Shreya Chappidi
Accountability Capture: How Record-Keeping to Support AI Transparency and Accountability (Re)shapes Algorithmic Oversight
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Accountability regimes typically encourage record-keeping to enable the transparency that supports oversight, investigation, contestation, and redress. However, implementing such record-keeping can introduce considerations, risks, and consequences, which so far remain under-explored. This paper examines how record-keeping practices bring algorithmic systems within accountability regimes, providing a basis to observe and understand their effects. For this, we introduce, describe, and elaborate 'accountability capture' -- the re-configuration of socio-technical processes and the associated downstream effects relating to record-keeping for algorithmic accountability. Surveying 100 practitioners, we evidence and characterise record-keeping issues in practice, identifying their alignment with accountability capture. We further document widespread record-keeping practices, tensions between internal and external accountability requirements, and evidence of employee resistance to practices imposed through accountability capture. We discuss these and other effects for surveillance, privacy, and data protection, highlighting considerations for algorithmic accountability communities. In all, we show that implementing record-keeping to support transparency in algorithmic accountability regimes can itself bring wider implications -- an issue requiring greater attention from practitioners, researchers, and policymakers alike.
Advancing Human-AI Complementarity: The Impact of User Expertise and Algorithmic Tuning on Joint Decision Making
Aug 16, 2022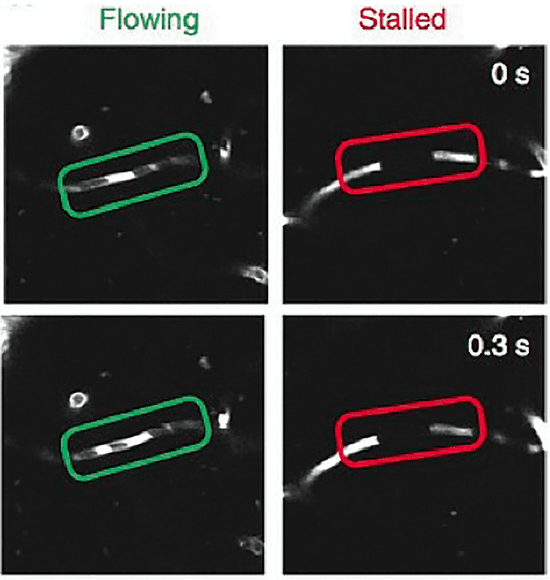

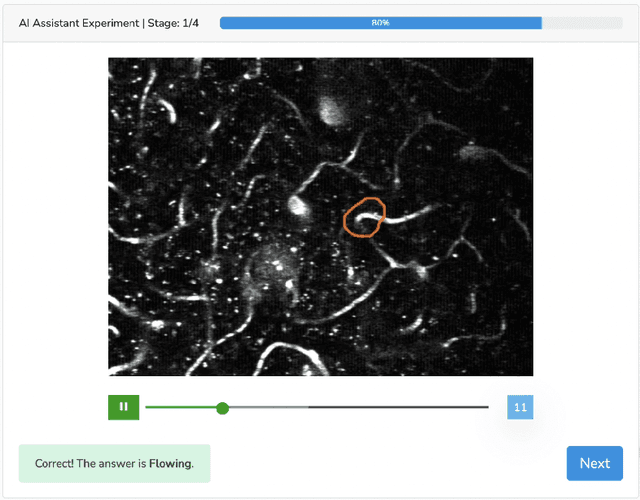
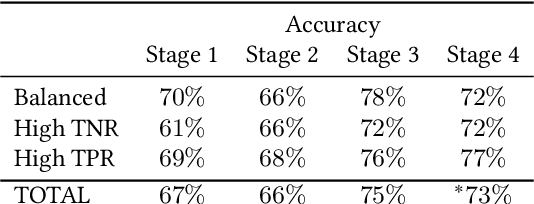
Abstract:Human-AI collaboration for decision-making strives to achieve team performance that exceeds the performance of humans or AI alone. However, many factors can impact success of Human-AI teams, including a user's domain expertise, mental models of an AI system, trust in recommendations, and more. This work examines users' interaction with three simulated algorithmic models, all with similar accuracy but different tuning on their true positive and true negative rates. Our study examined user performance in a non-trivial blood vessel labeling task where participants indicated whether a given blood vessel was flowing or stalled. Our results show that while recommendations from an AI-Assistant can aid user decision making, factors such as users' baseline performance relative to the AI and complementary tuning of AI error types significantly impact overall team performance. Novice users improved, but not to the accuracy level of the AI. Highly proficient users were generally able to discern when they should follow the AI recommendation and typically maintained or improved their performance. Mid-performers, who had a similar level of accuracy to the AI, were most variable in terms of whether the AI recommendations helped or hurt their performance. In addition, we found that users' perception of the AI's performance relative on their own also had a significant impact on whether their accuracy improved when given AI recommendations. This work provides insights on the complexity of factors related to Human-AI collaboration and provides recommendations on how to develop human-centered AI algorithms to complement users in decision-making tasks.
Who Goes First? Influences of Human-AI Workflow on Decision Making in Clinical Imaging
May 19, 2022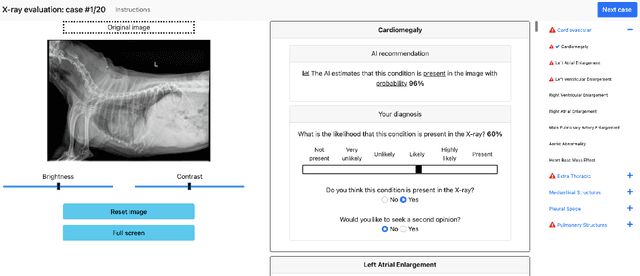
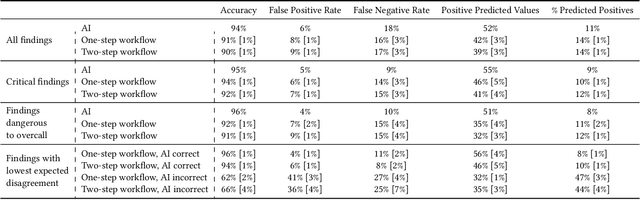
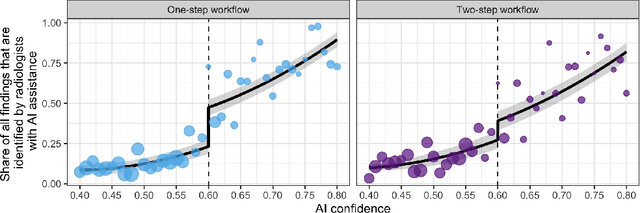
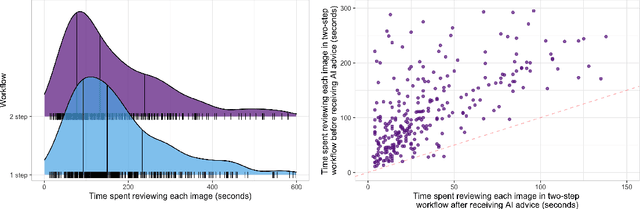
Abstract:Details of the designs and mechanisms in support of human-AI collaboration must be considered in the real-world fielding of AI technologies. A critical aspect of interaction design for AI-assisted human decision making are policies about the display and sequencing of AI inferences within larger decision-making workflows. We have a poor understanding of the influences of making AI inferences available before versus after human review of a diagnostic task at hand. We explore the effects of providing AI assistance at the start of a diagnostic session in radiology versus after the radiologist has made a provisional decision. We conducted a user study where 19 veterinary radiologists identified radiographic findings present in patients' X-ray images, with the aid of an AI tool. We employed two workflow configurations to analyze (i) anchoring effects, (ii) human-AI team diagnostic performance and agreement, (iii) time spent and confidence in decision making, and (iv) perceived usefulness of the AI. We found that participants who are asked to register provisional responses in advance of reviewing AI inferences are less likely to agree with the AI regardless of whether the advice is accurate and, in instances of disagreement with the AI, are less likely to seek the second opinion of a colleague. These participants also reported the AI advice to be less useful. Surprisingly, requiring provisional decisions on cases in advance of the display of AI inferences did not lengthen the time participants spent on the task. The study provides generalizable and actionable insights for the deployment of clinical AI tools in human-in-the-loop systems and introduces a methodology for studying alternative designs for human-AI collaboration. We make our experimental platform available as open source to facilitate future research on the influence of alternate designs on human-AI workflows.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge