Kori Inkpen
IRL Dittos: Embodied Multimodal AI Agent Interactions in Open Spaces
Apr 30, 2025


Abstract:We introduce the In Real Life (IRL) Ditto, an AI-driven embodied agent designed to represent remote colleagues in shared office spaces, creating opportunities for real-time exchanges even in their absence. IRL Ditto offers a unique hybrid experience by allowing in-person colleagues to encounter a digital version of their remote teammates, initiating greetings, updates, or small talk as they might in person. Our research question examines: How can the IRL Ditto influence interactions and relationships among colleagues in a shared office space? Through a four-day study, we assessed IRL Ditto's ability to strengthen social ties by simulating presence and enabling meaningful interactions across different levels of social familiarity. We find that enhancing social relationships depended deeply on the foundation of the relationship participants had with the source of the IRL Ditto. This study provides insights into the role of embodied agents in enriching workplace dynamics for distributed teams.
AI-Instruments: Embodying Prompts as Instruments to Abstract & Reflect Graphical Interface Commands as General-Purpose Tools
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Chat-based prompts respond with verbose linear-sequential texts, making it difficult to explore and refine ambiguous intents, back up and reinterpret, or shift directions in creative AI-assisted design work. AI-Instruments instead embody "prompts" as interface objects via three key principles: (1) Reification of user-intent as reusable direct-manipulation instruments; (2) Reflection of multiple interpretations of ambiguous user-intents (Reflection-in-intent) as well as the range of AI-model responses (Reflection-in-response) to inform design "moves" towards a desired result; and (3) Grounding to instantiate an instrument from an example, result, or extrapolation directly from another instrument. Further, AI-Instruments leverage LLM's to suggest, vary, and refine new instruments, enabling a system that goes beyond hard-coded functionality by generating its own instrumental controls from content. We demonstrate four technology probes, applied to image generation, and qualitative insights from twelve participants, showing how AI-Instruments address challenges of intent formulation, steering via direct manipulation, and non-linear iterative workflows to reflect and resolve ambiguous intents.
How Aligned are Generative Models to Humans in High-Stakes Decision-Making?
Oct 20, 2024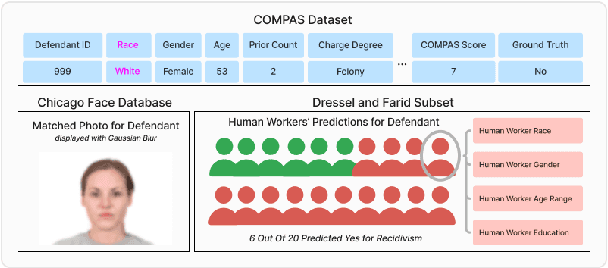

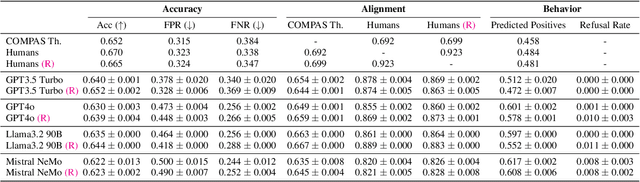
Abstract:Large generative models (LMs) are increasingly being considered for high-stakes decision-making. This work considers how such models compare to humans and predictive AI models on a specific case of recidivism prediction. We combine three datasets -- COMPAS predictive AI risk scores, human recidivism judgements, and photos -- into a dataset on which we study the properties of several state-of-the-art, multimodal LMs. Beyond accuracy and bias, we focus on studying human-LM alignment on the task of recidivism prediction. We investigate if these models can be steered towards human decisions, the impact of adding photos, and whether anti-discimination prompting is effective. We find that LMs can be steered to outperform humans and COMPAS using in context-learning. We find anti-discrimination prompting to have unintended effects, causing some models to inhibit themselves and significantly reduce their number of positive predictions.
Advancing Human-AI Complementarity: The Impact of User Expertise and Algorithmic Tuning on Joint Decision Making
Aug 16, 2022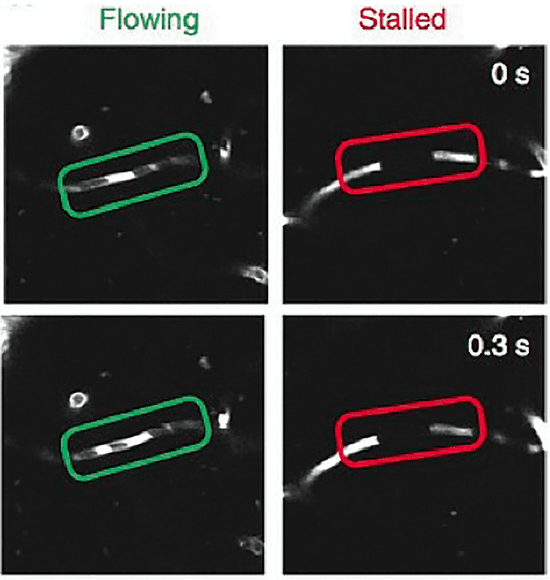

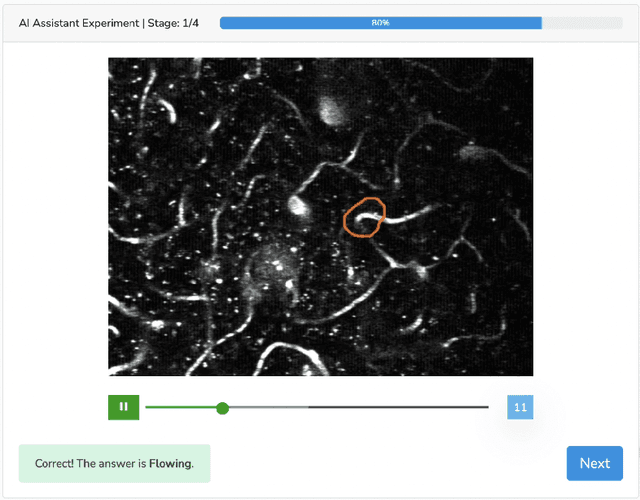
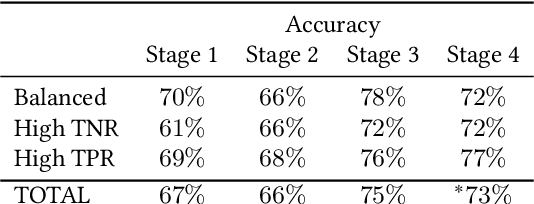
Abstract:Human-AI collaboration for decision-making strives to achieve team performance that exceeds the performance of humans or AI alone. However, many factors can impact success of Human-AI teams, including a user's domain expertise, mental models of an AI system, trust in recommendations, and more. This work examines users' interaction with three simulated algorithmic models, all with similar accuracy but different tuning on their true positive and true negative rates. Our study examined user performance in a non-trivial blood vessel labeling task where participants indicated whether a given blood vessel was flowing or stalled. Our results show that while recommendations from an AI-Assistant can aid user decision making, factors such as users' baseline performance relative to the AI and complementary tuning of AI error types significantly impact overall team performance. Novice users improved, but not to the accuracy level of the AI. Highly proficient users were generally able to discern when they should follow the AI recommendation and typically maintained or improved their performance. Mid-performers, who had a similar level of accuracy to the AI, were most variable in terms of whether the AI recommendations helped or hurt their performance. In addition, we found that users' perception of the AI's performance relative on their own also had a significant impact on whether their accuracy improved when given AI recommendations. This work provides insights on the complexity of factors related to Human-AI collaboration and provides recommendations on how to develop human-centered AI algorithms to complement users in decision-making tasks.
Who Goes First? Influences of Human-AI Workflow on Decision Making in Clinical Imaging
May 19, 2022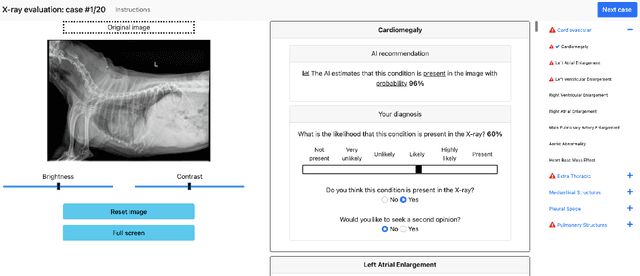
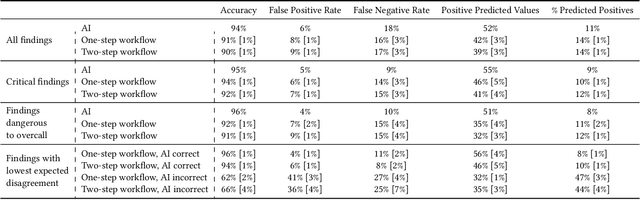
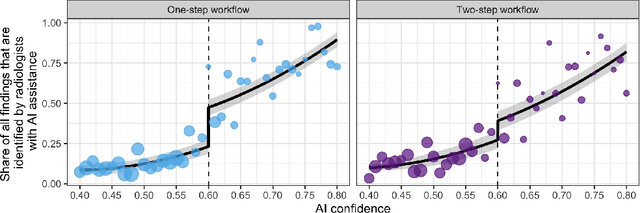
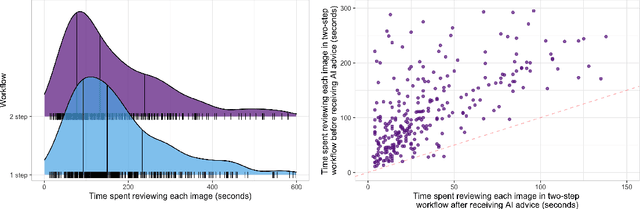
Abstract:Details of the designs and mechanisms in support of human-AI collaboration must be considered in the real-world fielding of AI technologies. A critical aspect of interaction design for AI-assisted human decision making are policies about the display and sequencing of AI inferences within larger decision-making workflows. We have a poor understanding of the influences of making AI inferences available before versus after human review of a diagnostic task at hand. We explore the effects of providing AI assistance at the start of a diagnostic session in radiology versus after the radiologist has made a provisional decision. We conducted a user study where 19 veterinary radiologists identified radiographic findings present in patients' X-ray images, with the aid of an AI tool. We employed two workflow configurations to analyze (i) anchoring effects, (ii) human-AI team diagnostic performance and agreement, (iii) time spent and confidence in decision making, and (iv) perceived usefulness of the AI. We found that participants who are asked to register provisional responses in advance of reviewing AI inferences are less likely to agree with the AI regardless of whether the advice is accurate and, in instances of disagreement with the AI, are less likely to seek the second opinion of a colleague. These participants also reported the AI advice to be less useful. Surprisingly, requiring provisional decisions on cases in advance of the display of AI inferences did not lengthen the time participants spent on the task. The study provides generalizable and actionable insights for the deployment of clinical AI tools in human-in-the-loop systems and introduces a methodology for studying alternative designs for human-AI collaboration. We make our experimental platform available as open source to facilitate future research on the influence of alternate designs on human-AI workflows.
Investigations of Performance and Bias in Human-AI Teamwork in Hiring
Feb 21, 2022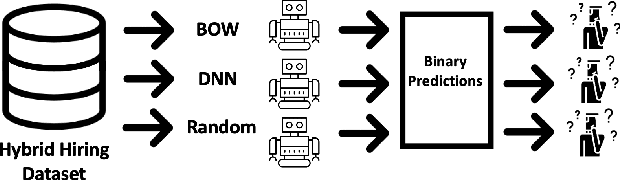
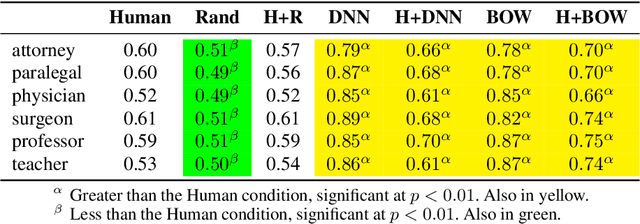
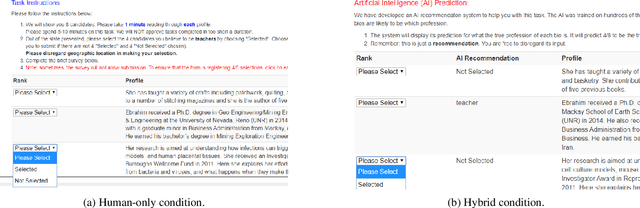
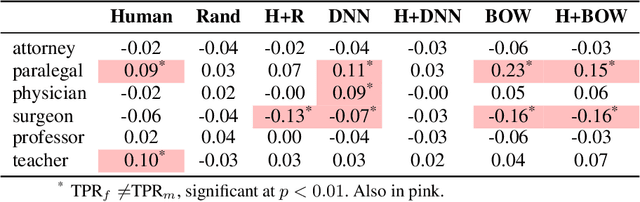
Abstract:In AI-assisted decision-making, effective hybrid (human-AI) teamwork is not solely dependent on AI performance alone, but also on its impact on human decision-making. While prior work studies the effects of model accuracy on humans, we endeavour here to investigate the complex dynamics of how both a model's predictive performance and bias may transfer to humans in a recommendation-aided decision task. We consider the domain of ML-assisted hiring, where humans -- operating in a constrained selection setting -- can choose whether they wish to utilize a trained model's inferences to help select candidates from written biographies. We conduct a large-scale user study leveraging a re-created dataset of real bios from prior work, where humans predict the ground truth occupation of given candidates with and without the help of three different NLP classifiers (random, bag-of-words, and deep neural network). Our results demonstrate that while high-performance models significantly improve human performance in a hybrid setting, some models mitigate hybrid bias while others accentuate it. We examine these findings through the lens of decision conformity and observe that our model architecture choices have an impact on human-AI conformity and bias, motivating the explicit need to assess these complex dynamics prior to deployment.
What You See Is What You Get? The Impact of Representation Criteria on Human Bias in Hiring
Sep 08, 2019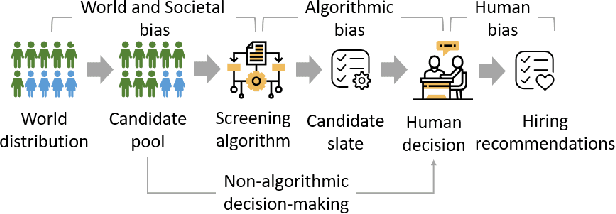
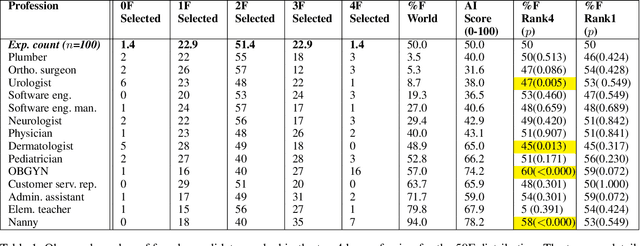
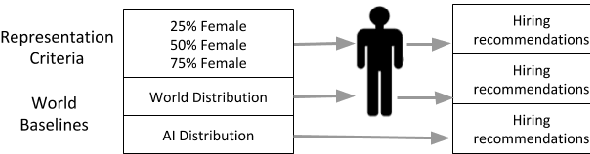
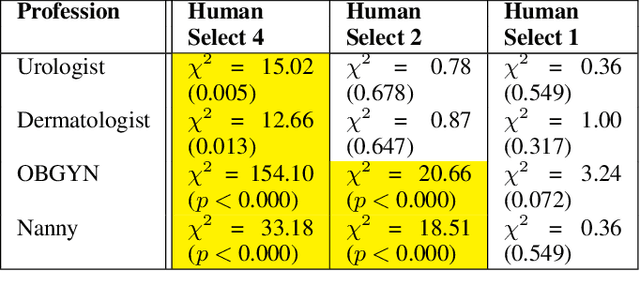
Abstract:Although systematic biases in decision-making are widely documented, the ways in which they emerge from different sources is less understood. We present a controlled experimental platform to study gender bias in hiring by decoupling the effect of world distribution (the gender breakdown of candidates in a specific profession) from bias in human decision-making. We explore the effectiveness of \textit{representation criteria}, fixed proportional display of candidates, as an intervention strategy for mitigation of gender bias by conducting experiments measuring human decision-makers' rankings for who they would recommend as potential hires. Experiments across professions with varying gender proportions show that balancing gender representation in candidate slates can correct biases for some professions where the world distribution is skewed, although doing so has no impact on other professions where human persistent preferences are at play. We show that the gender of the decision-maker, complexity of the decision-making task and over- and under-representation of genders in the candidate slate can all impact the final decision. By decoupling sources of bias, we can better isolate strategies for bias mitigation in human-in-the-loop systems.
Investigating Human + Machine Complementarity for Recidivism Predictions
Aug 28, 2018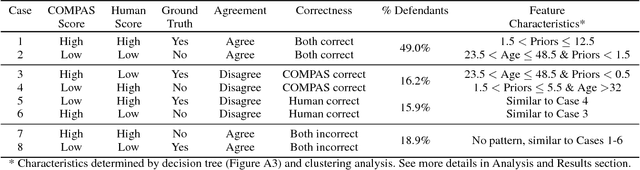
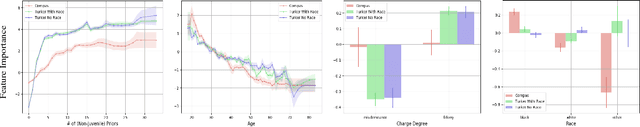
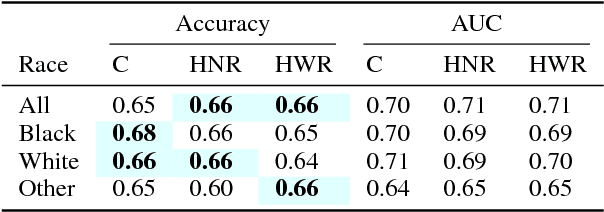
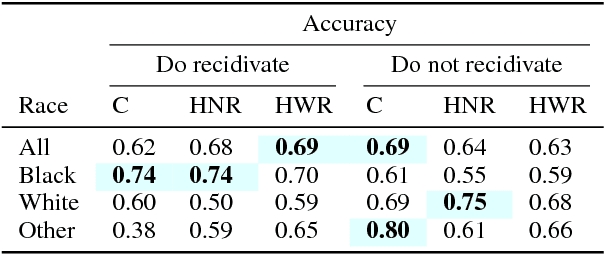
Abstract:When might human input help (or not) when assessing risk in fairness-related domains? Dressel and Farid asked Mechanical Turk workers to evaluate a subset of individuals in the ProPublica COMPAS data set for risk of recidivism, and concluded that COMPAS predictions were no more accurate or fair than predictions made by humans. We delve deeper into this claim in this paper. We construct a Human Risk Score based on the predictions made by multiple Mechanical Turk workers on the same individual, study the agreement and disagreement between COMPAS and Human Scores on subgroups of individuals, and construct hybrid Human+AI models to predict recidivism. Our key finding is that on this data set, human and COMPAS decision making differed, but not in ways that could be leveraged to significantly improve ground truth prediction. We present the results of our analyses and suggestions for how machine and human input may have complementary strengths to address challenges in the fairness domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge