Arnold P. Boedihardjo
Robust Regression via Online Feature Selection under Adversarial Data Corruption
Feb 05, 2019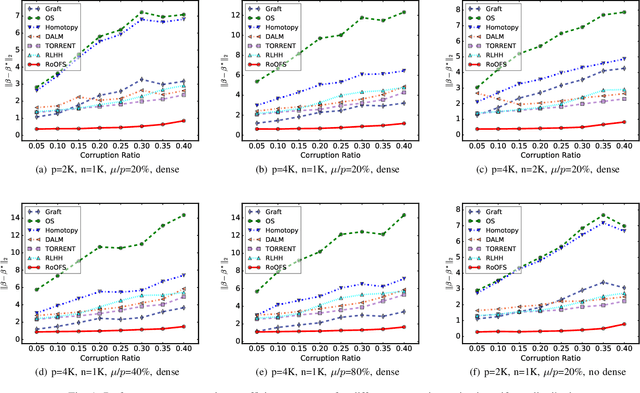
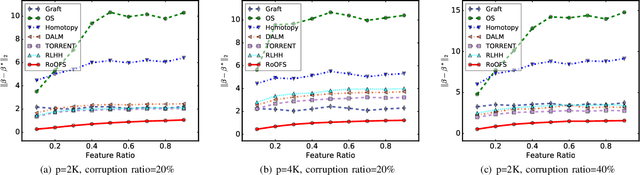
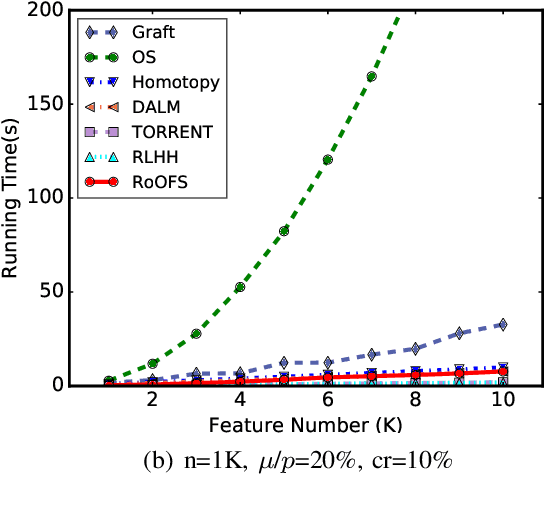
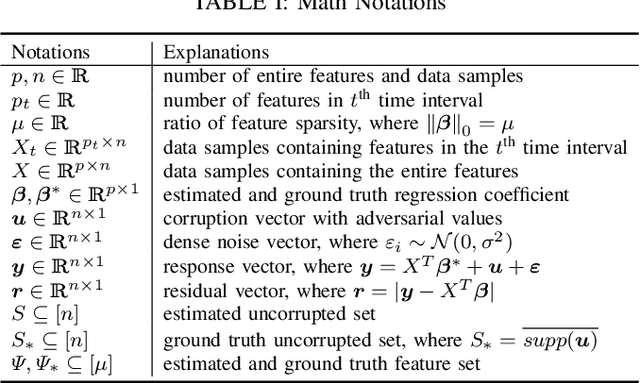
Abstract:The presence of data corruption in user-generated streaming data, such as social media, motivates a new fundamental problem that learns reliable regression coefficient when features are not accessible entirely at one time. Until now, several important challenges still cannot be handled concurrently: 1) corrupted data estimation when only partial features are accessible; 2) online feature selection when data contains adversarial corruption; and 3) scaling to a massive dataset. This paper proposes a novel RObust regression algorithm via Online Feature Selection (\textit{RoOFS}) that concurrently addresses all the above challenges. Specifically, the algorithm iteratively updates the regression coefficients and the uncorrupted set via a robust online feature substitution method. We also prove that our algorithm has a restricted error bound compared to the optimal solution. Extensive empirical experiments in both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrated that the effectiveness of our new method is superior to that of existing methods in the recovery of both feature selection and regression coefficients, with very competitive efficiency.
Multimodal Storytelling via Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning
Dec 05, 2017



Abstract:Deriving event storylines is an effective summarization method to succinctly organize extensive information, which can significantly alleviate the pain of information overload. The critical challenge is the lack of widely recognized definition of storyline metric. Prior studies have developed various approaches based on different assumptions about users' interests. These works can extract interesting patterns, but their assumptions do not guarantee that the derived patterns will match users' preference. On the other hand, their exclusiveness of single modality source misses cross-modality information. This paper proposes a method, multimodal imitation learning via generative adversarial networks(MIL-GAN), to directly model users' interests as reflected by various data. In particular, the proposed model addresses the critical challenge by imitating users' demonstrated storylines. Our proposed model is designed to learn the reward patterns given user-provided storylines and then applies the learned policy to unseen data. The proposed approach is demonstrated to be capable of acquiring the user's implicit intent and outperforming competing methods by a substantial margin with a user study.
Online and Distributed Robust Regressions under Adversarial Data Corruption
Oct 02, 2017



Abstract:In today's era of big data, robust least-squares regression becomes a more challenging problem when considering the adversarial corruption along with explosive growth of datasets. Traditional robust methods can handle the noise but suffer from several challenges when applied in huge dataset including 1) computational infeasibility of handling an entire dataset at once, 2) existence of heterogeneously distributed corruption, and 3) difficulty in corruption estimation when data cannot be entirely loaded. This paper proposes online and distributed robust regression approaches, both of which can concurrently address all the above challenges. Specifically, the distributed algorithm optimizes the regression coefficients of each data block via heuristic hard thresholding and combines all the estimates in a distributed robust consolidation. Furthermore, an online version of the distributed algorithm is proposed to incrementally update the existing estimates with new incoming data. We also prove that our algorithms benefit from strong robustness guarantees in terms of regression coefficient recovery with a constant upper bound on the error of state-of-the-art batch methods. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real datasets demonstrate that our approaches are superior to those of existing methods in effectiveness, with competitive efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge