Jorge Oliveira
Self-Supervised Ultrasound Screen Detection
Nov 17, 2025



Abstract:Ultrasound (US) machines display images on a built-in monitor, but routine transfer to hospital systems relies on DICOM. We propose a self-supervised pipeline to extract the US image from a photograph of the monitor. This removes the DICOM bottleneck and enables rapid testing and prototyping of new algorithms. In a proof-of-concept study, the rectified images retained enough visual fidelity to classify cardiac views with a balanced accuracy of 0.79 with respect to the native DICOMs.
HumAIne-Chatbot: Real-Time Personalized Conversational AI via Reinforcement Learning
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Current conversational AI systems often provide generic, one-size-fits-all interactions that overlook individual user characteristics and lack adaptive dialogue management. To address this gap, we introduce \textbf{HumAIne-chatbot}, an AI-driven conversational agent that personalizes responses through a novel user profiling framework. The system is pre-trained on a diverse set of GPT-generated virtual personas to establish a broad prior over user types. During live interactions, an online reinforcement learning agent refines per-user models by combining implicit signals (e.g. typing speed, sentiment, engagement duration) with explicit feedback (e.g., likes and dislikes). This profile dynamically informs the chatbot dialogue policy, enabling real-time adaptation of both content and style. To evaluate the system, we performed controlled experiments with 50 synthetic personas in multiple conversation domains. The results showed consistent improvements in user satisfaction, personalization accuracy, and task achievement when personalization features were enabled. Statistical analysis confirmed significant differences between personalized and nonpersonalized conditions, with large effect sizes across key metrics. These findings highlight the effectiveness of AI-driven user profiling and provide a strong foundation for future real-world validation.
Multi-Site Class-Incremental Learning with Weighted Experts in Echocardiography
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Building an echocardiography view classifier that maintains performance in real-life cases requires diverse multi-site data, and frequent updates with newly available data to mitigate model drift. Simply fine-tuning on new datasets results in "catastrophic forgetting", and cannot adapt to variations of view labels between sites. Alternatively, collecting all data on a single server and re-training may not be feasible as data sharing agreements may restrict image transfer, or datasets may only become available at different times. Furthermore, time and cost associated with re-training grows with every new dataset. We propose a class-incremental learning method which learns an expert network for each dataset, and combines all expert networks with a score fusion model. The influence of ``unqualified experts'' is minimised by weighting each contribution with a learnt in-distribution score. These weights promote transparency as the contribution of each expert is known during inference. Instead of using the original images, we use learned features from each dataset, which are easier to share and raise fewer licensing and privacy concerns. We validate our work on six datasets from multiple sites, demonstrating significant reductions in training time while improving view classification performance.
BackMix: Mitigating Shortcut Learning in Echocardiography with Minimal Supervision
Jun 27, 2024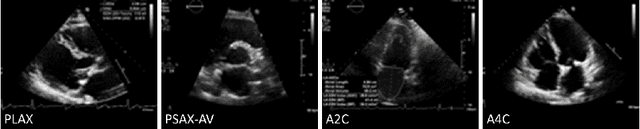
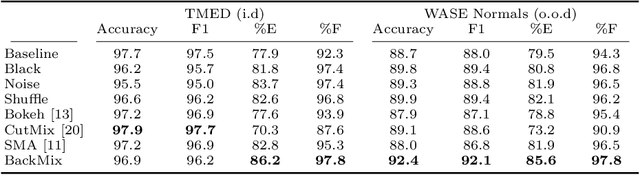
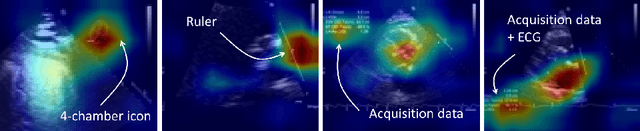
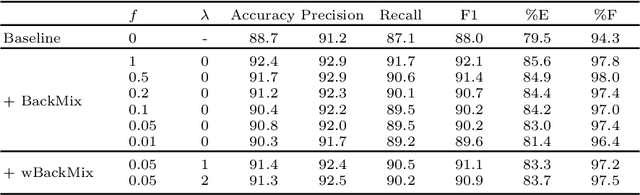
Abstract:Neural networks can learn spurious correlations that lead to the correct prediction in a validation set, but generalise poorly because the predictions are right for the wrong reason. This undesired learning of naive shortcuts (Clever Hans effect) can happen for example in echocardiogram view classification when background cues (e.g. metadata) are biased towards a class and the model learns to focus on those background features instead of on the image content. We propose a simple, yet effective random background augmentation method called BackMix, which samples random backgrounds from other examples in the training set. By enforcing the background to be uncorrelated with the outcome, the model learns to focus on the data within the ultrasound sector and becomes invariant to the regions outside this. We extend our method in a semi-supervised setting, finding that the positive effects of BackMix are maintained with as few as 5% of segmentation labels. A loss weighting mechanism, wBackMix, is also proposed to increase the contribution of the augmented examples. We validate our method on both in-distribution and out-of-distribution datasets, demonstrating significant improvements in classification accuracy, region focus and generalisability. Our source code is available at: https://github.com/kitbransby/BackMix
Beyond Heart Murmur Detection: Automatic Murmur Grading from Phonocardiogram
Sep 27, 2022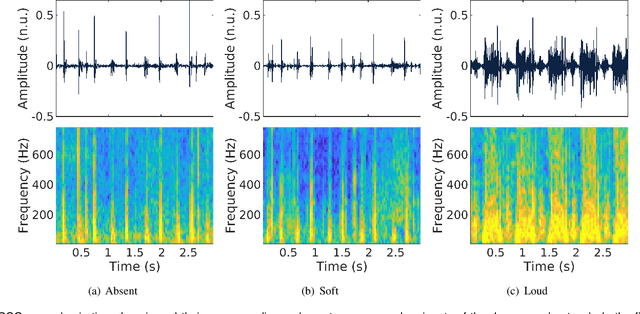
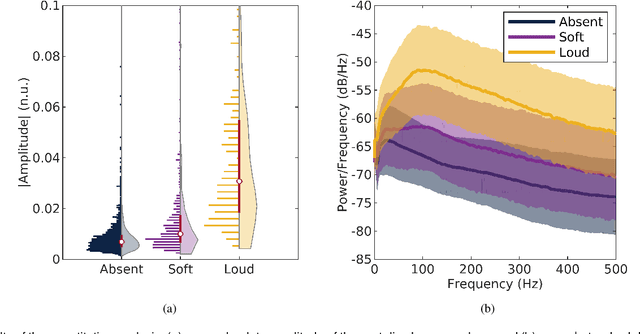
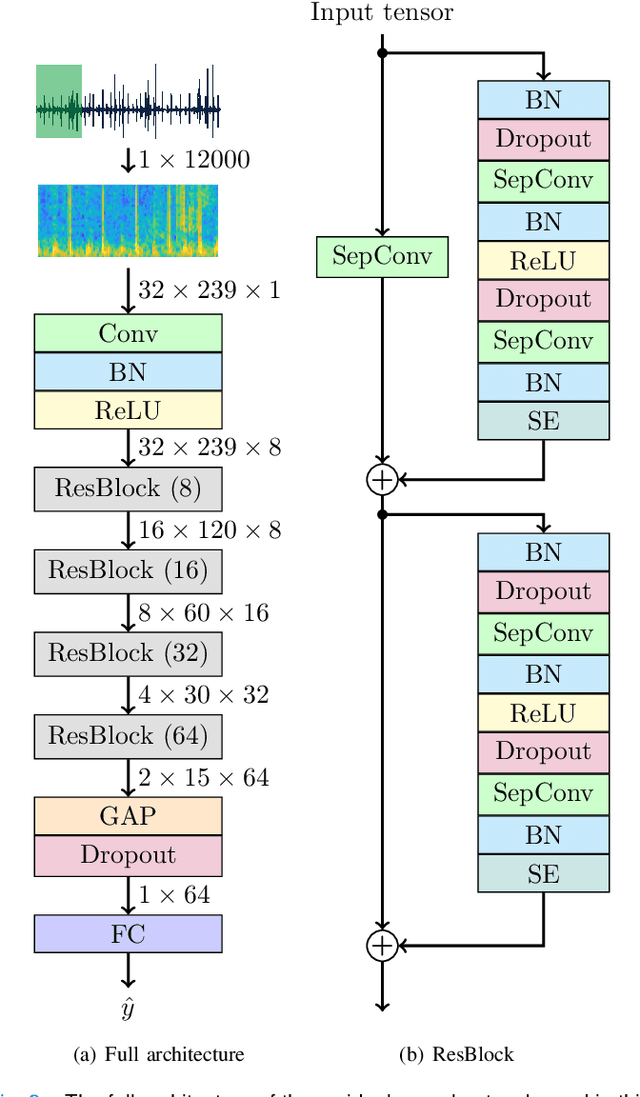
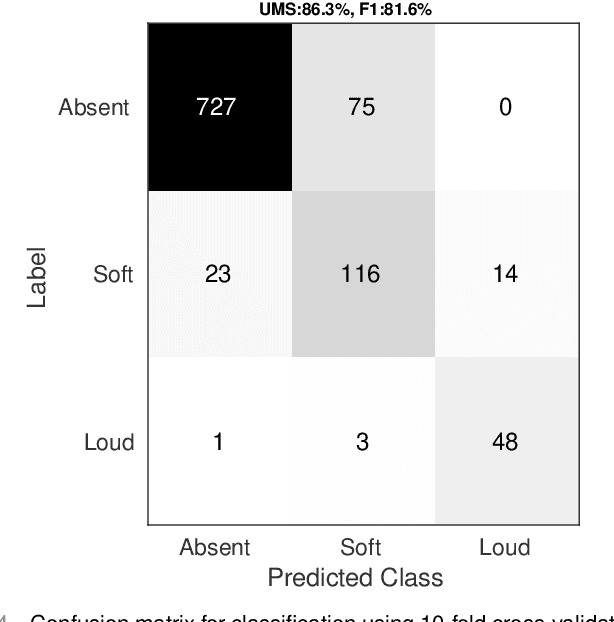
Abstract:Objective: Murmurs are abnormal heart sounds, identified by experts through cardiac auscultation. The murmur grade, a quantitative measure of the murmur intensity, is strongly correlated with the patient's clinical condition. This work aims to estimate each patient's murmur grade (i.e., absent, soft, loud) from multiple auscultation location phonocardiograms (PCGs) of a large population of pediatric patients from a low-resource rural area. Methods: The Mel spectrogram representation of each PCG recording is given to an ensemble of 15 convolutional residual neural networks with channel-wise attention mechanisms to classify each PCG recording. The final murmur grade for each patient is derived based on the proposed decision rule and considering all estimated labels for available recordings. The proposed method is cross-validated on a dataset consisting of 3456 PCG recordings from 1007 patients using a stratified ten-fold cross-validation. Additionally, the method was tested on a hidden test set comprised of 1538 PCG recordings from 442 patients. Results: The overall cross-validation performances for patient-level murmur gradings are 86.3% and 81.6% in terms of the unweighted average of sensitivities and F1-scores, respectively. The sensitivities (and F1-scores) for absent, soft, and loud murmurs are 90.7% (93.6%), 75.8% (66.8%), and 92.3% (84.2%), respectively. On the test set, the algorithm achieves an unweighted average of sensitivities of 80.4% and an F1-score of 75.8%. Conclusions: This study provides a potential approach for algorithmic pre-screening in low-resource settings with relatively high expert screening costs. Significance: The proposed method represents a significant step beyond detection of murmurs, providing characterization of intensity which may provide a enhanced classification of clinical outcomes.
Left Ventricle Contouring of Apical Three-Chamber Views on 2D Echocardiography
Jul 13, 2022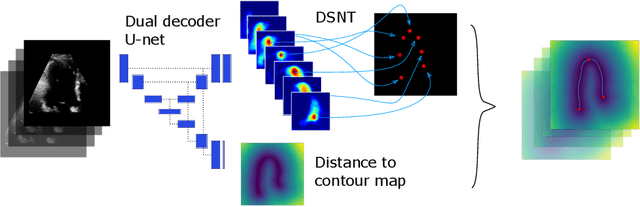
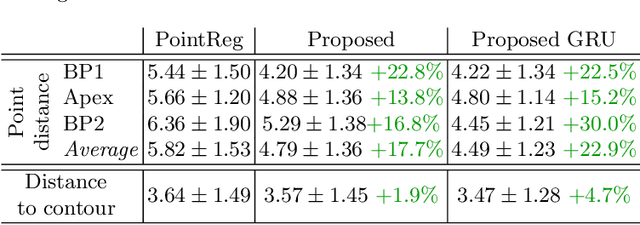
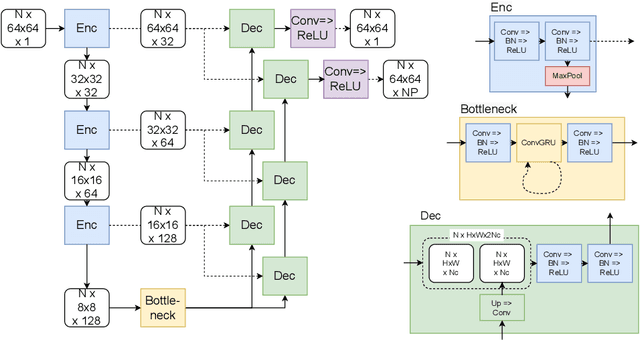
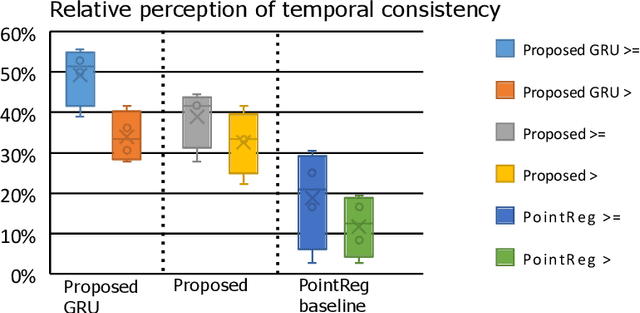
Abstract:We propose a new method to automatically contour the left ventricle on 2D echocardiographic images. Unlike most existing segmentation methods, which are based on predicting segmentation masks, we focus at predicting the endocardial contour and the key landmark points within this contour (basal points and apex). This provides a representation that is closer to how experts perform manual annotations and hence produce results that are physiologically more plausible. Our proposed method uses a two-headed network based on the U-Net architecture. One head predicts the 7 contour points, and the other head predicts a distance map to the contour. This approach was compared to the U-Net and to a point based approach, achieving performance gains of up to 30\% in terms of landmark localisation (<4.5mm) and distance to the ground truth contour (<3.5mm).
Contrastive Learning for View Classification of Echocardiograms
Aug 06, 2021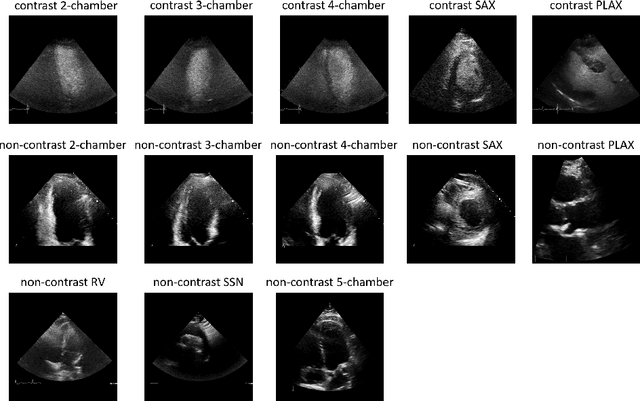
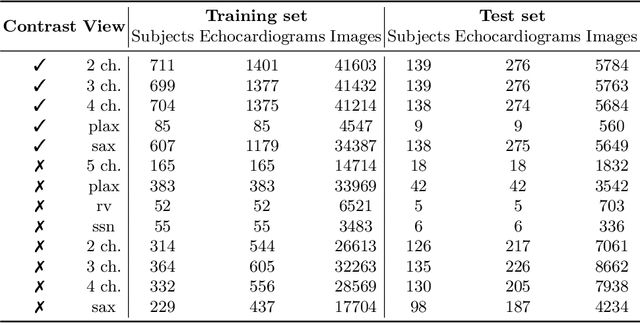
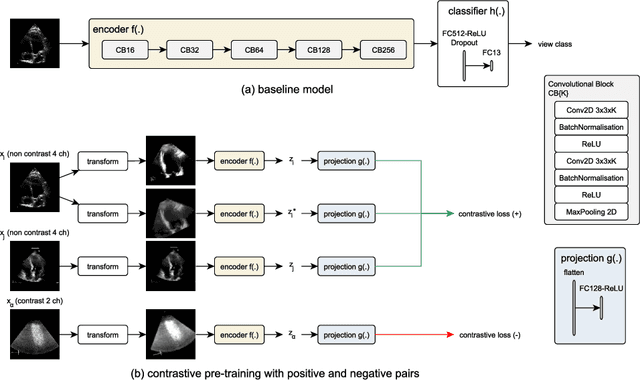
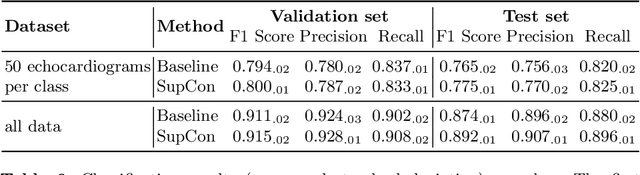
Abstract:Analysis of cardiac ultrasound images is commonly performed in routine clinical practice for quantification of cardiac function. Its increasing automation frequently employs deep learning networks that are trained to predict disease or detect image features. However, such models are extremely data-hungry and training requires labelling of many thousands of images by experienced clinicians. Here we propose the use of contrastive learning to mitigate the labelling bottleneck. We train view classification models for imbalanced cardiac ultrasound datasets and show improved performance for views/classes for which minimal labelled data is available. Compared to a naive baseline model, we achieve an improvement in F1 score of up to 26% in those views while maintaining state-of-the-art performance for the views with sufficiently many labelled training observations.
The CirCor DigiScope Dataset: From Murmur Detection to Murmur Classification
Aug 02, 2021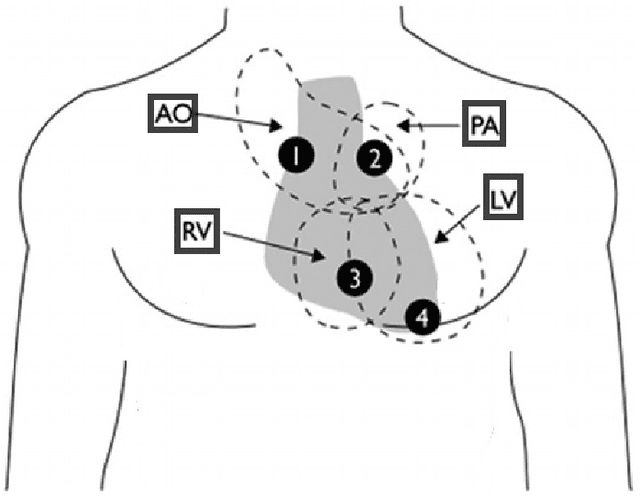
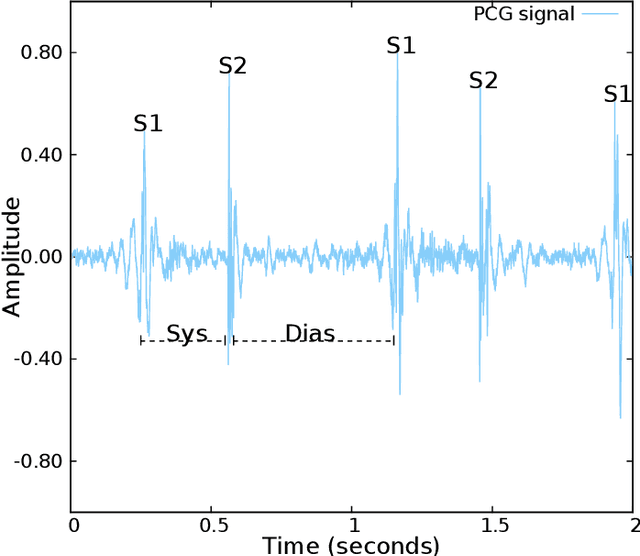

Abstract:Cardiac auscultation is one of the most cost-effective techniques used to detect and identify many heart conditions. Computer-assisted decision systems based on auscultation can support physicians in their decisions. Unfortunately, the application of such systems in clinical trials is still minimal since most of them only aim to detect the presence of extra or abnormal waves in the phonocardiogram signal. This is mainly due to the lack of large publicly available datasets, where a more detailed description of such abnormal waves (e.g., cardiac murmurs) exists. As a result, current machine learning algorithms are unable to classify such waves. To pave the way to more effective research on healthcare recommendation systems based on auscultation, our team has prepared the currently largest pediatric heart sound dataset. A total of 5282 recordings have been collected from the four main auscultation locations of 1568 patients, in the process 215780 heart sounds have been manually annotated. Furthermore, and for the first time, each cardiac murmur has been manually annotated by an expert annotator according to its timing, shape, pitch, grading and quality. In addition, the auscultation locations where the murmur is present were identified as well as the auscultation location where the murmur is detected more intensively.
Segmentation and Optimal Region Selection of Physiological Signals using Deep Neural Networks and Combinatorial Optimization
Mar 17, 2020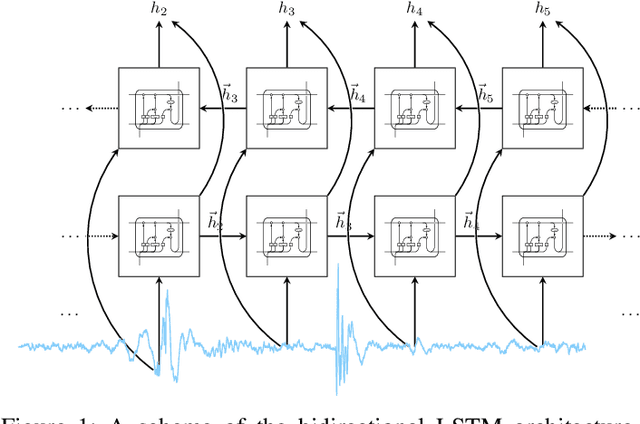
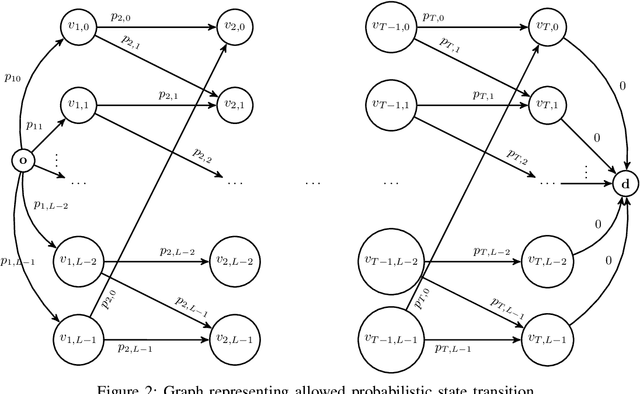
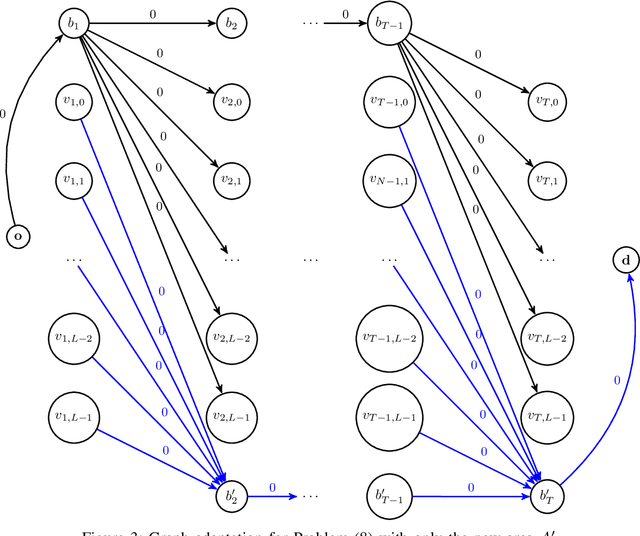
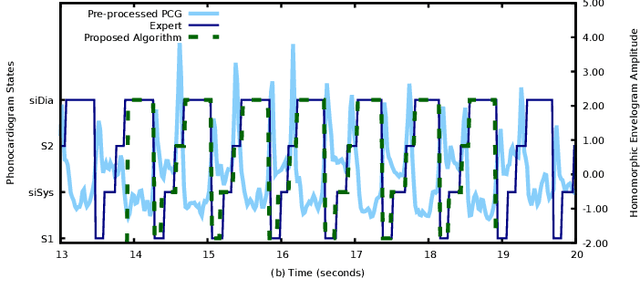
Abstract:Physiological signals, such as the electrocardiogram and the phonocardiogram are very often corrupted by noisy sources. Usually, artificial intelligent algorithms analyze the signal regardless of its quality. On the other hand, physicians use a completely orthogonal strategy. They do not assess the entire recording, instead they search for a segment where the fundamental and abnormal waves are easily detected, and only then a prognostic is attempted. Inspired by this fact, a new algorithm that automatically selects an optimal segment for a post-processing stage, according to a criteria defined by the user is proposed. In the process, a Neural Network is used to compute the output state probability distribution for each sample. Using the aforementioned quantities, a graph is designed, whereas state transition constraints are physically imposed into the graph and a set of constraints are used to retrieve a subset of the recording that maximizes the likelihood function, proposed by the user. The developed framework is tested and validated in two applications. In both cases, the system performance is boosted significantly, e.g in heart sound segmentation, sensitivity increases 2.4% when compared to the standard approaches in the literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge