Towards Learning a Universal Non-Semantic Representation of Speech
Paper and Code
Mar 02, 2020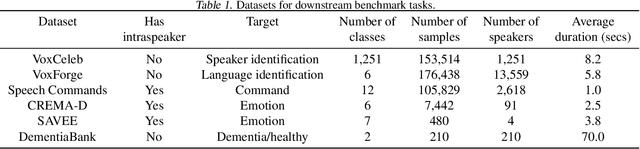
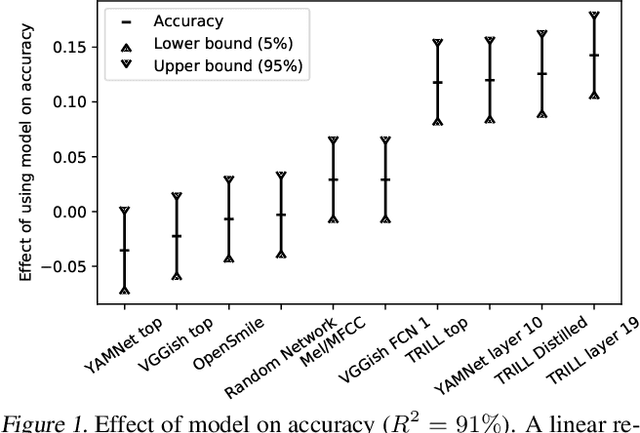
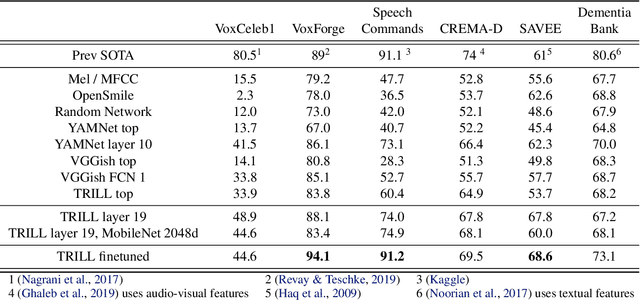
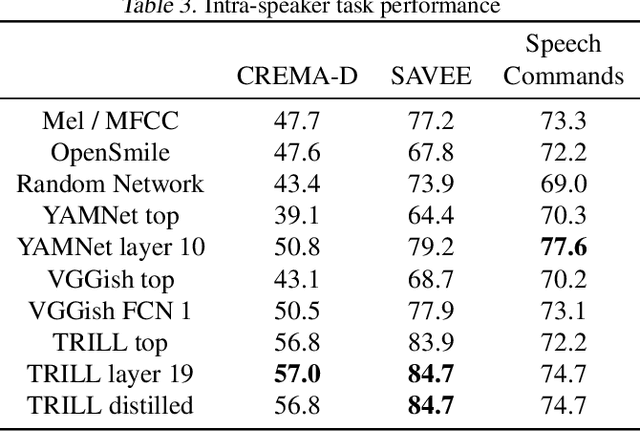
The ultimate goal of transfer learning is to reduce labeled data requirements by exploiting a pre-existing embedding model trained for different datasets or tasks. While significant progress has been made in the visual and language domains, the speech community has yet to identify a strategy with wide-reaching applicability across tasks. This paper describes a representation of speech based on an unsupervised triplet-loss objective, which exceeds state-of-the-art performance on a number of transfer learning tasks drawn from the non-semantic speech domain. The embedding is trained on a publicly available dataset, and it is tested on a variety of low-resource downstream tasks, including personalization tasks and medical domain. The model will be publicly released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge