Shuo Lei
DC-Gaussian: Improving 3D Gaussian Splatting for Reflective Dash Cam Videos
May 29, 2024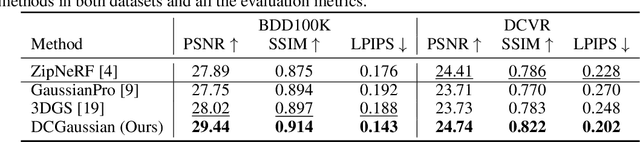

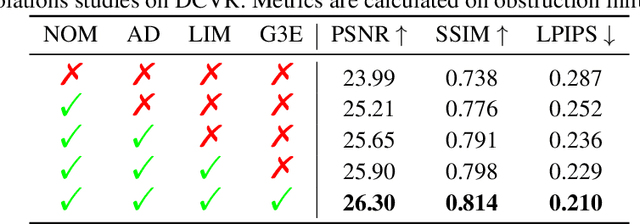
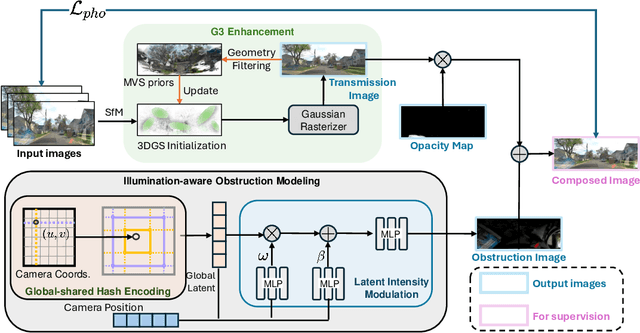
Abstract:We present DC-Gaussian, a new method for generating novel views from in-vehicle dash cam videos. While neural rendering techniques have made significant strides in driving scenarios, existing methods are primarily designed for videos collected by autonomous vehicles. However, these videos are limited in both quantity and diversity compared to dash cam videos, which are more widely used across various types of vehicles and capture a broader range of scenarios. Dash cam videos often suffer from severe obstructions such as reflections and occlusions on the windshields, which significantly impede the application of neural rendering techniques. To address this challenge, we develop DC-Gaussian based on the recent real-time neural rendering technique 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Our approach includes an adaptive image decomposition module to model reflections and occlusions in a unified manner. Additionally, we introduce illumination-aware obstruction modeling to manage reflections and occlusions under varying lighting conditions. Lastly, we employ a geometry-guided Gaussian enhancement strategy to improve rendering details by incorporating additional geometry priors. Experiments on self-captured and public dash cam videos show that our method not only achieves state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis, but also accurately reconstructing captured scenes getting rid of obstructions.
Exploring the Deceptive Power of LLM-Generated Fake News: A Study of Real-World Detection Challenges
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled the creation of fake news, particularly in complex fields like healthcare. Studies highlight the gap in the deceptive power of LLM-generated fake news with and without human assistance, yet the potential of prompting techniques has not been fully explored. Thus, this work aims to determine whether prompting strategies can effectively narrow this gap. Current LLM-based fake news attacks require human intervention for information gathering and often miss details and fail to maintain context consistency. Therefore, to better understand threat tactics, we propose a strong fake news attack method called conditional Variational-autoencoder-Like Prompt (VLPrompt). Unlike current methods, VLPrompt eliminates the need for additional data collection while maintaining contextual coherence and preserving the intricacies of the original text. To propel future research on detecting VLPrompt attacks, we created a new dataset named VLPrompt fake news (VLPFN) containing real and fake texts. Our experiments, including various detection methods and novel human study metrics, were conducted to assess their performance on our dataset, yielding numerous findings.
Can LLM find the green circle? Investigation and Human-guided tool manipulation for compositional generalization
Dec 12, 2023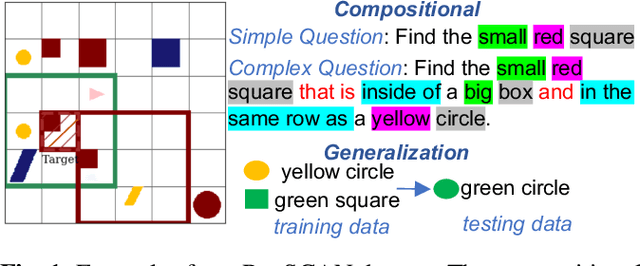
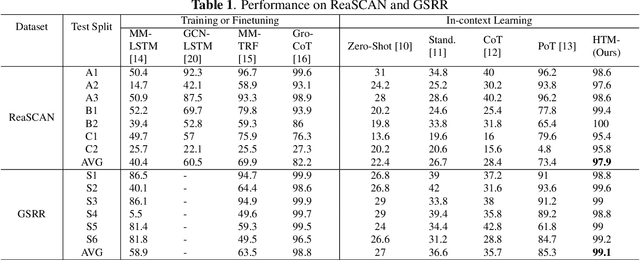
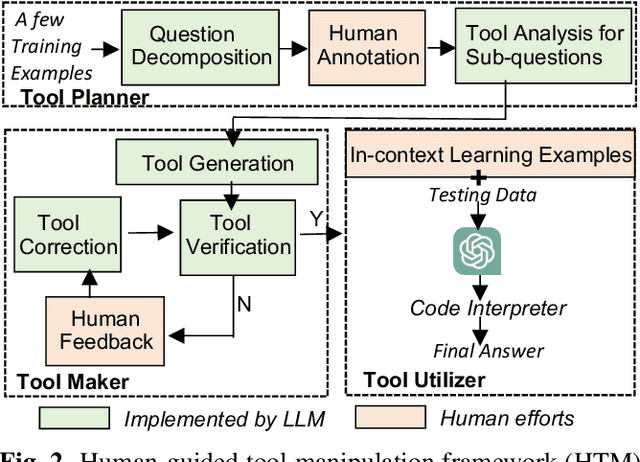
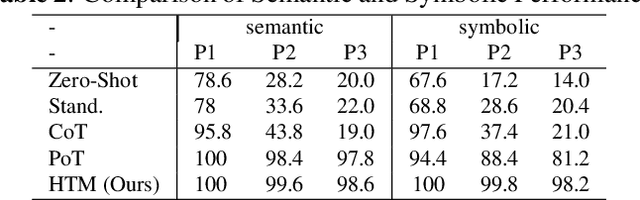
Abstract:The meaning of complex phrases in natural language is composed of their individual components. The task of compositional generalization evaluates a model's ability to understand new combinations of components. Previous studies trained smaller, task-specific models, which exhibited poor generalization. While large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive generalization abilities on many tasks through in-context learning (ICL), their potential for compositional generalization remains unexplored. In this paper, we first empirically investigate prevailing ICL methods in compositional generalization. We find that they struggle with complex compositional questions due to cumulative errors in long reasoning steps and intricate logic required for tool-making. Consequently, we propose a human-guided tool manipulation framework (HTM) that generates tools for sub-questions and integrates multiple tools. Our method enhances the effectiveness of tool creation and usage with minimal human effort. Experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two compositional generalization benchmarks and outperforms existing methods on the most challenging test split by 70%.
Uncertainty Estimation on Sequential Labeling via Uncertainty Transmission
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:Sequential labeling is a task predicting labels for each token in a sequence, such as Named Entity Recognition (NER). NER tasks aim to extract entities and predict their labels given a text, which is important in information extraction. Although previous works have shown great progress in improving NER performance, uncertainty estimation on NER (UE-NER) is still underexplored but essential. This work focuses on UE-NER, which aims to estimate uncertainty scores for the NER predictions. Previous uncertainty estimation models often overlook two unique characteristics of NER: the connection between entities (i.e., one entity embedding is learned based on the other ones) and wrong span cases in the entity extraction subtask. Therefore, we propose a Sequential Labeling Posterior Network (SLPN) to estimate uncertainty scores for the extracted entities, considering uncertainty transmitted from other tokens. Moreover, we have defined an evaluation strategy to address the specificity of wrong-span cases. Our SLPN has achieved significant improvements on two datasets, such as a 5.54-point improvement in AUPR on the MIT-Restaurant dataset.
Self-Correlation and Cross-Correlation Learning for Few-Shot Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
Sep 15, 2023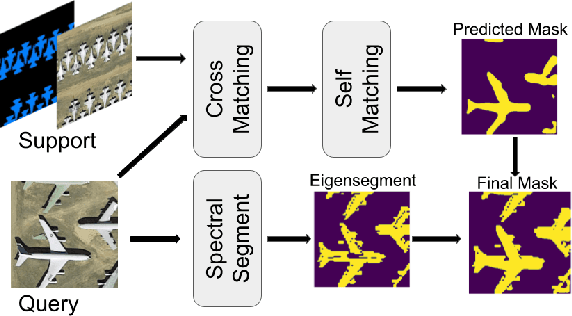

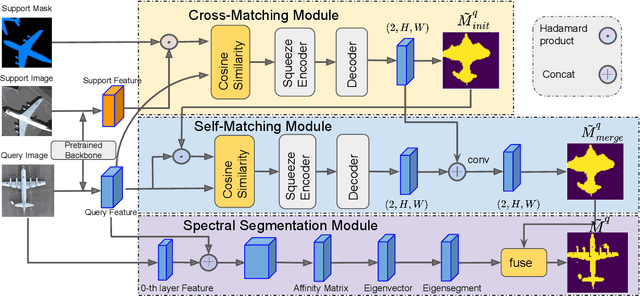

Abstract:Remote sensing image semantic segmentation is an important problem for remote sensing image interpretation. Although remarkable progress has been achieved, existing deep neural network methods suffer from the reliance on massive training data. Few-shot remote sensing semantic segmentation aims at learning to segment target objects from a query image using only a few annotated support images of the target class. Most existing few-shot learning methods stem primarily from their sole focus on extracting information from support images, thereby failing to effectively address the large variance in appearance and scales of geographic objects. To tackle these challenges, we propose a Self-Correlation and Cross-Correlation Learning Network for the few-shot remote sensing image semantic segmentation. Our model enhances the generalization by considering both self-correlation and cross-correlation between support and query images to make segmentation predictions. To further explore the self-correlation with the query image, we propose to adopt a classical spectral method to produce a class-agnostic segmentation mask based on the basic visual information of the image. Extensive experiments on two remote sensing image datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our model in few-shot remote sensing image semantic segmentation. Code and models will be accessed at https://github.com/linhanwang/SCCNet.
TART: Improved Few-shot Text Classification Using Task-Adaptive Reference Transformation
Jun 03, 2023
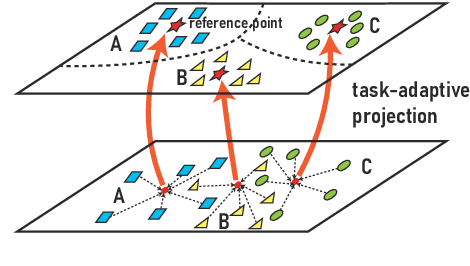
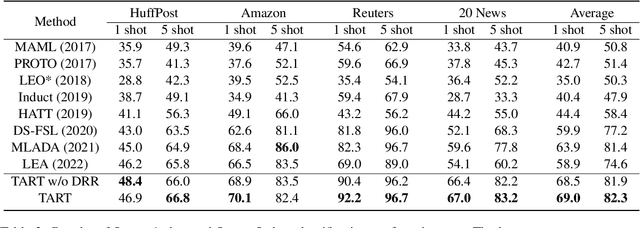
Abstract:Meta-learning has emerged as a trending technique to tackle few-shot text classification and achieve state-of-the-art performance. However, the performance of existing approaches heavily depends on the inter-class variance of the support set. As a result, it can perform well on tasks when the semantics of sampled classes are distinct while failing to differentiate classes with similar semantics. In this paper, we propose a novel Task-Adaptive Reference Transformation (TART) network, aiming to enhance the generalization by transforming the class prototypes to per-class fixed reference points in task-adaptive metric spaces. To further maximize divergence between transformed prototypes in task-adaptive metric spaces, TART introduces a discriminative reference regularization among transformed prototypes. Extensive experiments are conducted on four benchmark datasets and our method demonstrates clear superiority over the state-of-the-art models in all the datasets. In particular, our model surpasses the state-of-the-art method by 7.4% and 5.4% in 1-shot and 5-shot classification on the 20 Newsgroups dataset, respectively.
Semantic Editing On Segmentation Map Via Multi-Expansion Loss
Oct 16, 2020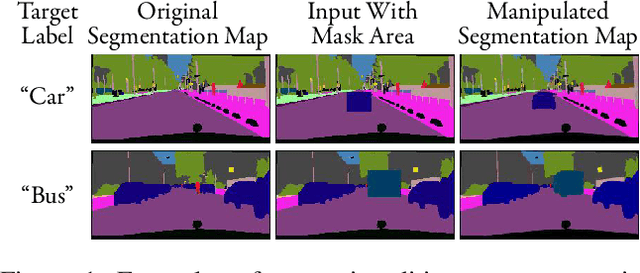
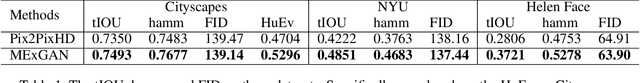
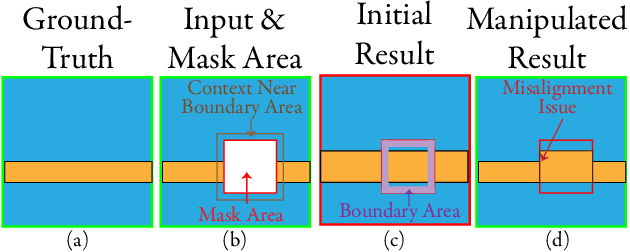
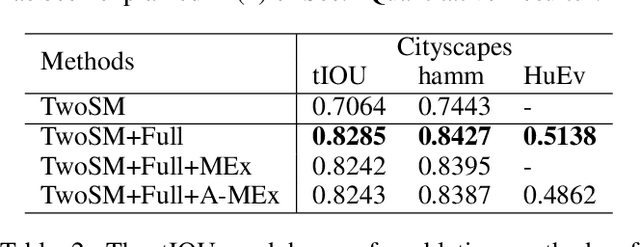
Abstract:Semantic editing on segmentation map has been proposed as an intermediate interface for image generation, because it provides flexible and strong assistance in various image generation tasks. This paper aims to improve quality of edited segmentation map conditioned on semantic inputs. Even though recent studies apply global and local adversarial losses extensively to generate images for higher image quality, we find that they suffer from the misalignment of the boundary area in the mask area. To address this, we propose MExGAN for semantic editing on segmentation map, which uses a novel Multi-Expansion (MEx) loss implemented by adversarial losses on MEx areas. Each MEx area has the mask area of the generation as the majority and the boundary of original context as the minority. To boost convenience and stability of MEx loss, we further propose an Approximated MEx (A-MEx) loss. Besides, in contrast to previous model that builds training data for semantic editing on segmentation map with part of the whole image, which leads to model performance degradation, MExGAN applies the whole image to build the training data. Extensive experiments on semantic editing on segmentation map and natural image inpainting show competitive results on four datasets.
Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation Augmented with Image-Level Weak Annotations
Jul 03, 2020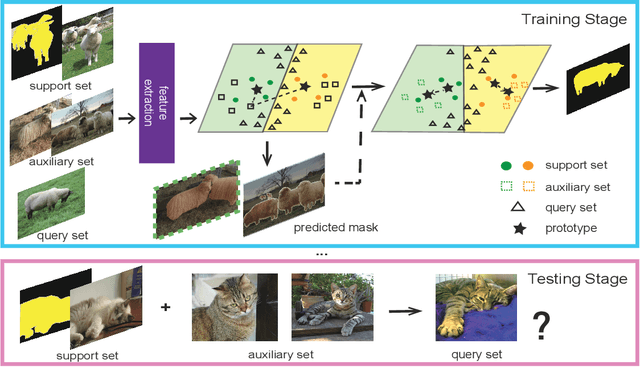
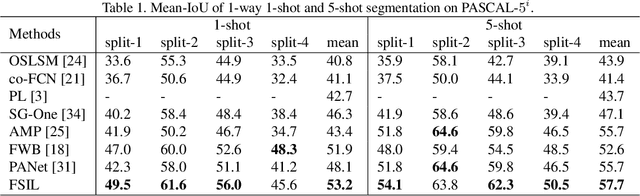
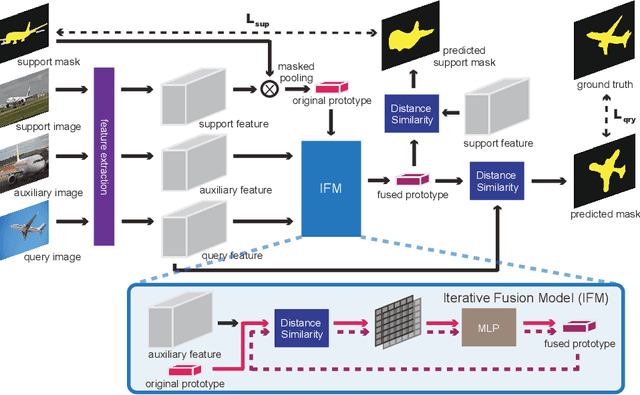
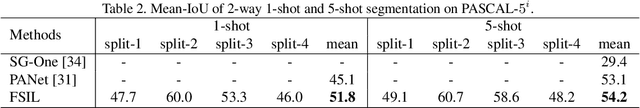
Abstract:Despite the great progress made by deep neural networks in the semantic segmentation task, traditional neural network-based methods typically suffer from a shortage of large amounts of pixel-level annotations. Recent progress in few-shot semantic segmentation tackles the issue by utilizing only a few pixel-level annotated examples. However, these few-shot approaches cannot easily be applied to utilize image-level weak annotations, which can easily be obtained and considerably improve performance in the semantic segmentation task. In this paper, we advance the few-shot segmentation paradigm towards a scenario where image-level annotations are available to help the training process of a few pixel-level annotations. Specifically, we propose a new framework to learn the class prototype representation in the metric space by integrating image-level annotations. Furthermore, a soft masked average pooling strategy is designed to handle distractions in image-level annotations. Extensive empirical results on PASCAL-5i show that our method can achieve 5.1% and 8.2% increases of mIoU score for one-shot settings with pixel-level and scribble annotations, respectively.
Robust Regression via Online Feature Selection under Adversarial Data Corruption
Feb 05, 2019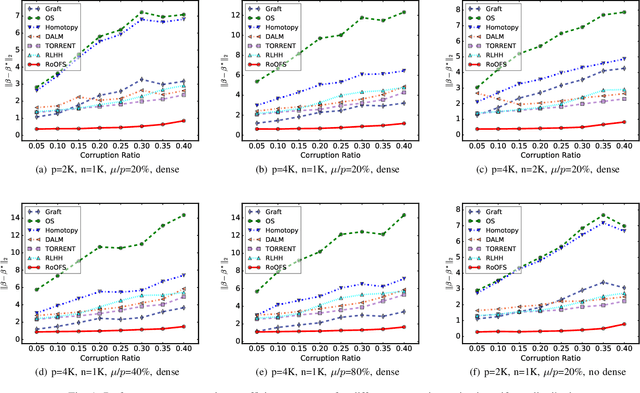
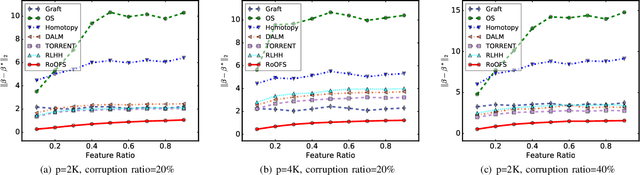
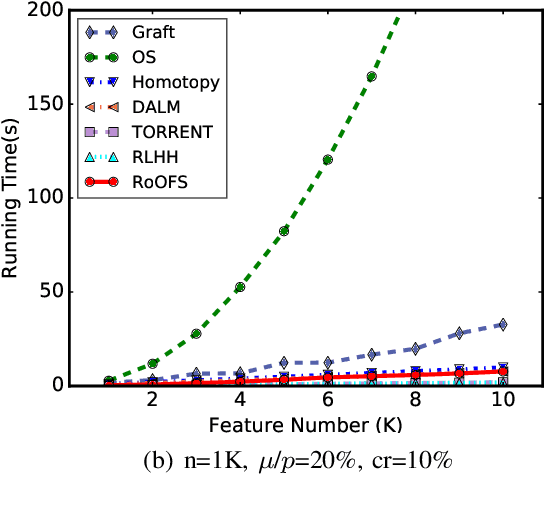
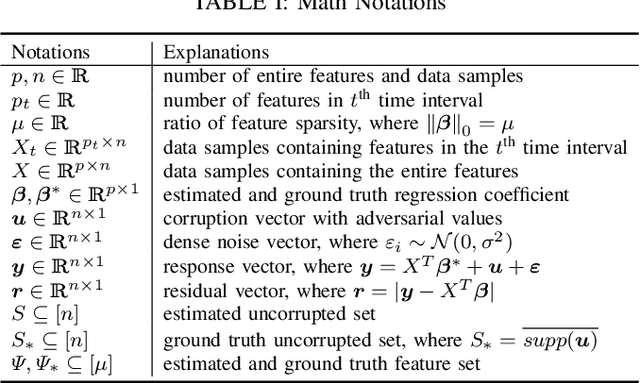
Abstract:The presence of data corruption in user-generated streaming data, such as social media, motivates a new fundamental problem that learns reliable regression coefficient when features are not accessible entirely at one time. Until now, several important challenges still cannot be handled concurrently: 1) corrupted data estimation when only partial features are accessible; 2) online feature selection when data contains adversarial corruption; and 3) scaling to a massive dataset. This paper proposes a novel RObust regression algorithm via Online Feature Selection (\textit{RoOFS}) that concurrently addresses all the above challenges. Specifically, the algorithm iteratively updates the regression coefficients and the uncorrupted set via a robust online feature substitution method. We also prove that our algorithm has a restricted error bound compared to the optimal solution. Extensive empirical experiments in both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrated that the effectiveness of our new method is superior to that of existing methods in the recovery of both feature selection and regression coefficients, with very competitive efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge