Jing Dai
Robustness study of the bio-inspired musculoskeletal arm robot based on the data-driven iterative learning algorithm
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:The human arm exhibits remarkable capabilities, including both explosive power and precision, which demonstrate dexterity, compliance, and robustness in unstructured environments. Developing robotic systems that emulate human-like operational characteristics through musculoskeletal structures has long been a research focus. In this study, we designed a novel lightweight tendon-driven musculoskeletal arm (LTDM-Arm), featuring a seven degree-of-freedom (DOF) skeletal joint system and a modularized artificial muscular system (MAMS) with 15 actuators. Additionally, we employed a Hilly-type muscle model and data-driven iterative learning control (DDILC) to learn and refine activation signals for repetitive tasks within a finite time frame. We validated the anti-interference capabilities of the musculoskeletal system through both simulations and experiments. The results show that the LTDM-Arm system can effectively achieve desired trajectory tracking tasks, even under load disturbances of 20 % in simulation and 15 % in experiments. This research lays the foundation for developing advanced robotic systems with human-like operational performance.
* 20 pages, 13 figures
Development of the Bioinspired Tendon-Driven DexHand 021 with Proprioceptive Compliance Control
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:The human hand plays a vital role in daily life and industrial applications, yet replicating its multifunctional capabilities-including motion, sensing, and coordinated manipulation-with robotic systems remains a formidable challenge. Developing a dexterous robotic hand requires balancing human-like agility with engineering constraints such as complexity, size-to-weight ratio, durability, and force-sensing performance. This letter presents Dex-Hand 021, a high-performance, cable-driven five-finger robotic hand with 12 active and 7 passive degrees of freedom (DoFs), achieving 19 DoFs dexterity in a lightweight 1 kg design. We propose a proprioceptive force-sensing-based admittance control method to enhance manipulation. Experimental results demonstrate its superior performance: a single-finger load capacity exceeding 10 N, fingertip repeatability under 0.001 m, and force estimation errors below 0.2 N. Compared to PID control, joint torques in multi-object grasping are reduced by 31.19%, significantly improves force-sensing capability while preventing overload during collisions. The hand excels in both power and precision grasps, successfully executing 33 GRASP taxonomy motions and complex manipulation tasks. This work advances the design of lightweight, industrial-grade dexterous hands and enhances proprioceptive control, contributing to robotic manipulation and intelligent manufacturing.
Enhancing Human Experience in Human-Agent Collaboration: A Human-Centered Modeling Approach Based on Positive Human Gain
Jan 28, 2024



Abstract:Existing game AI research mainly focuses on enhancing agents' abilities to win games, but this does not inherently make humans have a better experience when collaborating with these agents. For example, agents may dominate the collaboration and exhibit unintended or detrimental behaviors, leading to poor experiences for their human partners. In other words, most game AI agents are modeled in a "self-centered" manner. In this paper, we propose a "human-centered" modeling scheme for collaborative agents that aims to enhance the experience of humans. Specifically, we model the experience of humans as the goals they expect to achieve during the task. We expect that agents should learn to enhance the extent to which humans achieve these goals while maintaining agents' original abilities (e.g., winning games). To achieve this, we propose the Reinforcement Learning from Human Gain (RLHG) approach. The RLHG approach introduces a "baseline", which corresponds to the extent to which humans primitively achieve their goals, and encourages agents to learn behaviors that can effectively enhance humans in achieving their goals better. We evaluate the RLHG agent in the popular Multi-player Online Battle Arena (MOBA) game, Honor of Kings, by conducting real-world human-agent tests. Both objective performance and subjective preference results show that the RLHG agent provides participants better gaming experience.
Semi-supervised Domain Adaptation on Graphs with Contrastive Learning and Minimax Entropy
Sep 14, 2023



Abstract:Label scarcity in a graph is frequently encountered in real-world applications due to the high cost of data labeling. To this end, semi-supervised domain adaptation (SSDA) on graphs aims to leverage the knowledge of a labeled source graph to aid in node classification on a target graph with limited labels. SSDA tasks need to overcome the domain gap between the source and target graphs. However, to date, this challenging research problem has yet to be formally considered by the existing approaches designed for cross-graph node classification. To tackle the SSDA problem on graphs, a novel method called SemiGCL is proposed, which benefits from graph contrastive learning and minimax entropy training. SemiGCL generates informative node representations by contrasting the representations learned from a graph's local and global views. Additionally, SemiGCL is adversarially optimized with the entropy loss of unlabeled target nodes to reduce domain divergence. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that SemiGCL outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines on the SSDA tasks.
Computer-Aided Clinical Skin Disease Diagnosis Using CNN and Object Detection Models
Nov 20, 2019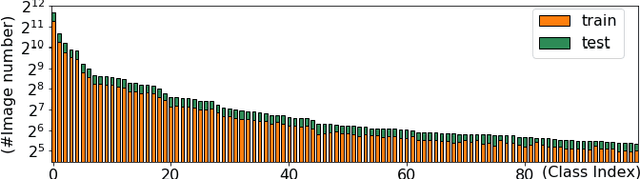
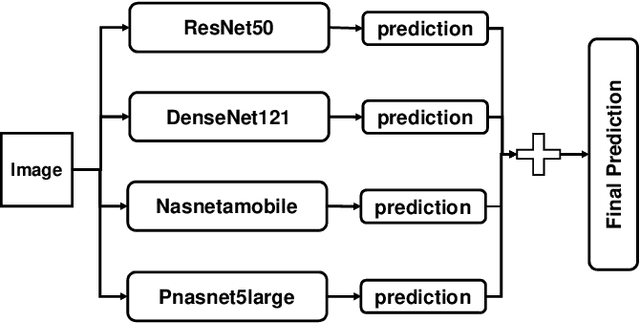
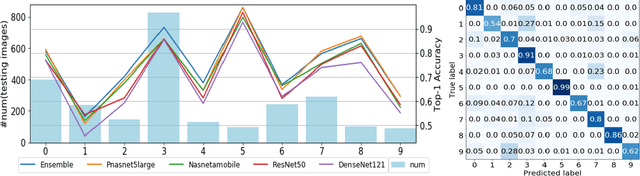
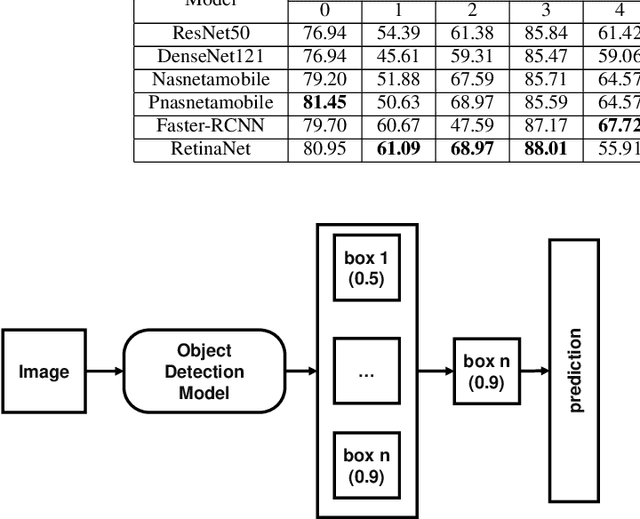
Abstract:Skin disease is one of the most common types of human diseases, which may happen to everyone regardless of age, gender or race. Due to the high visual diversity, human diagnosis highly relies on personal experience; and there is a serious shortage of experienced dermatologists in many countries. To alleviate this problem, computer-aided diagnosis with state-of-the-art (SOTA) machine learning techniques would be a promising solution. In this paper, we aim at understanding the performance of convolutional neural network (CNN) based approaches. We first build two versions of skin disease datasets from Internet images: (a) Skin-10, which contains 10 common classes of skin disease with a total of 10,218 images; (b) Skin-100, which is a larger dataset that consists of 19,807 images of 100 skin disease classes. Based on these datasets, we benchmark several SOTA CNN models and show that the accuracy of skin-100 is much lower than the accuracy of skin-10. We then implement an ensemble method based on several CNN models and achieve the best accuracy of 79.01\% for Skin-10 and 53.54\% for Skin-100. We also present an object detection based approach by introducing bounding boxes into the Skin-10 dataset. Our results show that object detection can help improve the accuracy of some skin disease classes.
Multimodal Storytelling via Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning
Dec 05, 2017



Abstract:Deriving event storylines is an effective summarization method to succinctly organize extensive information, which can significantly alleviate the pain of information overload. The critical challenge is the lack of widely recognized definition of storyline metric. Prior studies have developed various approaches based on different assumptions about users' interests. These works can extract interesting patterns, but their assumptions do not guarantee that the derived patterns will match users' preference. On the other hand, their exclusiveness of single modality source misses cross-modality information. This paper proposes a method, multimodal imitation learning via generative adversarial networks(MIL-GAN), to directly model users' interests as reflected by various data. In particular, the proposed model addresses the critical challenge by imitating users' demonstrated storylines. Our proposed model is designed to learn the reward patterns given user-provided storylines and then applies the learned policy to unseen data. The proposed approach is demonstrated to be capable of acquiring the user's implicit intent and outperforming competing methods by a substantial margin with a user study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge