), we demonstrate across ten case studies (e.g., multi-region cloud scheduling, mixture-of-experts load balancing, LLM-based SQL, transaction scheduling) that ADRS-generated solutions can match or even outperform human state-of-the-art designs. Based on these findings, we outline best practices (e.g., level of prompt specification, amount of feedback, robust evaluation) for effectively using ADRS, and we discuss future research directions and their implications. Although we do not yet have a universal recipe for applying ADRS across all of systems research, we hope our preliminary findings, together with the challenges we identify, offer meaningful guidance for future work as researcher effort shifts increasingly toward problem formulation and strategic oversight. Note: This paper is an extension of our prior work [14]. It adds extensive evaluation across multiple ADRS frameworks and provides deeper analysis and insights into best practices.
GSO: Challenging Software Optimization Tasks for Evaluating SWE-Agents
May 29, 2025Abstract:Developing high-performance software is a complex task that requires specialized expertise. We introduce GSO, a benchmark for evaluating language models' capabilities in developing high-performance software. We develop an automated pipeline that generates and executes performance tests to analyze repository commit histories to identify 102 challenging optimization tasks across 10 codebases, spanning diverse domains and programming languages. An agent is provided with a codebase and performance test as a precise specification, and tasked to improve the runtime efficiency, which is measured against the expert developer optimization. Our quantitative evaluation reveals that leading SWE-Agents struggle significantly, achieving less than 5% success rate, with limited improvements even with inference-time scaling. Our qualitative analysis identifies key failure modes, including difficulties with low-level languages, practicing lazy optimization strategies, and challenges in accurately localizing bottlenecks. We release the code and artifacts of our benchmark along with agent trajectories to enable future research.
Type-Constrained Code Generation with Language Models
Apr 12, 2025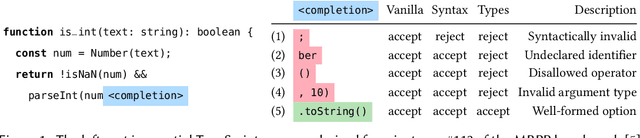
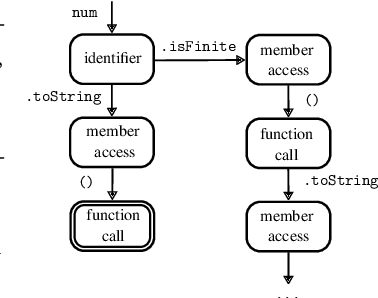
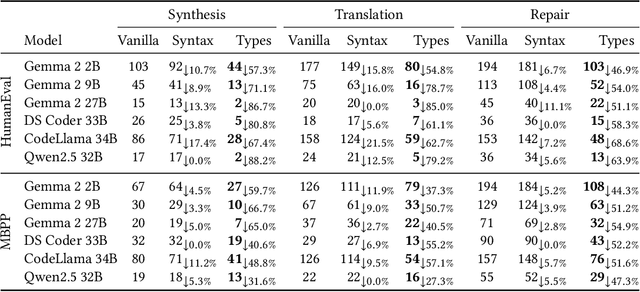
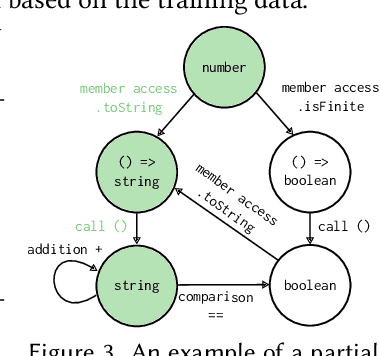
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved notable success in code generation. However, they still frequently produce uncompilable output because their next-token inference procedure does not model formal aspects of code. Although constrained decoding is a promising approach to alleviate this issue, it has only been applied to handle either domain-specific languages or syntactic language features. This leaves typing errors, which are beyond the domain of syntax and generally hard to adequately constrain. To address this challenge, we introduce a type-constrained decoding approach that leverages type systems to guide code generation. We develop novel prefix automata for this purpose and introduce a sound approach to enforce well-typedness based on type inference and a search over inhabitable types. We formalize our approach on a simply-typed language and extend it to TypeScript to demonstrate practicality. Our evaluation on HumanEval shows that our approach reduces compilation errors by more than half and increases functional correctness in code synthesis, translation, and repair tasks across LLMs of various sizes and model families, including SOTA open-weight models with more than 30B parameters.
R2E-Gym: Procedural Environments and Hybrid Verifiers for Scaling Open-Weights SWE Agents
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Improving open-source models on real-world SWE tasks (solving GITHUB issues) faces two key challenges: 1) scalable curation of execution environments to train these models, and, 2) optimal scaling of test-time compute. We introduce AgentGym, the largest procedurally-curated executable gym environment for training real-world SWE-agents, consisting of more than 8.7K tasks. AgentGym is powered by two main contributions: 1) SYNGEN: a synthetic data curation recipe that enables scalable curation of executable environments using test-generation and back-translation directly from commits, thereby reducing reliance on human-written issues or unit tests. We show that this enables more scalable training leading to pass@1 performance of 34.4% on SWE-Bench Verified benchmark with our 32B model. 2) Hybrid Test-time Scaling: we provide an in-depth analysis of two test-time scaling axes; execution-based and execution-free verifiers, demonstrating that they exhibit complementary strengths and limitations. Test-based verifiers suffer from low distinguishability, while execution-free verifiers are biased and often rely on stylistic features. Surprisingly, we find that while each approach individually saturates around 42-43%, significantly higher gains can be obtained by leveraging their complementary strengths. Overall, our approach achieves 51% on the SWE-Bench Verified benchmark, reflecting a new state-of-the-art for open-weight SWE-agents and for the first time showing competitive performance with proprietary models such as o1, o1-preview and sonnet-3.5-v2 (with tools). We will open-source our environments, models, and agent trajectories.
Challenges and Paths Towards AI for Software Engineering
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:AI for software engineering has made remarkable progress recently, becoming a notable success within generative AI. Despite this, there are still many challenges that need to be addressed before automated software engineering reaches its full potential. It should be possible to reach high levels of automation where humans can focus on the critical decisions of what to build and how to balance difficult tradeoffs while most routine development effort is automated away. Reaching this level of automation will require substantial research and engineering efforts across academia and industry. In this paper, we aim to discuss progress towards this in a threefold manner. First, we provide a structured taxonomy of concrete tasks in AI for software engineering, emphasizing the many other tasks in software engineering beyond code generation and completion. Second, we outline several key bottlenecks that limit current approaches. Finally, we provide an opinionated list of promising research directions toward making progress on these bottlenecks, hoping to inspire future research in this rapidly maturing field.
LangProBe: a Language Programs Benchmark
Feb 27, 2025
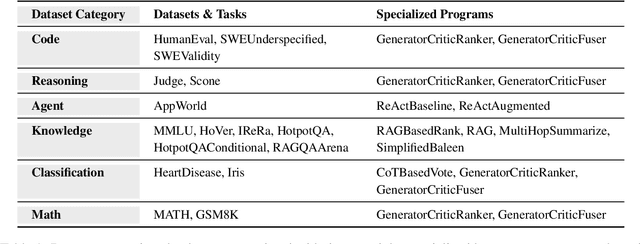
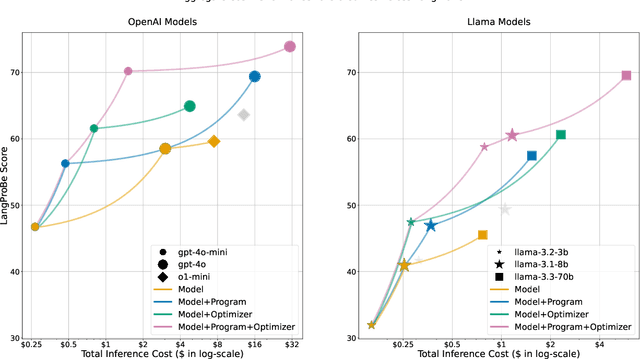
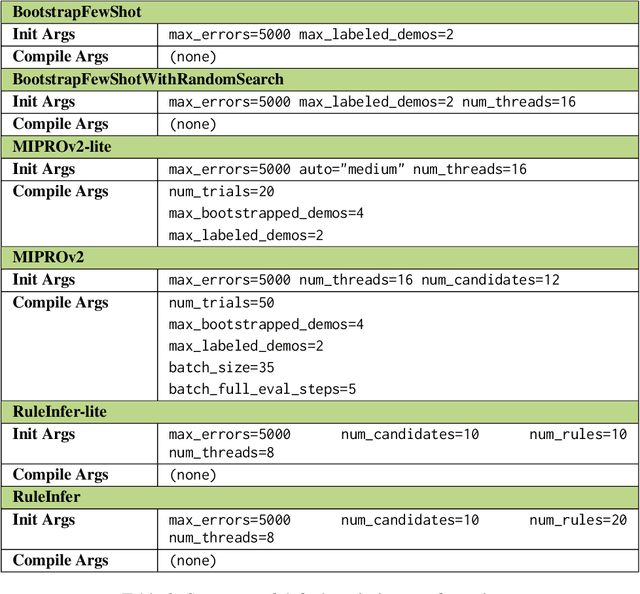
Abstract:Composing language models (LMs) into multi-step language programs and automatically optimizing their modular prompts is now a mainstream paradigm for building AI systems, but the tradeoffs in this space have only scarcely been studied before. We introduce LangProBe, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating the architectures and optimization strategies for language programs, with over 2000 combinations of tasks, architectures, optimizers, and choices of LMs. Using LangProBe, we are the first to study the impact of program architectures and optimizers (and their compositions together and with different models) on tradeoffs of quality and cost. We find that optimized language programs offer strong cost--quality Pareto improvement over raw calls to models, but simultaneously demonstrate that human judgment (or empirical decisions) about which compositions to pursue is still necessary for best performance. We will open source the code and evaluation data for LangProBe.
Syzygy: Dual Code-Test C to (safe) Rust Translation using LLMs and Dynamic Analysis
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Despite extensive usage in high-performance, low-level systems programming applications, C is susceptible to vulnerabilities due to manual memory management and unsafe pointer operations. Rust, a modern systems programming language, offers a compelling alternative. Its unique ownership model and type system ensure memory safety without sacrificing performance. In this paper, we present Syzygy, an automated approach to translate C to safe Rust. Our technique uses a synergistic combination of LLM-driven code and test translation guided by dynamic-analysis-generated execution information. This paired translation runs incrementally in a loop over the program in dependency order of the code elements while maintaining per-step correctness. Our approach exposes novel insights on combining the strengths of LLMs and dynamic analysis in the context of scaling and combining code generation with testing. We apply our approach to successfully translate Zopfli, a high-performance compression library with ~3000 lines of code and 98 functions. We validate the translation by testing equivalence with the source C program on a set of inputs. To our knowledge, this is the largest automated and test-validated C to safe Rust code translation achieved so far.
LiveCodeBench: Holistic and Contamination Free Evaluation of Large Language Models for Code
Mar 12, 2024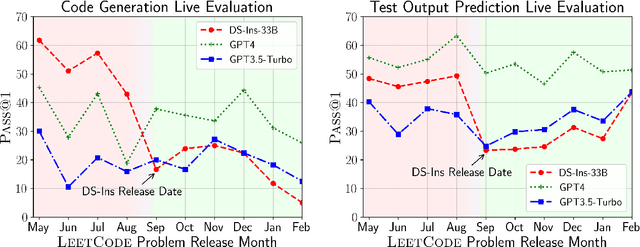


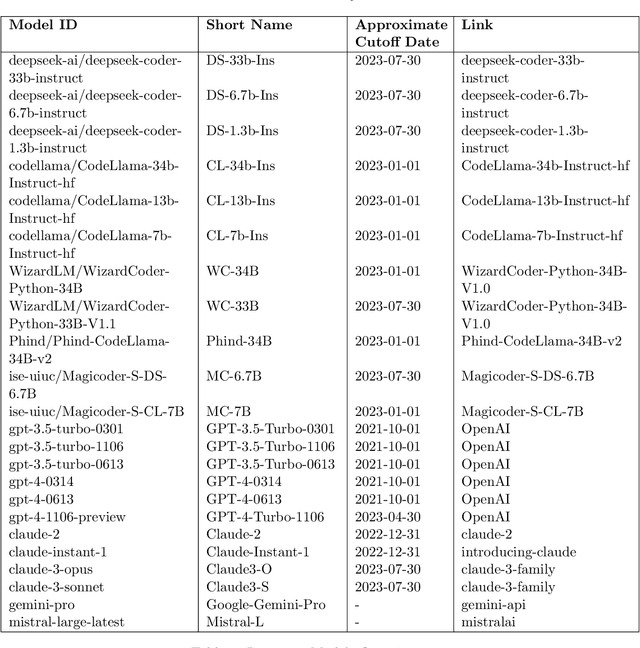
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) applied to code-related applications have emerged as a prominent field, attracting significant interest from both academia and industry. However, as new and improved LLMs are developed, existing evaluation benchmarks (e.g., HumanEval, MBPP) are no longer sufficient for assessing their capabilities. In this work, we propose LiveCodeBench, a comprehensive and contamination-free evaluation of LLMs for code, which continuously collects new problems over time from contests across three competition platforms, namely LeetCode, AtCoder, and CodeForces. Notably, our benchmark also focuses on a broader range of code related capabilities, such as self-repair, code execution, and test output prediction, beyond just code generation. Currently, LiveCodeBench hosts four hundred high-quality coding problems that were published between May 2023 and February 2024. We have evaluated 9 base LLMs and 20 instruction-tuned LLMs on LiveCodeBench. We present empirical findings on contamination, holistic performance comparisons, potential overfitting in existing benchmarks as well as individual model comparisons. We will release all prompts and model completions for further community analysis, along with a general toolkit for adding new scenarios and model
The Counterfeit Conundrum: Can Code Language Models Grasp the Nuances of Their Incorrect Generations?
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:While language models are increasingly more proficient at code generation, they still frequently generate incorrect programs. Many of these programs are obviously wrong, but others are more subtle and pass weaker correctness checks such as being able to compile. In this work, we focus on these counterfeit samples: programs sampled from a language model that 1) have a high enough log-probability to be generated at a moderate temperature and 2) pass weak correctness checks. Overall, we discover that most models have a very shallow understanding of counterfeits through three clear failure modes. First, models mistakenly classify them as correct. Second, models are worse at reasoning about the execution behaviour of counterfeits and often predict their execution results as if they were correct. Third, when asking models to fix counterfeits, the likelihood of a model successfully repairing a counterfeit is often even lower than that of sampling a correct program from scratch. Counterfeits also have very unexpected properties: first, counterfeit programs for problems that are easier for a model to solve are not necessarily easier to detect and only slightly easier to execute and repair. Second, counterfeits from a given model are just as confusing to the model itself as they are to other models. Finally, both strong and weak models are able to generate counterfeit samples that equally challenge all models. In light of our findings, we recommend that care and caution be taken when relying on models to understand their own samples, especially when no external feedback is incorporated.
CodeScholar: Growing Idiomatic Code Examples
Dec 23, 2023Abstract:Programmers often search for usage examples for API methods. A tool that could generate realistic, idiomatic, and contextual usage examples for one or more APIs would be immensely beneficial to developers. Such a tool would relieve the need for a deep understanding of the API landscape, augment existing documentation, and help discover interactions among APIs. We present CodeScholar, a tool that generates idiomatic code examples demonstrating the common usage of API methods. It includes a novel neural-guided search technique over graphs that grows the query APIs into idiomatic code examples. Our user study demonstrates that in 70% of cases, developers prefer CodeScholar generated examples over state-of-the-art large language models (LLM) like GPT3.5. We quantitatively evaluate 60 single and 25 multi-API queries from 6 popular Python libraries and show that across-the-board CodeScholar generates more realistic, diverse, and concise examples. In addition, we show that CodeScholar not only helps developers but also LLM-powered programming assistants generate correct code in a program synthesis setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge