Joel Shor
FEM-Bench: A Structured Scientific Reasoning Benchmark for Evaluating Code-Generating LLMs
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:As LLMs advance their reasoning capabilities about the physical world, the absence of rigorous benchmarks for evaluating their ability to generate scientifically valid physical models has become a critical gap. Computational mechanics, which develops and applies mathematical models and numerical methods to predict the behavior of physical systems under forces, deformation, and constraints, provides an ideal foundation for structured scientific reasoning evaluation. Problems follow clear mathematical structure, enforce strict physical and numerical constraints, and support objective verification. The discipline requires constructing explicit models of physical systems and reasoning about geometry, spatial relationships, and material behavior, connecting directly to emerging AI goals in physical reasoning and world modeling. We introduce FEM-Bench, a computational mechanics benchmark designed to evaluate the ability of LLMs to generate correct finite element method (FEM) and related code. FEM-Bench 2025 contains a suite of introductory but nontrivial tasks aligned with material from a first graduate course on computational mechanics. These tasks capture essential numerical and physical modeling challenges while representing only a small fraction of the complexity present in the discipline. Despite their simplicity, state-of-the-art LLMs do not reliably solve all of them. In a five attempt run, the best performing model at function writing, Gemini 3 Pro, completed 30/33 tasks at least once and 26/33 tasks all five times. The best performing model at unit test writing, GPT-5, had an Average Joint Success Rate of 73.8%. Other popular models showed broad performance variation. FEM-Bench establishes a structured foundation for evaluating AI-generated scientific code, and future iterations will incorporate increasingly sophisticated tasks to track progress as models evolve.
From Prompt to Product: A Human-Centered Benchmark of Agentic App Generation Systems
Dec 19, 2025


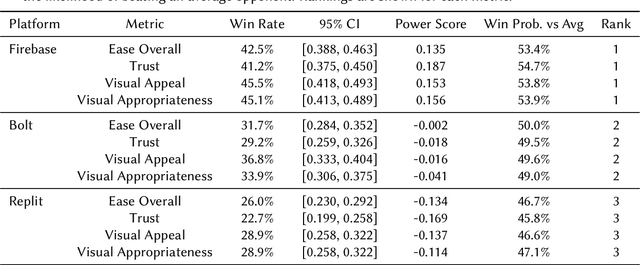
Abstract:Agentic AI systems capable of generating full-stack web applications from natural language prompts ("prompt- to-app") represent a significant shift in software development. However, evaluating these systems remains challenging, as visual polish, functional correctness, and user trust are often misaligned. As a result, it is unclear how existing prompt-to-app tools compare under realistic, human-centered evaluation criteria. In this paper, we introduce a human-centered benchmark for evaluating prompt-to-app systems and conduct a large-scale comparative study of three widely used platforms: Replit, Bolt, and Firebase Studio. Using a diverse set of 96 prompts spanning common web application tasks, we generate 288 unique application artifacts. We evaluate these systems through a large-scale human-rater study involving 205 participants and 1,071 quality-filtered pairwise comparisons, assessing task-based ease of use, visual appeal, perceived completeness, and user trust. Our results show that these systems are not interchangeable: Firebase Studio consistently outperforms competing platforms across all human-evaluated dimensions, achieving the highest win rates for ease of use, trust, visual appeal, and visual appropriateness. Bolt performs competitively on visual appeal but trails Firebase on usability and trust, while Replit underperforms relative to both across most metrics. These findings highlight a persistent gap between visual polish and functional reliability in prompt-to-app systems and demonstrate the necessity of interactive, task-based evaluation. We release our benchmark framework, prompt set, and generated artifacts to support reproducible evaluation and future research in agentic application generation.
Predicting Generalization of AI Colonoscopy Models to Unseen Data
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:$\textbf{Background}$: Generalizability of AI colonoscopy algorithms is important for wider adoption in clinical practice. However, current techniques for evaluating performance on unseen data require expensive and time-intensive labels. $\textbf{Methods}$: We use a "Masked Siamese Network" (MSN) to identify novel phenomena in unseen data and predict polyp detector performance. MSN is trained to predict masked out regions of polyp images, without any labels. We test MSN's ability to be trained on data only from Israel and detect unseen techniques, narrow-band imaging (NBI) and chromendoscoy (CE), on colonoscopes from Japan (354 videos, 128 hours). We also test MSN's ability to predict performance of Computer Aided Detection (CADe) of polyps on colonoscopies from both countries, even though MSN is not trained on data from Japan. $\textbf{Results}$: MSN correctly identifies NBI and CE as less similar to Israel whitelight than Japan whitelight (bootstrapped z-test, |z| > 496, p < 10^-8 for both) using the label-free Frechet distance. MSN detects NBI with 99% accuracy, predicts CE better than our heuristic (90% vs 79% accuracy) despite being trained only on whitelight, and is the only method that is robust to noisy labels. MSN predicts CADe polyp detector performance on in-domain Israel and out-of-domain Japan colonoscopies (r=0.79, 0.37 respectively). With few examples of Japan detector performance to train on, MSN prediction of Japan performance improves (r=0.56). $\textbf{Conclusion}$: Our technique can identify distribution shifts in clinical data and can predict CADe detector performance on unseen data, without labels. Our self-supervised approach can aid in detecting when data in practice is different from training, such as between hospitals or data has meaningfully shifted from training. MSN has potential for application to medical image domains beyond colonoscopy.
The unreasonable effectiveness of AI CADe polyp detectors to generalize to new countries
Dec 17, 2023Abstract:$\textbf{Background and aims}$: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Computer-Aided Detection (CADe) is commonly used for polyp detection, but data seen in clinical settings can differ from model training. Few studies evaluate how well CADe detectors perform on colonoscopies from countries not seen during training, and none are able to evaluate performance without collecting expensive and time-intensive labels. $\textbf{Methods}$: We trained a CADe polyp detector on Israeli colonoscopy videos (5004 videos, 1106 hours) and evaluated on Japanese videos (354 videos, 128 hours) by measuring the True Positive Rate (TPR) versus false alarms per minute (FAPM). We introduce a colonoscopy dissimilarity measure called "MAsked mediCal Embedding Distance" (MACE) to quantify differences between colonoscopies, without labels. We evaluated CADe on all Japan videos and on those with the highest MACE. $\textbf{Results}$: MACE correctly quantifies that narrow-band imaging (NBI) and chromoendoscopy (CE) frames are less similar to Israel data than Japan whitelight (bootstrapped z-test, |z| > 690, p < $10^{-8}$ for both). Despite differences in the data, CADe performance on Japan colonoscopies was non-inferior to Israel ones without additional training (TPR at 0.5 FAPM: 0.957 and 0.972 for Israel and Japan; TPR at 1.0 FAPM: 0.972 and 0.989 for Israel and Japan; superiority test t > 45.2, p < $10^{-8}$). Despite not being trained on NBI or CE, TPR on those subsets were non-inferior to Japan overall (non-inferiority test t > 47.3, p < $10^{-8}$, $\delta$ = 1.5% for both). $\textbf{Conclusion}$: Differences that prevent CADe detectors from performing well in non-medical settings do not degrade the performance of our AI CADe polyp detector when applied to data from a new country. MACE can help medical AI models internationalize by identifying the most "dissimilar" data on which to evaluate models.
Clinical BERTScore: An Improved Measure of Automatic Speech Recognition Performance in Clinical Settings
Mar 13, 2023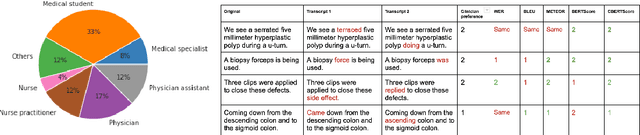
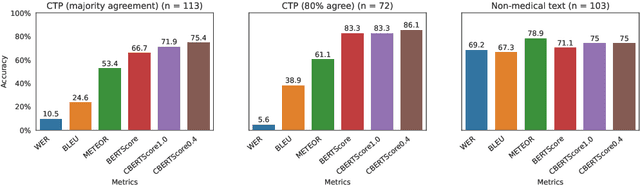
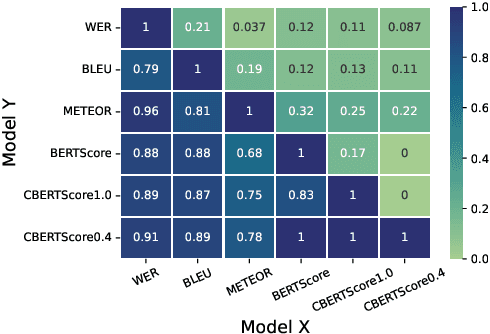
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) in medical contexts has the potential to save time, cut costs, increase report accuracy, and reduce physician burnout. However, the healthcare industry has been slower to adopt this technology, in part due to the importance of avoiding medically-relevant transcription mistakes. In this work, we present the Clinical BERTScore (CBERTScore), an ASR metric that penalizes clinically-relevant mistakes more than others. We demonstrate that this metric more closely aligns with clinician preferences on medical sentences as compared to other metrics (WER, BLUE, METEOR, etc), sometimes by wide margins. We collect a benchmark of 13 clinician preferences on 149 realistic medical sentences called the Clinician Transcript Preference benchmark (CTP), demonstrate that CBERTScore more closely matches what clinicians prefer, and release the benchmark for the community to further develop clinically-aware ASR metrics.
Knowledge distillation for fast and accurate DNA sequence correction
Nov 17, 2022



Abstract:Accurate genome sequencing can improve our understanding of biology and the genetic basis of disease. The standard approach for generating DNA sequences from PacBio instruments relies on HMM-based models. Here, we introduce Distilled DeepConsensus - a distilled transformer-encoder model for sequence correction, which improves upon the HMM-based methods with runtime constraints in mind. Distilled DeepConsensus is 1.3x faster and 1.5x smaller than its larger counterpart while improving the yield of high quality reads (Q30) over the HMM-based method by 1.69x (vs. 1.73x for larger model). With improved accuracy of genomic sequences, Distilled DeepConsensus improves downstream applications of genomic sequence analysis such as reducing variant calling errors by 39% (34% for larger model) and improving genome assembly quality by 3.8% (4.2% for larger model). We show that the representations learned by Distilled DeepConsensus are similar between faster and slower models.
The Need for Medically Aware Video Compression in Gastroenterology
Nov 02, 2022



Abstract:Compression is essential to storing and transmitting medical videos, but the effect of compression on downstream medical tasks is often ignored. Furthermore, systems in practice rely on standard video codecs, which naively allocate bits between medically relevant frames or parts of frames. In this work, we present an empirical study of some deficiencies of classical codecs on gastroenterology videos, and motivate our ongoing work to train a learned compression model for colonoscopy videos. We show that two of the most common classical codecs, H264 and HEVC, compress medically relevant frames statistically significantly worse than medically nonrelevant ones, and that polyp detector performance degrades rapidly as compression increases. We explain how a learned compressor could allocate bits to important regions and allow detection performance to degrade more gracefully. Many of our proposed techniques generalize to medical video domains beyond gastroenterology
TRILLsson: Distilled Universal Paralinguistic Speech Representations
Mar 20, 2022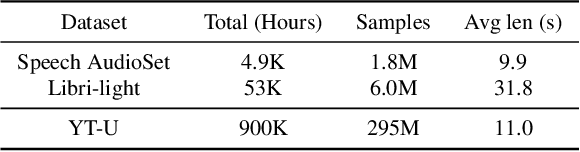
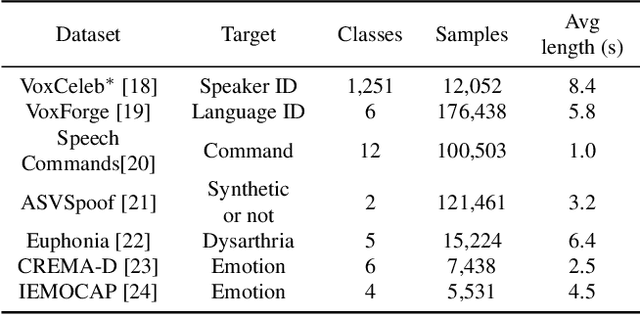
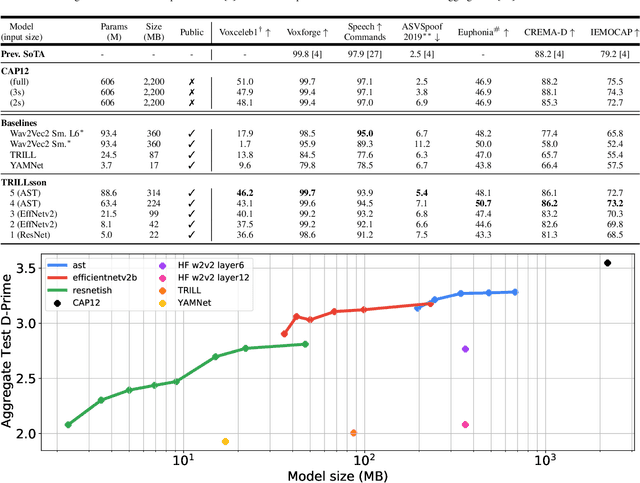
Abstract:Recent advances in self-supervision have dramatically improved the quality of speech representations. However, deployment of state-of-the-art embedding models on devices has been restricted due to their limited public availability and large resource footprint. Our work addresses these issues by publicly releasing a collection of paralinguistic speech models that are small and near state-of-the-art performance. Our approach is based on knowledge distillation, and our models are distilled on public data only. We explore different architectures and thoroughly evaluate our models on the Non-Semantic Speech (NOSS) benchmark. Our largest distilled model is less than 15% the size of the original model (314MB vs 2.2GB), achieves over 96% the accuracy on 6 of 7 tasks, and is trained on 6.5% the data. The smallest model is 1% in size (22MB) and achieves over 90% the accuracy on 6 of 7 tasks. Our models outperform the open source Wav2Vec 2.0 model on 6 of 7 tasks, and our smallest model outperforms the open source Wav2Vec 2.0 on both emotion recognition tasks despite being 7% the size.
Universal Paralinguistic Speech Representations Using Self-Supervised Conformers
Oct 09, 2021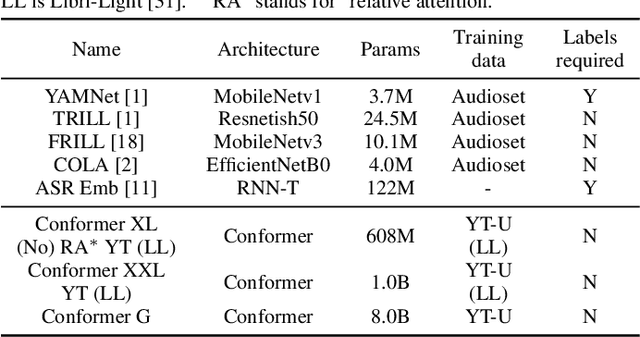
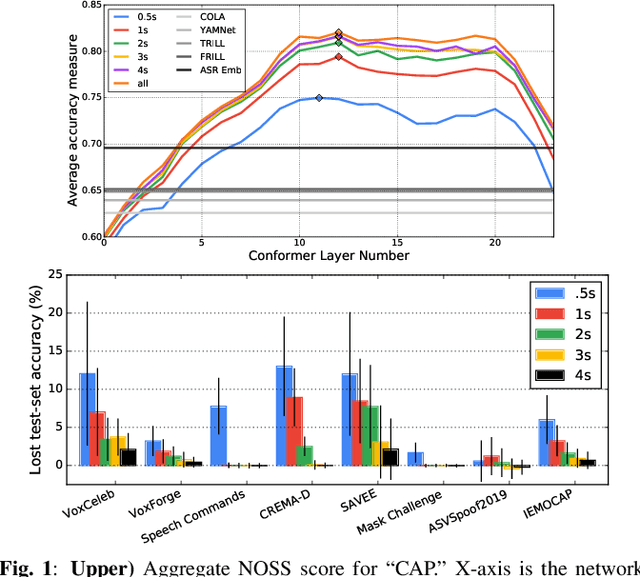
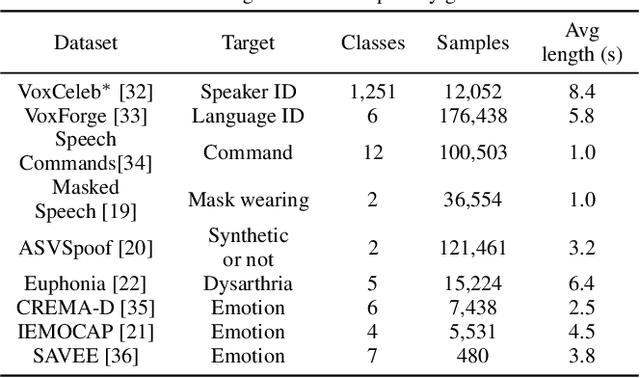
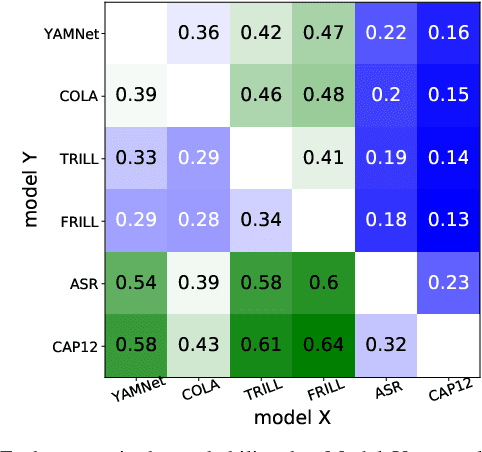
Abstract:Many speech applications require understanding aspects beyond the words being spoken, such as recognizing emotion, detecting whether the speaker is wearing a mask, or distinguishing real from synthetic speech. In this work, we introduce a new state-of-the-art paralinguistic representation derived from large-scale, fully self-supervised training of a 600M+ parameter Conformer-based architecture. We benchmark on a diverse set of speech tasks and demonstrate that simple linear classifiers trained on top of our time-averaged representation outperform nearly all previous results, in some cases by large margins. Our analyses of context-window size demonstrate that, surprisingly, 2 second context-windows achieve 98% the performance of the Conformers that use the full long-term context. Furthermore, while the best per-task representations are extracted internally in the network, stable performance across several layers allows a single universal representation to reach near optimal performance on all tasks.
BigSSL: Exploring the Frontier of Large-Scale Semi-Supervised Learning for Automatic Speech Recognition
Oct 01, 2021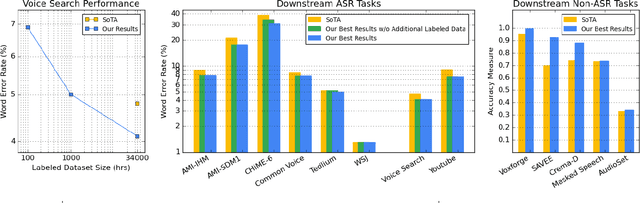
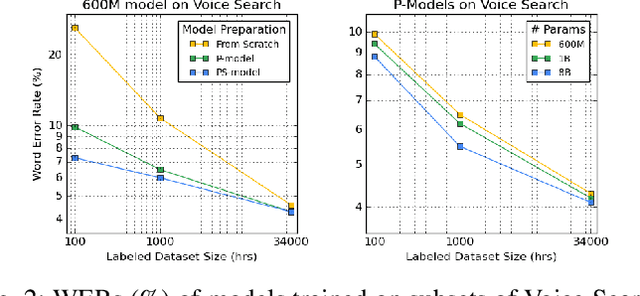
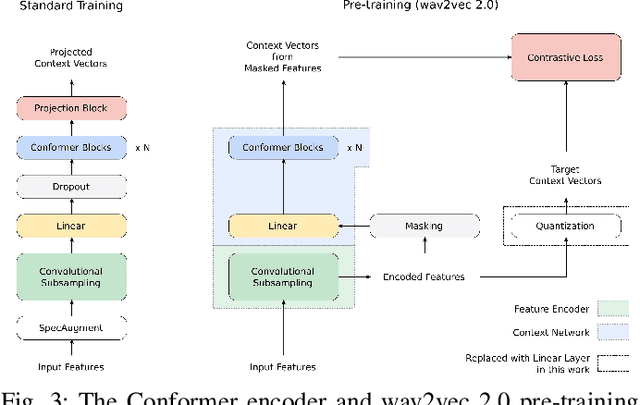
Abstract:We summarize the results of a host of efforts using giant automatic speech recognition (ASR) models pre-trained using large, diverse unlabeled datasets containing approximately a million hours of audio. We find that the combination of pre-training, self-training and scaling up model size greatly increases data efficiency, even for extremely large tasks with tens of thousands of hours of labeled data. In particular, on an ASR task with 34k hours of labeled data, by fine-tuning an 8 billion parameter pre-trained Conformer model we can match state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance with only 3% of the training data and significantly improve SoTA with the full training set. We also report on the universal benefits gained from using big pre-trained and self-trained models for a large set of downstream tasks that cover a wide range of speech domains and span multiple orders of magnitudes of dataset sizes, including obtaining SoTA performance on many public benchmarks. In addition, we utilize the learned representation of pre-trained networks to achieve SoTA results on non-ASR tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge