Jingke Meng
ProEdit: Inversion-based Editing From Prompts Done Right
Dec 26, 2025



Abstract:Inversion-based visual editing provides an effective and training-free way to edit an image or a video based on user instructions. Existing methods typically inject source image information during the sampling process to maintain editing consistency. However, this sampling strategy overly relies on source information, which negatively affects the edits in the target image (e.g., failing to change the subject's atributes like pose, number, or color as instructed). In this work, we propose ProEdit to address this issue both in the attention and the latent aspects. In the attention aspect, we introduce KV-mix, which mixes KV features of the source and the target in the edited region, mitigating the influence of the source image on the editing region while maintaining background consistency. In the latent aspect, we propose Latents-Shift, which perturbs the edited region of the source latent, eliminating the influence of the inverted latent on the sampling. Extensive experiments on several image and video editing benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA performance. In addition, our design is plug-and-play, which can be seamlessly integrated into existing inversion and editing methods, such as RF-Solver, FireFlow and UniEdit.
ChainHOI: Joint-based Kinematic Chain Modeling for Human-Object Interaction Generation
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:We propose ChainHOI, a novel approach for text-driven human-object interaction (HOI) generation that explicitly models interactions at both the joint and kinetic chain levels. Unlike existing methods that implicitly model interactions using full-body poses as tokens, we argue that explicitly modeling joint-level interactions is more natural and effective for generating realistic HOIs, as it directly captures the geometric and semantic relationships between joints, rather than modeling interactions in the latent pose space. To this end, ChainHOI introduces a novel joint graph to capture potential interactions with objects, and a Generative Spatiotemporal Graph Convolution Network to explicitly model interactions at the joint level. Furthermore, we propose a Kinematics-based Interaction Module that explicitly models interactions at the kinetic chain level, ensuring more realistic and biomechanically coherent motions. Evaluations on two public datasets demonstrate that ChainHOI significantly outperforms previous methods, generating more realistic, and semantically consistent HOIs. Code is available \href{https://github.com/qinghuannn/ChainHOI}{here}.
LLMDet: Learning Strong Open-Vocabulary Object Detectors under the Supervision of Large Language Models
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:Recent open-vocabulary detectors achieve promising performance with abundant region-level annotated data. In this work, we show that an open-vocabulary detector co-training with a large language model by generating image-level detailed captions for each image can further improve performance. To achieve the goal, we first collect a dataset, GroundingCap-1M, wherein each image is accompanied by associated grounding labels and an image-level detailed caption. With this dataset, we finetune an open-vocabulary detector with training objectives including a standard grounding loss and a caption generation loss. We take advantage of a large language model to generate both region-level short captions for each region of interest and image-level long captions for the whole image. Under the supervision of the large language model, the resulting detector, LLMDet, outperforms the baseline by a clear margin, enjoying superior open-vocabulary ability. Further, we show that the improved LLMDet can in turn build a stronger large multi-modal model, achieving mutual benefits. The code, model, and dataset is available at https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/LLMDet.
Towards Completeness: A Generalizable Action Proposal Generator for Zero-Shot Temporal Action Localization
Aug 25, 2024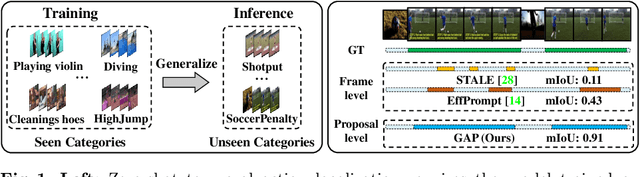
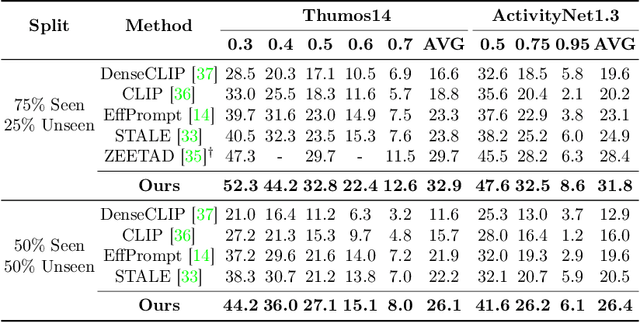
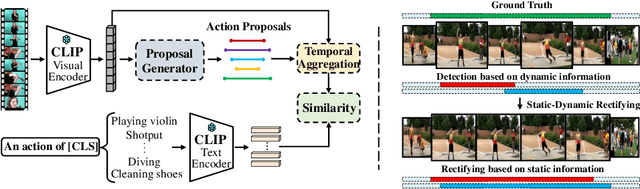
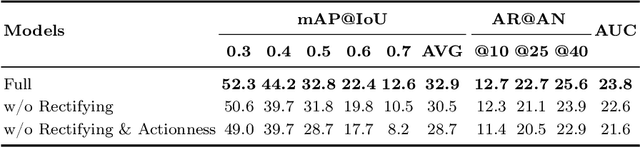
Abstract:To address the zero-shot temporal action localization (ZSTAL) task, existing works develop models that are generalizable to detect and classify actions from unseen categories. They typically develop a category-agnostic action detector and combine it with the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) model to solve ZSTAL. However, these methods suffer from incomplete action proposals generated for \textit{unseen} categories, since they follow a frame-level prediction paradigm and require hand-crafted post-processing to generate action proposals. To address this problem, in this work, we propose a novel model named Generalizable Action Proposal generator (GAP), which can interface seamlessly with CLIP and generate action proposals in a holistic way. Our GAP is built in a query-based architecture and trained with a proposal-level objective, enabling it to estimate proposal completeness and eliminate the hand-crafted post-processing. Based on this architecture, we propose an Action-aware Discrimination loss to enhance the category-agnostic dynamic information of actions. Besides, we introduce a Static-Dynamic Rectifying module that incorporates the generalizable static information from CLIP to refine the predicted proposals, which improves proposal completeness in a generalizable manner. Our experiments show that our GAP achieves state-of-the-art performance on two challenging ZSTAL benchmarks, i.e., Thumos14 and ActivityNet1.3. Specifically, our model obtains significant performance improvement over previous works on the two benchmarks, i.e., +3.2% and +3.4% average mAP, respectively.
Loc4Plan: Locating Before Planning for Outdoor Vision and Language Navigation
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:Vision and Language Navigation (VLN) is a challenging task that requires agents to understand instructions and navigate to the destination in a visual environment.One of the key challenges in outdoor VLN is keeping track of which part of the instruction was completed. To alleviate this problem, previous works mainly focus on grounding the natural language to the visual input, but neglecting the crucial role of the agent's spatial position information in the grounding process. In this work, we first explore the substantial effect of spatial position locating on the grounding of outdoor VLN, drawing inspiration from human navigation. In real-world navigation scenarios, before planning a path to the destination, humans typically need to figure out their current location. This observation underscores the pivotal role of spatial localization in the navigation process. In this work, we introduce a novel framework, Locating be for Planning (Loc4Plan), designed to incorporate spatial perception for action planning in outdoor VLN tasks. The main idea behind Loc4Plan is to perform the spatial localization before planning a decision action based on corresponding guidance, which comprises a block-aware spatial locating (BAL) module and a spatial-aware action planning (SAP) module. Specifically, to help the agent perceive its spatial location in the environment, we propose to learn a position predictor that measures how far the agent is from the next intersection for reflecting its position, which is achieved by the BAL module. After the locating process, we propose the SAP module to incorporate spatial information to ground the corresponding guidance and enhance the precision of action planning. Extensive experiments on the Touchdown and map2seq datasets show that the proposed Loc4Plan outperforms the SOTA methods.
PRET: Planning with Directed Fidelity Trajectory for Vision and Language Navigation
Jul 16, 2024



Abstract:Vision and language navigation is a task that requires an agent to navigate according to a natural language instruction. Recent methods predict sub-goals on constructed topology map at each step to enable long-term action planning. However, they suffer from high computational cost when attempting to support such high-level predictions with GCN-like models. In this work, we propose an alternative method that facilitates navigation planning by considering the alignment between instructions and directed fidelity trajectories, which refers to a path from the initial node to the candidate locations on a directed graph without detours. This planning strategy leads to an efficient model while achieving strong performance. Specifically, we introduce a directed graph to illustrate the explored area of the environment, emphasizing directionality. Then, we firstly define the trajectory representation as a sequence of directed edge features, which are extracted from the panorama based on the corresponding orientation. Ultimately, we assess and compare the alignment between instruction and different trajectories during navigation to determine the next navigation target. Our method outperforms previous SOTA method BEVBert on RxR dataset and is comparable on R2R dataset while largely reducing the computational cost. Code is available: https://github.com/iSEE-Laboratory/VLN-PRET.
Cross-Modal Adaptive Dual Association for Text-to-Image Person Retrieval
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:Text-to-image person re-identification (ReID) aims to retrieve images of a person based on a given textual description. The key challenge is to learn the relations between detailed information from visual and textual modalities. Existing works focus on learning a latent space to narrow the modality gap and further build local correspondences between two modalities. However, these methods assume that image-to-text and text-to-image associations are modality-agnostic, resulting in suboptimal associations. In this work, we show the discrepancy between image-to-text association and text-to-image association and propose CADA: Cross-Modal Adaptive Dual Association that finely builds bidirectional image-text detailed associations. Our approach features a decoder-based adaptive dual association module that enables full interaction between visual and textual modalities, allowing for bidirectional and adaptive cross-modal correspondence associations. Specifically, the paper proposes a bidirectional association mechanism: Association of text Tokens to image Patches (ATP) and Association of image Regions to text Attributes (ARA). We adaptively model the ATP based on the fact that aggregating cross-modal features based on mistaken associations will lead to feature distortion. For modeling the ARA, since the attributes are typically the first distinguishing cues of a person, we propose to explore the attribute-level association by predicting the masked text phrase using the related image region. Finally, we learn the dual associations between texts and images, and the experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our dual formulation. Codes will be made publicly available.
DiffuVolume: Diffusion Model for Volume based Stereo Matching
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:Stereo matching is a significant part in many computer vision tasks and driving-based applications. Recently cost volume-based methods have achieved great success benefiting from the rich geometry information in paired images. However, the redundancy of cost volume also interferes with the model training and limits the performance. To construct a more precise cost volume, we pioneeringly apply the diffusion model to stereo matching. Our method, termed DiffuVolume, considers the diffusion model as a cost volume filter, which will recurrently remove the redundant information from the cost volume. Two main designs make our method not trivial. Firstly, to make the diffusion model more adaptive to stereo matching, we eschew the traditional manner of directly adding noise into the image but embed the diffusion model into a task-specific module. In this way, we outperform the traditional diffusion stereo matching method by 22% EPE improvement and 240 times inference acceleration. Secondly, DiffuVolume can be easily embedded into any volume-based stereo matching network with boost performance but slight parameters rise (only 2%). By adding the DiffuVolume into well-performed methods, we outperform all the published methods on Scene Flow, KITTI2012, KITTI2015 benchmarks and zero-shot generalization setting. It is worth mentioning that the proposed model ranks 1st on KITTI 2012 leader board, 2nd on KITTI 2015 leader board since 15, July 2023.
Event-Guided Procedure Planning from Instructional Videos with Text Supervision
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:In this work, we focus on the task of procedure planning from instructional videos with text supervision, where a model aims to predict an action sequence to transform the initial visual state into the goal visual state. A critical challenge of this task is the large semantic gap between observed visual states and unobserved intermediate actions, which is ignored by previous works. Specifically, this semantic gap refers to that the contents in the observed visual states are semantically different from the elements of some action text labels in a procedure. To bridge this semantic gap, we propose a novel event-guided paradigm, which first infers events from the observed states and then plans out actions based on both the states and predicted events. Our inspiration comes from that planning a procedure from an instructional video is to complete a specific event and a specific event usually involves specific actions. Based on the proposed paradigm, we contribute an Event-guided Prompting-based Procedure Planning (E3P) model, which encodes event information into the sequential modeling process to support procedure planning. To further consider the strong action associations within each event, our E3P adopts a mask-and-predict approach for relation mining, incorporating a probabilistic masking scheme for regularization. Extensive experiments on three datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model.
Weakly Supervised Person Re-Identification
May 28, 2019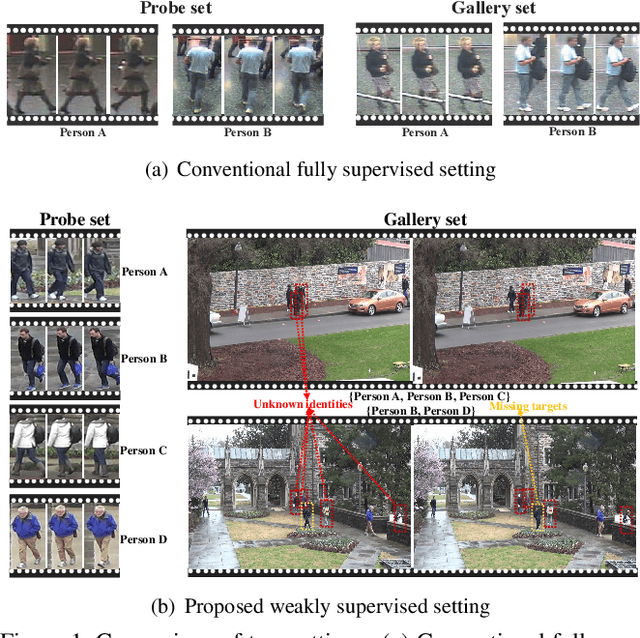
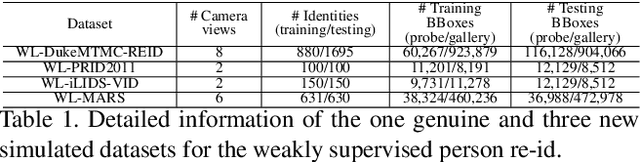
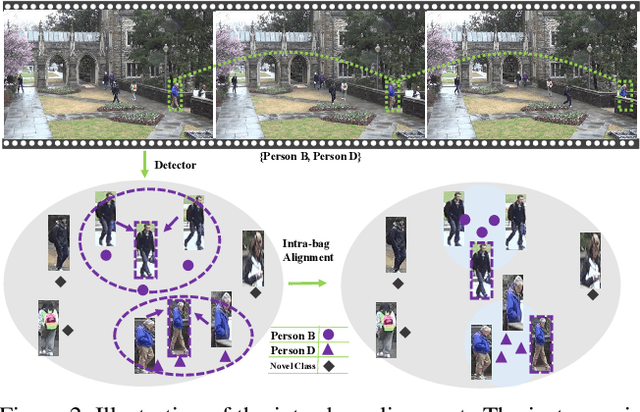
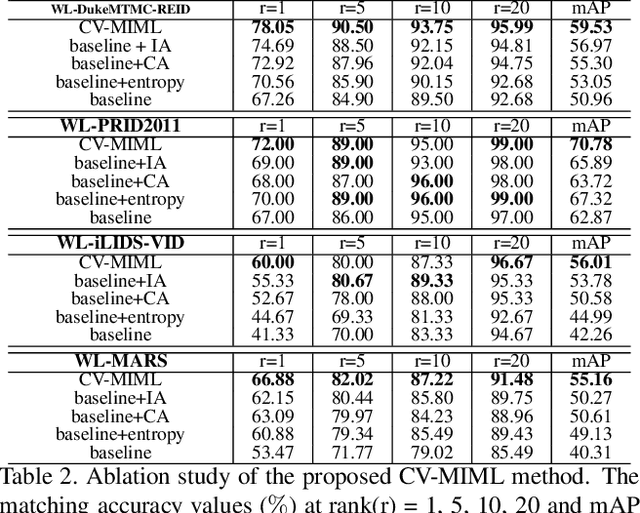
Abstract:In the conventional person re-id setting, it is assumed that the labeled images are the person images within the bounding box for each individual; this labeling across multiple nonoverlapping camera views from raw video surveillance is costly and time-consuming. To overcome this difficulty, we consider weakly supervised person re-id modeling. The weak setting refers to matching a target person with an untrimmed gallery video where we only know that the identity appears in the video without the requirement of annotating the identity in any frame of the video during the training procedure. Hence, for a video, there could be multiple video-level labels. We cast this weakly supervised person re-id challenge into a multi-instance multi-label learning (MIML) problem. In particular, we develop a Cross-View MIML (CV-MIML) method that is able to explore potential intraclass person images from all the camera views by incorporating the intra-bag alignment and the cross-view bag alignment. Finally, the CV-MIML method is embedded into an existing deep neural network for developing the Deep Cross-View MIML (Deep CV-MIML) model. We have performed extensive experiments to show the feasibility of the proposed weakly supervised setting and verify the effectiveness of our method compared to related methods on four weakly labeled datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge