Johan Verjans
Australian Institute for Machine Learning, South Australian Health and Medical Research Institute
Localizing Before Answering: A Hallucination Evaluation Benchmark for Grounded Medical Multimodal LLMs
May 05, 2025Abstract:Medical Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in medical data interpretation. However, these models frequently generate hallucinations contradicting source evidence, particularly due to inadequate localization reasoning. This work reveals a critical limitation in current medical LMMs: instead of analyzing relevant pathological regions, they often rely on linguistic patterns or attend to irrelevant image areas when responding to disease-related queries. To address this, we introduce HEAL-MedVQA (Hallucination Evaluation via Localization MedVQA), a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate LMMs' localization abilities and hallucination robustness. HEAL-MedVQA features (i) two innovative evaluation protocols to assess visual and textual shortcut learning, and (ii) a dataset of 67K VQA pairs, with doctor-annotated anatomical segmentation masks for pathological regions. To improve visual reasoning, we propose the Localize-before-Answer (LobA) framework, which trains LMMs to localize target regions of interest and self-prompt to emphasize segmented pathological areas, generating grounded and reliable answers. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art biomedical LMMs on the challenging HEAL-MedVQA benchmark, advancing robustness in medical VQA.
A Survey of Medical Vision-and-Language Applications and Their Techniques
Nov 19, 2024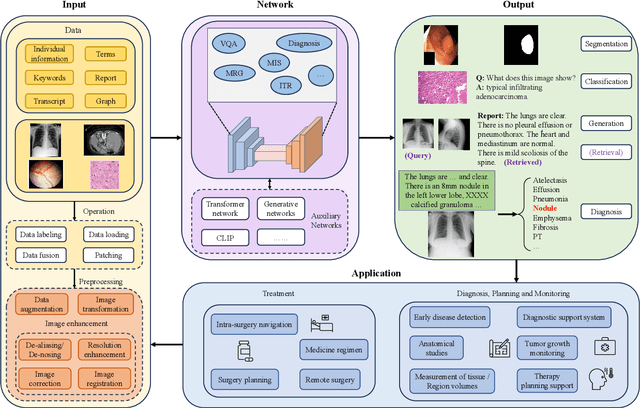
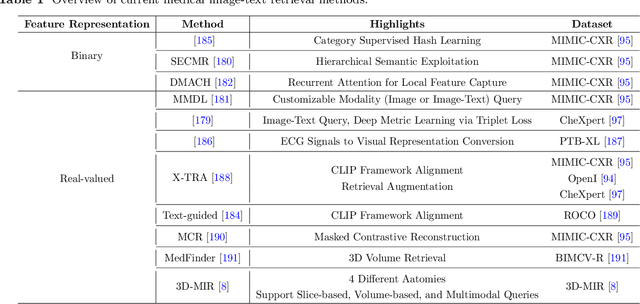
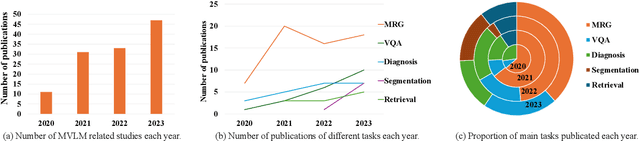
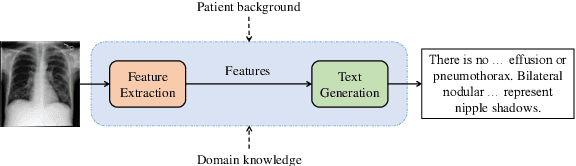
Abstract:Medical vision-and-language models (MVLMs) have attracted substantial interest due to their capability to offer a natural language interface for interpreting complex medical data. Their applications are versatile and have the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and decision-making for individual patients while also contributing to enhanced public health monitoring, disease surveillance, and policy-making through more efficient analysis of large data sets. MVLMS integrate natural language processing with medical images to enable a more comprehensive and contextual understanding of medical images alongside their corresponding textual information. Unlike general vision-and-language models trained on diverse, non-specialized datasets, MVLMs are purpose-built for the medical domain, automatically extracting and interpreting critical information from medical images and textual reports to support clinical decision-making. Popular clinical applications of MVLMs include automated medical report generation, medical visual question answering, medical multimodal segmentation, diagnosis and prognosis and medical image-text retrieval. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of MVLMs and the various medical tasks to which they have been applied. We conduct a detailed analysis of various vision-and-language model architectures, focusing on their distinct strategies for cross-modal integration/exploitation of medical visual and textual features. We also examine the datasets used for these tasks and compare the performance of different models based on standardized evaluation metrics. Furthermore, we highlight potential challenges and summarize future research trends and directions. The full collection of papers and codes is available at: https://github.com/YtongXie/Medical-Vision-and-Language-Tasks-and-Methodologies-A-Survey.
Multi-Head Multi-Loss Model Calibration
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:Delivering meaningful uncertainty estimates is essential for a successful deployment of machine learning models in the clinical practice. A central aspect of uncertainty quantification is the ability of a model to return predictions that are well-aligned with the actual probability of the model being correct, also known as model calibration. Although many methods have been proposed to improve calibration, no technique can match the simple, but expensive approach of training an ensemble of deep neural networks. In this paper we introduce a form of simplified ensembling that bypasses the costly training and inference of deep ensembles, yet it keeps its calibration capabilities. The idea is to replace the common linear classifier at the end of a network by a set of heads that are supervised with different loss functions to enforce diversity on their predictions. Specifically, each head is trained to minimize a weighted Cross-Entropy loss, but the weights are different among the different branches. We show that the resulting averaged predictions can achieve excellent calibration without sacrificing accuracy in two challenging datasets for histopathological and endoscopic image classification. Our experiments indicate that Multi-Head Multi-Loss classifiers are inherently well-calibrated, outperforming other recent calibration techniques and even challenging Deep Ensembles' performance. Code to reproduce our experiments can be found at \url{https://github.com/agaldran/mhml_calibration} .
Mutual information neural estimation for unsupervised multi-modal registration of brain images
Jan 25, 2022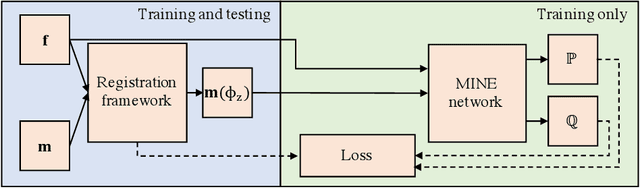
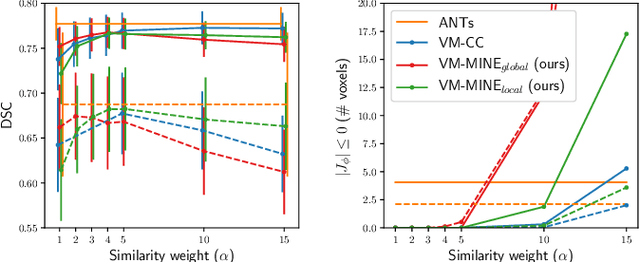
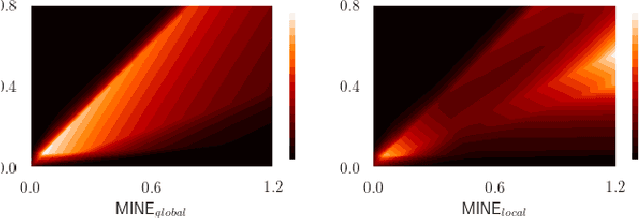

Abstract:Many applications in image-guided surgery and therapy require fast and reliable non-linear, multi-modal image registration. Recently proposed unsupervised deep learning-based registration methods have demonstrated superior performance compared to iterative methods in just a fraction of the time. Most of the learning-based methods have focused on mono-modal image registration. The extension to multi-modal registration depends on the use of an appropriate similarity function, such as the mutual information (MI). We propose guiding the training of a deep learning-based registration method with MI estimation between an image-pair in an end-to-end trainable network. Our results show that a small, 2-layer network produces competitive results in both mono- and multimodal registration, with sub-second run-times. Comparisons to both iterative and deep learning-based methods show that our MI-based method produces topologically and qualitatively superior results with an extremely low rate of non-diffeomorphic transformations. Real-time clinical application will benefit from a better visual matching of anatomical structures and less registration failures/outliers.
Pairwise Relation Learning for Semi-supervised Gland Segmentation
Aug 06, 2020



Abstract:Accurate and automated gland segmentation on histology tissue images is an essential but challenging task in the computer-aided diagnosis of adenocarcinoma. Despite their prevalence, deep learning models always require a myriad number of densely annotated training images, which are difficult to obtain due to extensive labor and associated expert costs related to histology image annotations. In this paper, we propose the pairwise relation-based semi-supervised (PRS^2) model for gland segmentation on histology images. This model consists of a segmentation network (S-Net) and a pairwise relation network (PR-Net). The S-Net is trained on labeled data for segmentation, and PR-Net is trained on both labeled and unlabeled data in an unsupervised way to enhance its image representation ability via exploiting the semantic consistency between each pair of images in the feature space. Since both networks share their encoders, the image representation ability learned by PR-Net can be transferred to S-Net to improve its segmentation performance. We also design the object-level Dice loss to address the issues caused by touching glands and combine it with other two loss functions for S-Net. We evaluated our model against five recent methods on the GlaS dataset and three recent methods on the CRAG dataset. Our results not only demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed PR-Net and object-level Dice loss, but also indicate that our PRS^2 model achieves the state-of-the-art gland segmentation performance on both benchmarks.
End-to-End Diagnosis and Segmentation Learning from Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Oct 23, 2018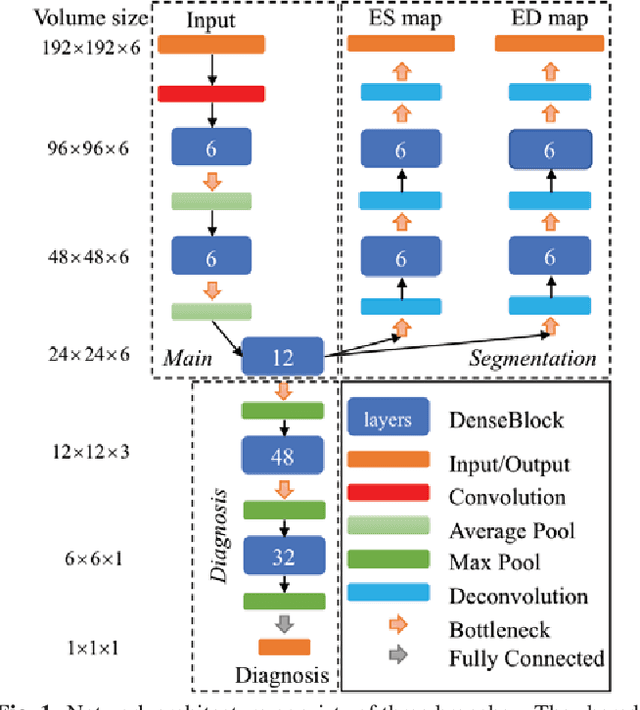
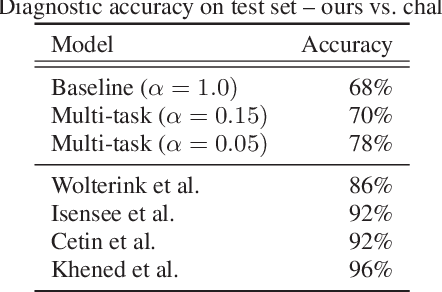


Abstract:Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) is used extensively in the diagnosis and management of cardiovascular disease. Deep learning methods have proven to deliver segmentation results comparable to human experts in CMR imaging, but there have been no convincing results for the problem of end-to-end segmentation and diagnosis from CMR. This is in part due to a lack of sufficiently large datasets required to train robust diagnosis models. In this paper, we propose a learning method to train diagnosis models, where our approach is designed to work with relatively small datasets. In particular, the optimisation loss is based on multi-task learning that jointly trains for the tasks of segmentation and diagnosis classification. We hypothesize that segmentation has a regularizing effect on the learning of features relevant for diagnosis. Using the 100 training and 50 testing samples available from the Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge (ACDC) dataset, which has a balanced distribution of 5 cardiac diagnoses, we observe a reduction of the classification error from 32% to 22%, and a faster convergence compared to a baseline without segmentation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the best diagnosis results from CMR using an end-to-end diagnosis and segmentation learning method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge