Junjie Zhao
HAL: Inducing Human-likeness in LLMs with Alignment
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Conversational human-likeness plays a central role in human-AI interaction, yet it has remained difficult to define, measure, and optimize. As a result, improvements in human-like behavior are largely driven by scale or broad supervised training, rather than targeted alignment. We introduce Human Aligning LLMs (HAL), a framework for aligning language models to conversational human-likeness using an interpretable, data-driven reward. HAL derives explicit conversational traits from contrastive dialogue data, combines them into a compact scalar score, and uses this score as a transparent reward signal for alignment with standard preference optimization methods. Using this approach, we align models of varying sizes without affecting their overall performance. In large-scale human evaluations, models aligned with HAL are more frequently perceived as human-like in conversation. Because HAL operates over explicit, interpretable traits, it enables inspection of alignment behavior and diagnosis of unintended effects. More broadly, HAL demonstrates how soft, qualitative properties of language--previously outside the scope for alignment--can be made measurable and aligned in an interpretable and explainable way.
DentalGPT: Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:Reliable interpretation of multimodal data in dentistry is essential for automated oral healthcare, yet current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle to capture fine-grained dental visual details and lack sufficient reasoning ability for precise diagnosis. To address these limitations, we present DentalGPT, a specialized dental MLLM developed through high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. Specifically, the largest annotated multimodal dataset for dentistry to date was constructed by aggregating over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions that highlight diagnostically relevant visual features, making it the multimodal dataset with the most extensive collection of dental images to date. Training on this dataset significantly enhances the MLLM's visual understanding of dental conditions, while the subsequent reinforcement learning stage further strengthens its capability for multimodal complex reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on intraoral and panoramic benchmarks, along with dental subsets of medical VQA benchmarks, show that DentalGPT achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs despite having only 7B parameters. These results demonstrate that high-quality dental data combined with staged adaptation provides an effective pathway for building capable and domain-specialized dental MLLMs.
TransMPC: Transformer-based Explicit MPC with Variable Prediction Horizon
Sep 09, 2025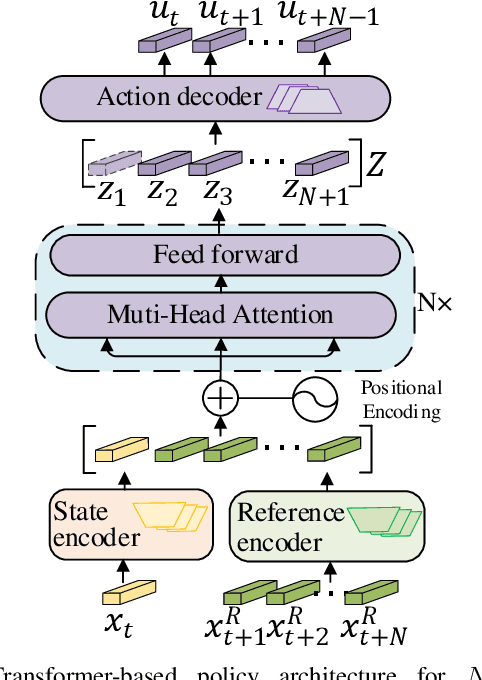
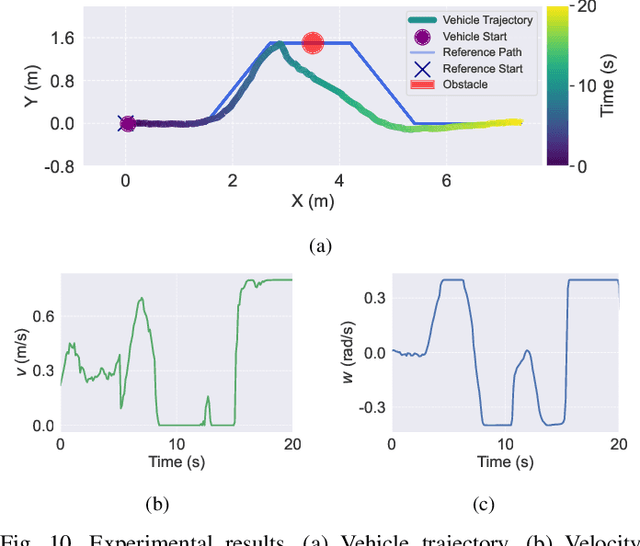
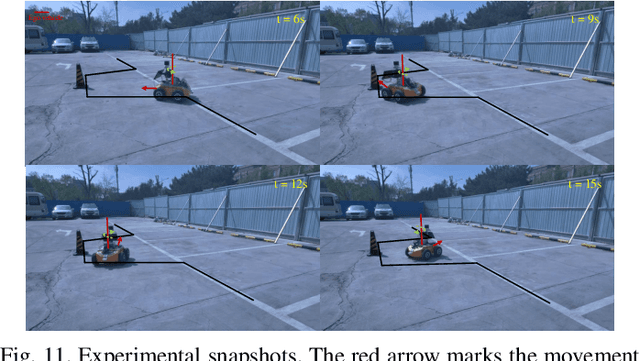
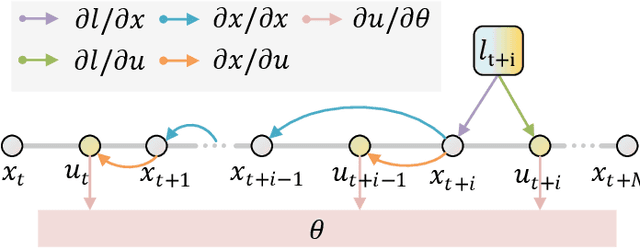
Abstract:Traditional online Model Predictive Control (MPC) methods often suffer from excessive computational complexity, limiting their practical deployment. Explicit MPC mitigates online computational load by pre-computing control policies offline; however, existing explicit MPC methods typically rely on simplified system dynamics and cost functions, restricting their accuracy for complex systems. This paper proposes TransMPC, a novel Transformer-based explicit MPC algorithm capable of generating highly accurate control sequences in real-time for complex dynamic systems. Specifically, we formulate the MPC policy as an encoder-only Transformer leveraging bidirectional self-attention, enabling simultaneous inference of entire control sequences in a single forward pass. This design inherently accommodates variable prediction horizons while ensuring low inference latency. Furthermore, we introduce a direct policy optimization framework that alternates between sampling and learning phases. Unlike imitation-based approaches dependent on precomputed optimal trajectories, TransMPC directly optimizes the true finite-horizon cost via automatic differentiation. Random horizon sampling combined with a replay buffer provides independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) training samples, ensuring robust generalization across varying states and horizon lengths. Extensive simulations and real-world vehicle control experiments validate the effectiveness of TransMPC in terms of solution accuracy, adaptability to varying horizons, and computational efficiency.
WideSearch: Benchmarking Agentic Broad Info-Seeking
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:From professional research to everyday planning, many tasks are bottlenecked by wide-scale information seeking, which is more repetitive than cognitively complex. With the rapid development of Large Language Models (LLMs), automated search agents powered by LLMs offer a promising solution to liberate humans from this tedious work. However, the capability of these agents to perform such "wide-context" collection reliably and completely remains largely unevaluated due to a lack of suitable benchmarks. To bridge this gap, we introduce WideSearch, a new benchmark engineered to evaluate agent reliability on these large-scale collection tasks. The benchmark features 200 manually curated questions (100 in English, 100 in Chinese) from over 15 diverse domains, grounded in real user queries. Each task requires agents to collect large-scale atomic information, which could be verified one by one objectively, and arrange it into a well-organized output. A rigorous five-stage quality control pipeline ensures the difficulty, completeness, and verifiability of the dataset. We benchmark over 10 state-of-the-art agentic search systems, including single-agent, multi-agent frameworks, and end-to-end commercial systems. Most systems achieve overall success rates near 0\%, with the best performer reaching just 5\%. However, given sufficient time, cross-validation by multiple human testers can achieve a near 100\% success rate. These results demonstrate that present search agents have critical deficiencies in large-scale information seeking, underscoring urgent areas for future research and development in agentic search. Our dataset, evaluation pipeline, and benchmark results have been publicly released at https://widesearch-seed.github.io/
Learning from Expert Factors: Trajectory-level Reward Shaping for Formulaic Alpha Mining
Jul 27, 2025
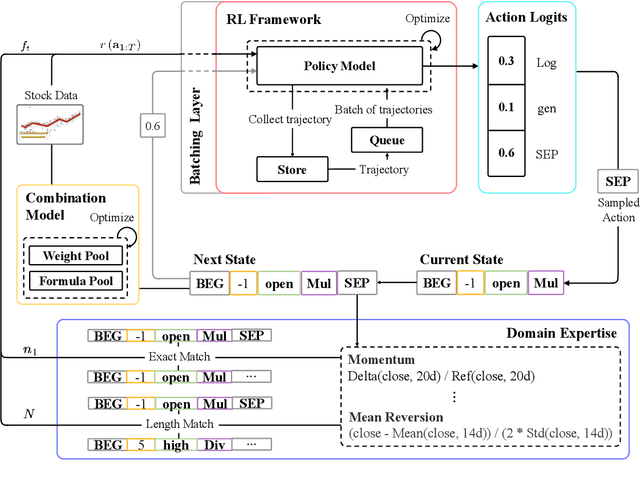
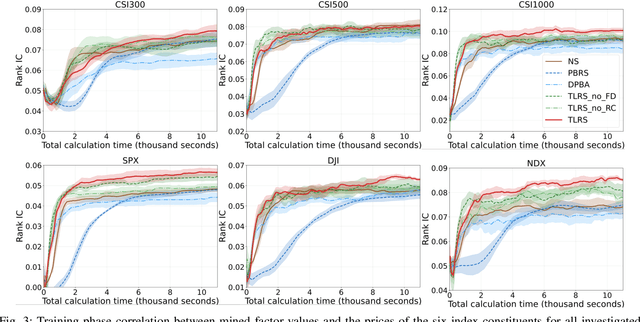
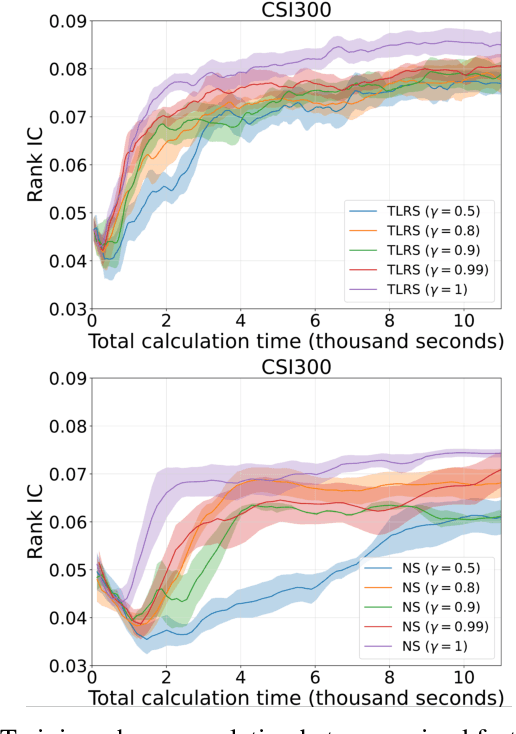
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has successfully automated the complex process of mining formulaic alpha factors, for creating interpretable and profitable investment strategies. However, existing methods are hampered by the sparse rewards given the underlying Markov Decision Process. This inefficiency limits the exploration of the vast symbolic search space and destabilizes the training process. To address this, Trajectory-level Reward Shaping (TLRS), a novel reward shaping method, is proposed. TLRS provides dense, intermediate rewards by measuring the subsequence-level similarity between partially generated expressions and a set of expert-designed formulas. Furthermore, a reward centering mechanism is introduced to reduce training variance. Extensive experiments on six major Chinese and U.S. stock indices show that TLRS significantly improves the predictive power of mined factors, boosting the Rank Information Coefficient by 9.29% over existing potential-based shaping algorithms. Notably, TLRS achieves a major leap in computational efficiency by reducing its time complexity with respect to the feature dimension from linear to constant, which is a significant improvement over distance-based baselines.
QuantFactor REINFORCE: Mining Steady Formulaic Alpha Factors with Variance-bounded REINFORCE
Sep 08, 2024Abstract:The goal of alpha factor mining is to discover indicative signals of investment opportunities from the historical financial market data of assets. Deep learning based alpha factor mining methods have shown to be powerful, which, however, lack of the interpretability, making them unacceptable in the risk-sensitive real markets. Alpha factors in formulaic forms are more interpretable and therefore favored by market participants, while the search space is complex and powerful explorative methods are urged. Recently, a promising framework is proposed for generating formulaic alpha factors using deep reinforcement learning, and quickly gained research focuses from both academia and industries. This paper first argues that the originally employed policy training method, i.e., Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), faces several important issues in the context of alpha factors mining, making it ineffective to explore the search space of the formula. Herein, a novel reinforcement learning based on the well-known REINFORCE algorithm is proposed. Given that the underlying state transition function adheres to the Dirac distribution, the Markov Decision Process within this framework exhibit minimal environmental variability, making REINFORCE algorithm more appropriate than PPO. A new dedicated baseline is designed to theoretically reduce the commonly suffered high variance of REINFORCE. Moreover, the information ratio is introduced as a reward shaping mechanism to encourage the generation of steady alpha factors that can better adapt to changes in market volatility. Experimental evaluations on various real assets data show that the proposed algorithm can increase the correlation with asset returns by 3.83%, and a stronger ability to obtain excess returns compared to the latest alpha factors mining methods, which meets the theoretical results well.
Interior Object Geometry via Fitted Frames
Jul 19, 2024
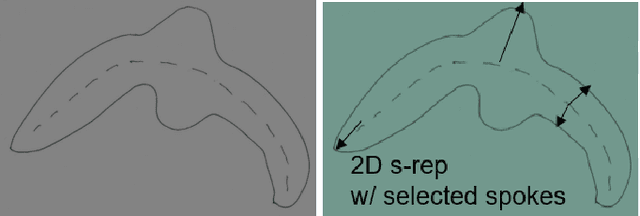
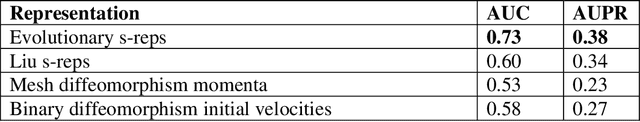
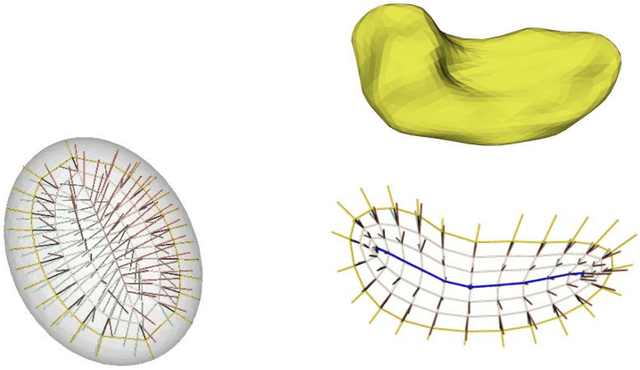
Abstract:We describe a representation targeted for anatomic objects which is designed to enable strong locational correspondence within object populations and thus to provide powerful object statistics. The method generates fitted frames on the boundary and in the interior of objects and produces alignment-free geometric features from them. It accomplishes this by understanding an object as the diffeomorphic deformation of an ellipsoid and using a skeletal representation fitted throughout the deformation to produce a model of the target object, where the object is provided initially in the form of a boundary mesh. Via classification performance on hippocampi shape between individuals with a disorder vs. others, we compare our method to two state-of-the-art methods for producing object representations that are intended to capture geometric correspondence across a population of objects and to yield geometric features useful for statistics, and we show improved classification performance by this new representation, which we call the evolutionary s-rep. The geometric features that are derived from each of the representations, especially via fitted frames, is discussed.
Knowledge-Aware Multi-Intent Contrastive Learning for Multi-Behavior Recommendation
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:Multi-behavioral recommendation optimizes user experiences by providing users with more accurate choices based on their diverse behaviors, such as view, add to cart, and purchase. Current studies on multi-behavioral recommendation mainly explore the connections and differences between multi-behaviors from an implicit perspective. Specifically, they directly model those relations using black-box neural networks. In fact, users' interactions with items under different behaviors are driven by distinct intents. For instance, when users view products, they tend to pay greater attention to information such as ratings and brands. However, when it comes to the purchasing phase, users become more price-conscious. To tackle this challenge and data sparsity problem in the multi-behavioral recommendation, we propose a novel model: Knowledge-Aware Multi-Intent Contrastive Learning (KAMCL) model. This model uses relationships in the knowledge graph to construct intents, aiming to mine the connections between users' multi-behaviors from the perspective of intents to achieve more accurate recommendations. KAMCL is equipped with two contrastive learning schemes to alleviate the data scarcity problem and further enhance user representations. Extensive experiments on three real datasets demonstrate the superiority of our model.
Reconstruction of Cortical Surfaces with Spherical Topology from Infant Brain MRI via Recurrent Deformation Learning
Dec 10, 2023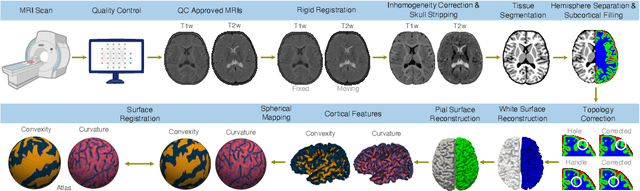
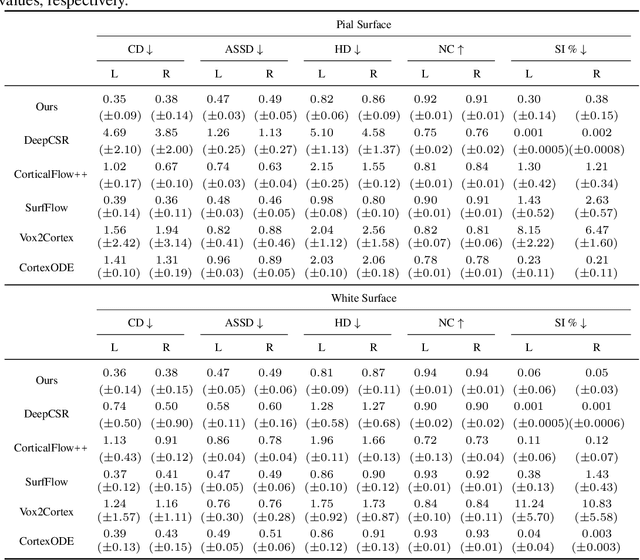
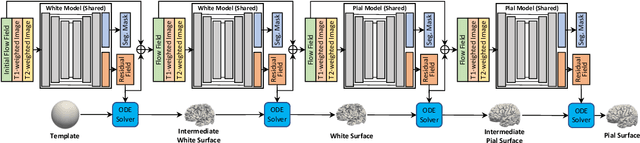
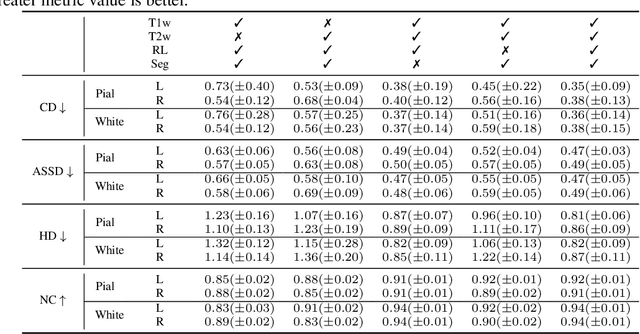
Abstract:Cortical surface reconstruction (CSR) from MRI is key to investigating brain structure and function. While recent deep learning approaches have significantly improved the speed of CSR, a substantial amount of runtime is still needed to map the cortex to a topologically-correct spherical manifold to facilitate downstream geometric analyses. Moreover, this mapping is possible only if the topology of the surface mesh is homotopic to a sphere. Here, we present a method for simultaneous CSR and spherical mapping efficiently within seconds. Our approach seamlessly connects two sub-networks for white and pial surface generation. Residual diffeomorphic deformations are learned iteratively to gradually warp a spherical template mesh to the white and pial surfaces while preserving mesh topology and uniformity. The one-to-one vertex correspondence between the template sphere and the cortical surfaces allows easy and direct mapping of geometric features like convexity and curvature to the sphere for visualization and downstream processing. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach on infant brain MRI, which poses significant challenges to CSR due to tissue contrast changes associated with rapid brain development during the first postnatal year. Performance evaluation based on a dataset of infants from 0 to 12 months demonstrates that our method substantially enhances mesh regularity and reduces geometric errors, outperforming state-of-the-art deep learning approaches, all while maintaining high computational efficiency.
Improved deep learning techniques in gravitational-wave data analysis
Nov 09, 2020
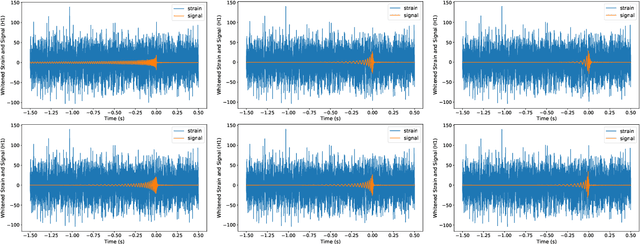
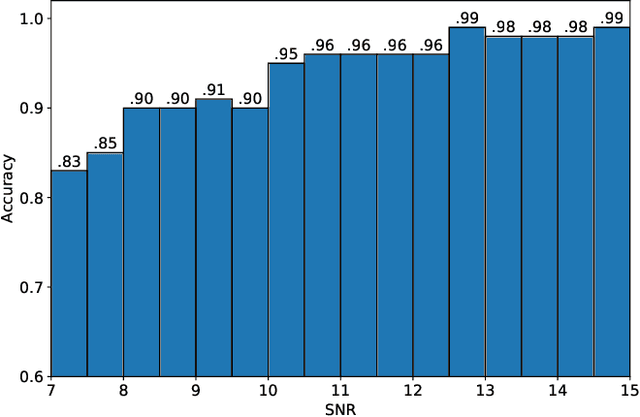
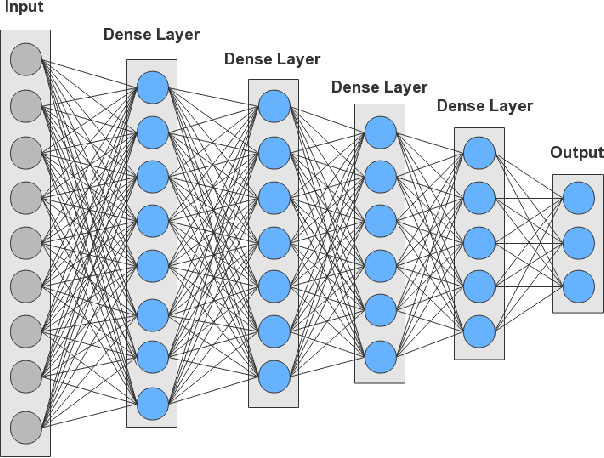
Abstract:In recent years, convolutional neural network (CNN) and other deep learning models have been gradually introduced into the area of gravitational-wave (GW) data processing. Compared with the traditional matched-filtering techniques, CNN has significant advantages in efficiency in GW signal detection tasks. In addition, matched-filtering techniques are based on the template bank of the existing theoretical waveform, which makes it difficult to find GW signals beyond theoretical expectation. In this paper, based on the task of GW detection of binary black holes, we introduce the optimization techniques of deep learning, such as batch normalization and dropout, to CNN models. Detailed studies of model performance are carried out. Through this study, we recommend to use batch normalization and dropout techniques in CNN models in GW signal detection tasks. Furthermore, we investigate the generalization ability of CNN models on different parameter ranges of GW signals. We point out that CNN models are robust to the variation of the parameter range of the GW waveform. This is a major advantage of deep learning models over matched-filtering techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge