Jun Zhan
RIS-Enhanced Information-Decoupled Symbiotic Radio Over Broadcasting Signals
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:This paper studies a reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-enhanced decoupled symbiotic radio (SR) system in which a primary transmitter delivers common data to multiple primary receivers (PRs), while a RIS-based backscatter device sends secondary data to a backscatter receiver (BRx). Unlike conventional SR, the BRx performs energy detection and never decodes the primary signal, thereby removing ambiguity and preventing exposure of the primary payload to unintended receivers. In this paper, we formulate the problem as the minimization of the transmit power subject to a common broadcast rate constraint across all PRs and a bit error rate (BER) constraint at the BRx. The problem is nonconvex due to the unit-modulus RIS constraint and coupled quadratic forms. Leveraging a rate-balanced reformulation and a monotonic BER ratio characterization, we develop a low-complexity penalty-based block coordinate descent algorithm with closed-form updates. Numerical results show fast convergence of the proposed algorithm and reduced power consumption of the considered RIS-enhanced information-decoupled SR system over conventional SR baselines.
YuE: Scaling Open Foundation Models for Long-Form Music Generation
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:We tackle the task of long-form music generation--particularly the challenging \textbf{lyrics-to-song} problem--by introducing YuE, a family of open foundation models based on the LLaMA2 architecture. Specifically, YuE scales to trillions of tokens and generates up to five minutes of music while maintaining lyrical alignment, coherent musical structure, and engaging vocal melodies with appropriate accompaniment. It achieves this through (1) track-decoupled next-token prediction to overcome dense mixture signals, (2) structural progressive conditioning for long-context lyrical alignment, and (3) a multitask, multiphase pre-training recipe to converge and generalize. In addition, we redesign the in-context learning technique for music generation, enabling versatile style transfer (e.g., converting Japanese city pop into an English rap while preserving the original accompaniment) and bidirectional generation. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate that YuE matches or even surpasses some of the proprietary systems in musicality and vocal agility. In addition, fine-tuning YuE enables additional controls and enhanced support for tail languages. Furthermore, beyond generation, we show that YuE's learned representations can perform well on music understanding tasks, where the results of YuE match or exceed state-of-the-art methods on the MARBLE benchmark. Keywords: lyrics2song, song generation, long-form, foundation model, music generation
Data Mixing Laws: Optimizing Data Mixtures by Predicting Language Modeling Performance
Mar 25, 2024



Abstract:Pretraining data of large language models composes multiple domains (e.g., web texts, academic papers, codes), whose mixture proportions crucially impact the competence of outcome models. While existing endeavors rely on heuristics or qualitative strategies to tune the proportions, we discover the quantitative predictability of model performance regarding the mixture proportions in function forms, which we refer to as the data mixing laws. Fitting such functions on sample mixtures unveils model performance on unseen mixtures before actual runs, thus guiding the selection of an ideal data mixture. Furthermore, we propose nested use of the scaling laws of training steps, model sizes, and our data mixing law to enable predicting the performance of large models trained on massive data under various mixtures with only small-scale training. Moreover, experimental results verify that our method effectively optimizes the training mixture of a 1B model trained for 100B tokens in RedPajama, reaching a performance comparable to the one trained for 48% more steps on the default mixture. Extending the application of data mixing laws to continual training accurately predicts the critical mixture proportion that avoids catastrophic forgetting and outlooks the potential for dynamic data schedules
AnyGPT: Unified Multimodal LLM with Discrete Sequence Modeling
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:We introduce AnyGPT, an any-to-any multimodal language model that utilizes discrete representations for the unified processing of various modalities, including speech, text, images, and music. AnyGPT can be trained stably without any alterations to the current large language model (LLM) architecture or training paradigms. Instead, it relies exclusively on data-level preprocessing, facilitating the seamless integration of new modalities into LLMs, akin to the incorporation of new languages. We build a multimodal text-centric dataset for multimodal alignment pre-training. Utilizing generative models, we synthesize the first large-scale any-to-any multimodal instruction dataset. It consists of 108k samples of multi-turn conversations that intricately interweave various modalities, thus equipping the model to handle arbitrary combinations of multimodal inputs and outputs. Experimental results demonstrate that AnyGPT is capable of facilitating any-to-any multimodal conversation while achieving performance comparable to specialized models across all modalities, proving that discrete representations can effectively and conveniently unify multiple modalities within a language model. Demos are shown in https://junzhan2000.github.io/AnyGPT.github.io/
SpeechGPT-Gen: Scaling Chain-of-Information Speech Generation
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Benefiting from effective speech modeling, current Speech Large Language Models (SLLMs) have demonstrated exceptional capabilities in in-context speech generation and efficient generalization to unseen speakers. However, the prevailing information modeling process is encumbered by certain redundancies, leading to inefficiencies in speech generation. We propose Chain-of-Information Generation (CoIG), a method for decoupling semantic and perceptual information in large-scale speech generation. Building on this, we develop SpeechGPT-Gen, an 8-billion-parameter SLLM efficient in semantic and perceptual information modeling. It comprises an autoregressive model based on LLM for semantic information modeling and a non-autoregressive model employing flow matching for perceptual information modeling. Additionally, we introduce the novel approach of infusing semantic information into the prior distribution to enhance the efficiency of flow matching. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that SpeechGPT-Gen markedly excels in zero-shot text-to-speech, zero-shot voice conversion, and speech-to-speech dialogue, underscoring CoIG's remarkable proficiency in capturing and modeling speech's semantic and perceptual dimensions. Code and models are available at https://github.com/0nutation/SpeechGPT.
SpeechGPT: Empowering Large Language Models with Intrinsic Cross-Modal Conversational Abilities
May 19, 2023Abstract:Multi-modal large language models are regarded as a crucial step towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and have garnered significant interest with the emergence of ChatGPT. However, current speech-language models typically adopt the cascade paradigm, preventing inter-modal knowledge transfer. In this paper, we propose SpeechGPT, a large language model with intrinsic cross-modal conversational abilities, capable of perceiving and generating multi-model content. With discrete speech representations, we first construct SpeechInstruct, a large-scale cross-modal speech instruction dataset. Additionally, we employ a three-stage training strategy that includes modality-adaptation pre-training, cross-modal instruction fine-tuning, and chain-of-modality instruction fine-tuning. The experimental results demonstrate that SpeechGPT has an impressive capacity to follow multi-modal human instructions and highlight the potential of handling multiple modalities with one model. Demos are shown in https://0nutation.github.io/SpeechGPT.github.io/.
HFN: Heterogeneous Feature Network for Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection
Nov 02, 2022Abstract:Network or physical attacks on industrial equipment or computer systems may cause massive losses. Therefore, a quick and accurate anomaly detection (AD) based on monitoring data, especially the multivariate time-series (MTS) data, is of great significance. As the key step of anomaly detection for MTS data, learning the relations among different variables has been explored by many approaches. However, most of the existing approaches do not consider the heterogeneity between variables, that is, different types of variables (continuous numerical variables, discrete categorical variables or hybrid variables) may have different and distinctive edge distributions. In this paper, we propose a novel semi-supervised anomaly detection framework based on a heterogeneous feature network (HFN) for MTS, learning heterogeneous structure information from a mass of unlabeled time-series data to improve the accuracy of anomaly detection, and using attention coefficient to provide an explanation for the detected anomalies. Specifically, we first combine the embedding similarity subgraph generated by sensor embedding and feature value similarity subgraph generated by sensor values to construct a time-series heterogeneous graph, which fully utilizes the rich heterogeneous mutual information among variables. Then, a prediction model containing nodes and channel attentions is jointly optimized to obtain better time-series representations. This approach fuses the state-of-the-art technologies of heterogeneous graph structure learning (HGSL) and representation learning. The experiments on four sensor datasets from real-world applications demonstrate that our approach detects the anomalies more accurately than those baseline approaches, thus providing a basis for the rapid positioning of anomalies.
An Unsupervised Short- and Long-Term Mask Representation for Multivariate Time Series Anomaly Detection
Aug 19, 2022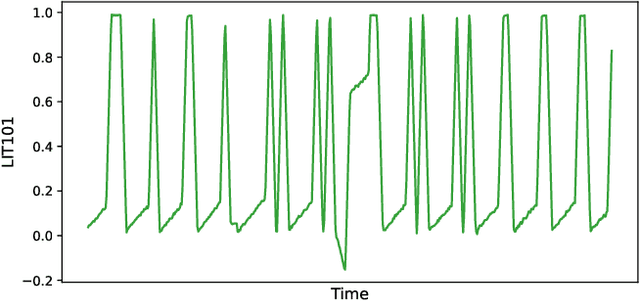
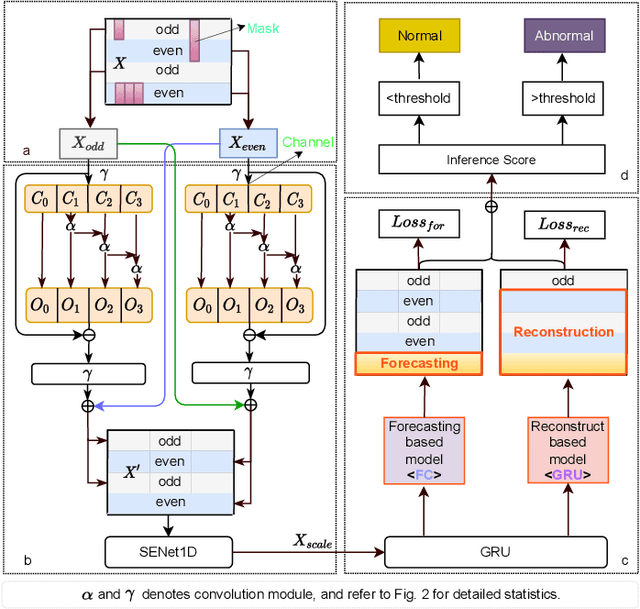

Abstract:Anomaly detection of multivariate time series is meaningful for system behavior monitoring. This paper proposes an anomaly detection method based on unsupervised Short- and Long-term Mask Representation learning (SLMR). The main idea is to extract short-term local dependency patterns and long-term global trend patterns of the multivariate time series by using multi-scale residual dilated convolution and Gated Recurrent Unit(GRU) respectively. Furthermore, our approach can comprehend temporal contexts and feature correlations by combining spatial-temporal masked self-supervised representation learning and sequence split. It considers the importance of features is different, and we introduce the attention mechanism to adjust the contribution of each feature. Finally, a forecasting-based model and a reconstruction-based model are integrated to focus on single timestamp prediction and latent representation of time series. Experiments show that the performance of our method outperforms other state-of-the-art models on three real-world datasets. Further analysis shows that our method is good at interpretability.
Aerodynamic Data Predictions Based on Multi-task Learning
Oct 15, 2020
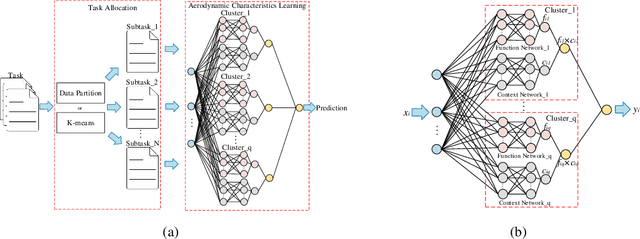

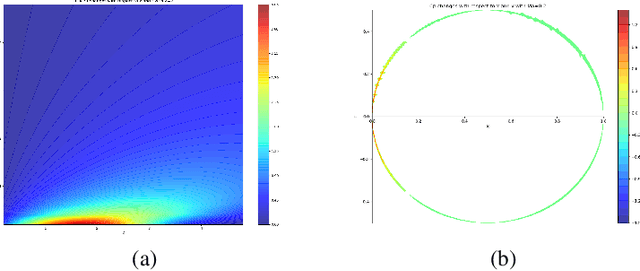
Abstract:The quality of datasets is one of the key factors that affect the accuracy of aerodynamic data models. For example, in the uniformly sampled Burgers' dataset, the insufficient high-speed data is overwhelmed by massive low-speed data. Predicting high-speed data is more difficult than predicting low-speed data, owing to that the number of high-speed data is limited, i.e. the quality of the Burgers' dataset is not satisfactory. To improve the quality of datasets, traditional methods usually employ the data resampling technology to produce enough data for the insufficient parts in the original datasets before modeling, which increases computational costs. Recently, the mixtures of experts have been used in natural language processing to deal with different parts of sentences, which provides a solution for eliminating the need for data resampling in aerodynamic data modeling. Motivated by this, we propose the multi-task learning (MTL), a datasets quality-adaptive learning scheme, which combines task allocation and aerodynamic characteristics learning together to disperse the pressure of the entire learning task. The task allocation divides a whole learning task into several independent subtasks, while the aerodynamic characteristics learning learns these subtasks simultaneously to achieve better precision. Two experiments with poor quality datasets are conducted to verify the data quality-adaptivity of the MTL to datasets. The results show than the MTL is more accurate than FCNs and GANs in poor quality datasets.
Deep Speech 2: End-to-End Speech Recognition in English and Mandarin
Dec 08, 2015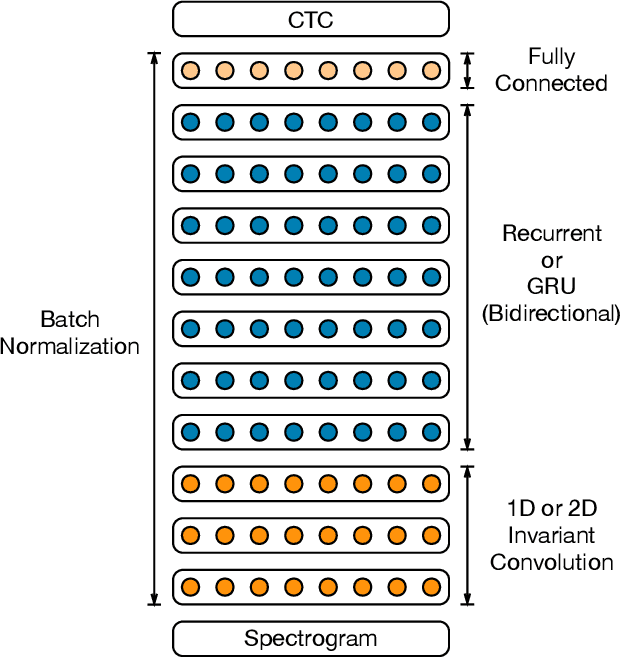
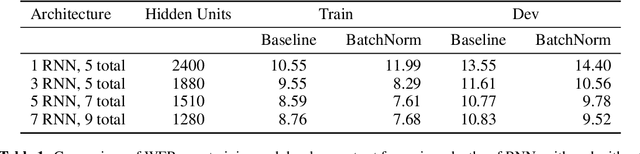
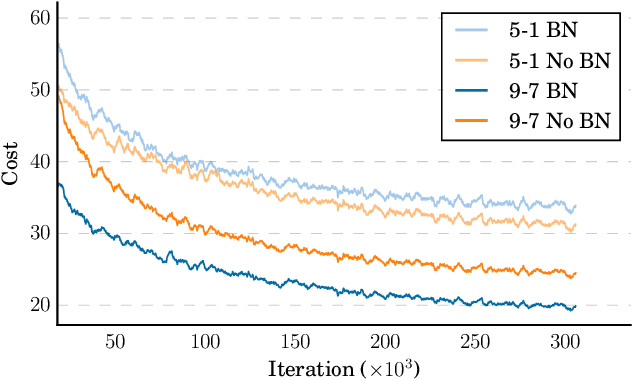
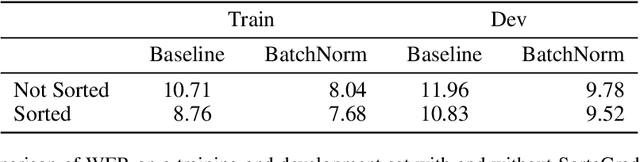
Abstract:We show that an end-to-end deep learning approach can be used to recognize either English or Mandarin Chinese speech--two vastly different languages. Because it replaces entire pipelines of hand-engineered components with neural networks, end-to-end learning allows us to handle a diverse variety of speech including noisy environments, accents and different languages. Key to our approach is our application of HPC techniques, resulting in a 7x speedup over our previous system. Because of this efficiency, experiments that previously took weeks now run in days. This enables us to iterate more quickly to identify superior architectures and algorithms. As a result, in several cases, our system is competitive with the transcription of human workers when benchmarked on standard datasets. Finally, using a technique called Batch Dispatch with GPUs in the data center, we show that our system can be inexpensively deployed in an online setting, delivering low latency when serving users at scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge