Michael J Ryan
SynthesizeMe! Inducing Persona-Guided Prompts for Personalized Reward Models in LLMs
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Recent calls for pluralistic alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs) encourage adapting models to diverse user preferences. However, most prior work on personalized reward models heavily rely on additional identity information, such as demographic details or a predefined set of preference categories. To this end, we introduce SynthesizeMe, an approach to inducing synthetic user personas from user interactions for personalized reward modeling. SynthesizeMe first generates and verifies reasoning to explain user preferences, then induces synthetic user personas from that reasoning, and finally filters to informative prior user interactions in order to build personalized prompts for a particular user. We show that using SynthesizeMe induced prompts improves personalized LLM-as-a-judge accuracy by 4.4% on Chatbot Arena. Combining SynthesizeMe derived prompts with a reward model achieves top performance on PersonalRewardBench: a new curation of user-stratified interactions with chatbots collected from 854 users of Chatbot Arena and PRISM.
LangProBe: a Language Programs Benchmark
Feb 27, 2025
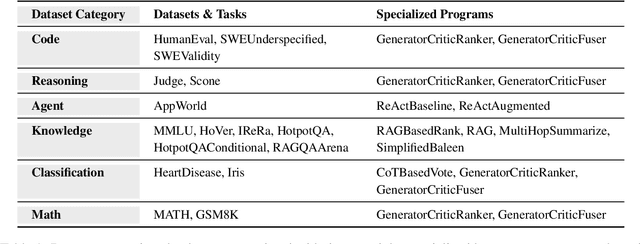
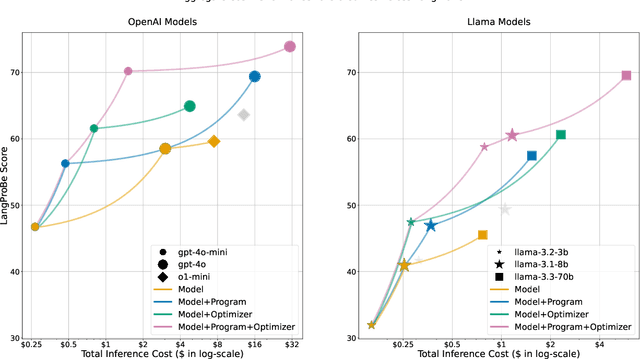
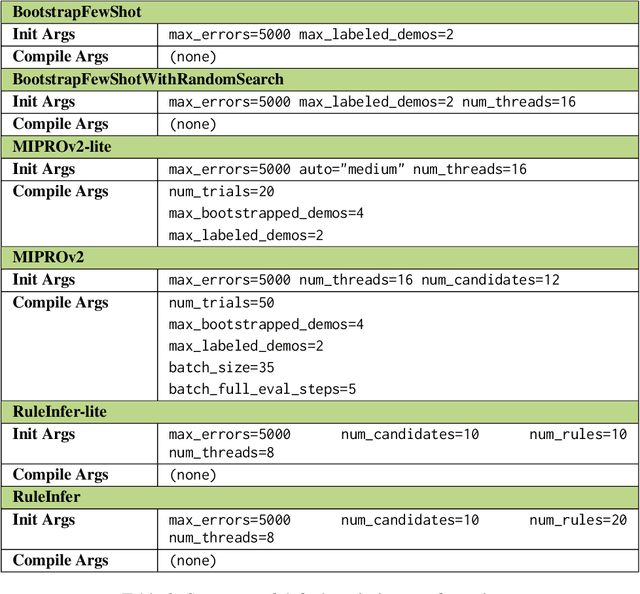
Abstract:Composing language models (LMs) into multi-step language programs and automatically optimizing their modular prompts is now a mainstream paradigm for building AI systems, but the tradeoffs in this space have only scarcely been studied before. We introduce LangProBe, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating the architectures and optimization strategies for language programs, with over 2000 combinations of tasks, architectures, optimizers, and choices of LMs. Using LangProBe, we are the first to study the impact of program architectures and optimizers (and their compositions together and with different models) on tradeoffs of quality and cost. We find that optimized language programs offer strong cost--quality Pareto improvement over raw calls to models, but simultaneously demonstrate that human judgment (or empirical decisions) about which compositions to pursue is still necessary for best performance. We will open source the code and evaluation data for LangProBe.
Mind the Gap! Static and Interactive Evaluations of Large Audio Models
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:As AI chatbots become ubiquitous, voice interaction presents a compelling way to enable rapid, high-bandwidth communication for both semantic and social signals. This has driven research into Large Audio Models (LAMs) to power voice-native experiences. However, aligning LAM development with user goals requires a clear understanding of user needs and preferences to establish reliable progress metrics. This study addresses these challenges by introducing an interactive approach to evaluate LAMs and collecting 7,500 LAM interactions from 484 participants. Through topic modeling of user queries, we identify primary use cases for audio interfaces. We then analyze user preference rankings and qualitative feedback to determine which models best align with user needs. Finally, we evaluate how static benchmarks predict interactive performance - our analysis reveals no individual benchmark strongly correlates with interactive results ($\tau \leq 0.33$ for all benchmarks). While combining multiple coarse-grained features yields modest predictive power ($R^2$=$0.30$), only two out of twenty datasets on spoken question answering and age prediction show significantly positive correlations. This suggests a clear need to develop LAM evaluations that better correlate with user preferences.
Optimizing Instructions and Demonstrations for Multi-Stage Language Model Programs
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Language Model Programs, i.e. sophisticated pipelines of modular language model (LM) calls, are increasingly advancing NLP tasks, but they require crafting prompts that are jointly effective for all modules. We study prompt optimization for LM programs, i.e. how to update these prompts to maximize a downstream metric without access to module-level labels or gradients. To make this tractable, we factorize our problem into optimizing the free-form instructions and few-shot demonstrations of every module and introduce several strategies to craft task-grounded instructions and navigate credit assignment across modules. Our strategies include (i) program- and data-aware techniques for proposing effective instructions, (ii) a stochastic mini-batch evaluation function for learning a surrogate model of our objective, and (iii) a meta-optimization procedure in which we refine how LMs construct proposals over time. Using these insights we develop MIPRO, a novel optimizer that outperforms baselines on five of six diverse LM programs using a best-in-class open-source model (Llama-3-8B), by as high as 12.9% accuracy. We will release our new optimizers and benchmark in DSPy at https://github.com/stanfordnlp/dspy
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge