Linhan Wang
Virginia Tech
Drive-JEPA: Video JEPA Meets Multimodal Trajectory Distillation for End-to-End Driving
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving increasingly leverages self-supervised video pretraining to learn transferable planning representations. However, pretraining video world models for scene understanding has so far brought only limited improvements. This limitation is compounded by the inherent ambiguity of driving: each scene typically provides only a single human trajectory, making it difficult to learn multimodal behaviors. In this work, we propose Drive-JEPA, a framework that integrates Video Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (V-JEPA) with multimodal trajectory distillation for end-to-end driving. First, we adapt V-JEPA for end-to-end driving, pretraining a ViT encoder on large-scale driving videos to produce predictive representations aligned with trajectory planning. Second, we introduce a proposal-centric planner that distills diverse simulator-generated trajectories alongside human trajectories, with a momentum-aware selection mechanism to promote stable and safe behavior. When evaluated on NAVSIM, the V-JEPA representation combined with a simple transformer-based decoder outperforms prior methods by 3 PDMS in the perception-free setting. The complete Drive-JEPA framework achieves 93.3 PDMS on v1 and 87.8 EPDMS on v2, setting a new state-of-the-art.
SemiETPicker: Fast and Label-Efficient Particle Picking for CryoET Tomography Using Semi-Supervised Learning
Oct 25, 2025Abstract:Cryogenic Electron Tomography (CryoET) combined with sub-volume averaging (SVA) is the only imaging modality capable of resolving protein structures inside cells at molecular resolution. Particle picking, the task of localizing and classifying target proteins in 3D CryoET volumes, remains the main bottleneck. Due to the reliance on time-consuming manual labels, the vast reserve of unlabeled tomograms remains underutilized. In this work, we present a fast, label-efficient semi-supervised framework that exploits this untapped data. Our framework consists of two components: (i) an end-to-end heatmap-supervised detection model inspired by keypoint detection, and (ii) a teacher-student co-training mechanism that enhances performance under sparse labeling conditions. Furthermore, we introduce multi-view pseudo-labeling and a CryoET-specific DropBlock augmentation strategy to further boost performance. Extensive evaluations on the large-scale CZII dataset show that our approach improves F1 by 10% over supervised baselines, underscoring the promise of semi-supervised learning for leveraging unlabeled CryoET data.
Chasing the Timber Trail: Machine Learning to Reveal Harvest Location Misrepresentation
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:Illegal logging poses a significant threat to global biodiversity, climate stability, and depresses international prices for legal wood harvesting and responsible forest products trade, affecting livelihoods and communities across the globe. Stable isotope ratio analysis (SIRA) is rapidly becoming an important tool for determining the harvest location of traded, organic, products. The spatial pattern in stable isotope ratio values depends on factors such as atmospheric and environmental conditions and can thus be used for geographical identification. We present here the results of a deployed machine learning pipeline where we leverage both isotope values and atmospheric variables to determine timber harvest location. Additionally, the pipeline incorporates uncertainty estimation to facilitate the interpretation of harvest location determination for analysts. We present our experiments on a collection of oak (Quercus spp.) tree samples from its global range. Our pipeline outperforms comparable state-of-the-art models determining geographic harvest origin of commercially traded wood products, and has been used by European enforcement agencies to identify illicit Russian and Belarusian timber entering the EU market. We also identify opportunities for further advancement of our framework and how it can be generalized to help identify the origin of falsely labeled organic products throughout the supply chain.
Downscaling Precipitation with Bias-informed Conditional Diffusion Model
Dec 19, 2024

Abstract:Climate change is intensifying rainfall extremes, making high-resolution precipitation projections crucial for society to better prepare for impacts such as flooding. However, current Global Climate Models (GCMs) operate at spatial resolutions too coarse for localized analyses. To address this limitation, deep learning-based statistical downscaling methods offer promising solutions, providing high-resolution precipitation projections with a moderate computational cost. In this work, we introduce a bias-informed conditional diffusion model for statistical downscaling of precipitation. Specifically, our model leverages a conditional diffusion approach to learn distribution priors from large-scale, high-resolution precipitation datasets. The long-tail distribution of precipitation poses a unique challenge for training diffusion models; to address this, we apply gamma correction during preprocessing. Additionally, to correct biases in the downscaled results, we employ a guided-sampling strategy to enhance bias correction. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed model achieves highly accurate results in an 8 times downscaling setting, outperforming previous deterministic methods. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/RoseLV/research_super-resolution
DC-Gaussian: Improving 3D Gaussian Splatting for Reflective Dash Cam Videos
May 29, 2024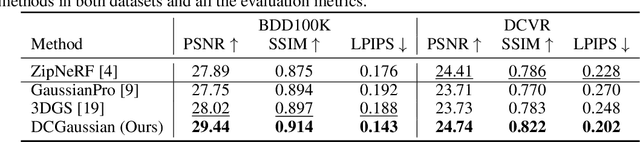

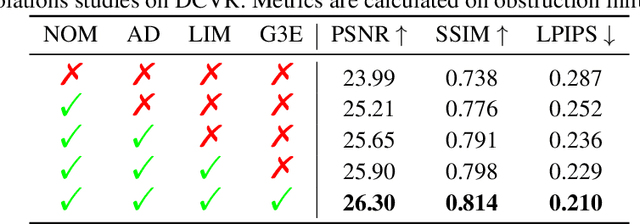
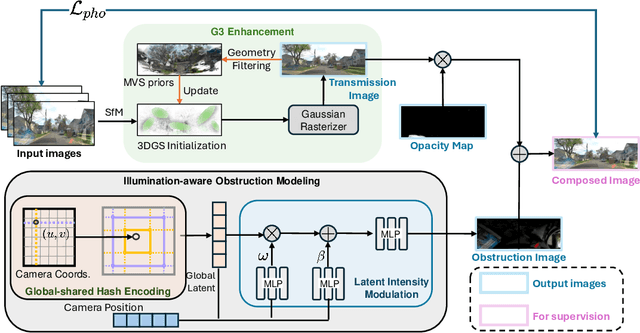
Abstract:We present DC-Gaussian, a new method for generating novel views from in-vehicle dash cam videos. While neural rendering techniques have made significant strides in driving scenarios, existing methods are primarily designed for videos collected by autonomous vehicles. However, these videos are limited in both quantity and diversity compared to dash cam videos, which are more widely used across various types of vehicles and capture a broader range of scenarios. Dash cam videos often suffer from severe obstructions such as reflections and occlusions on the windshields, which significantly impede the application of neural rendering techniques. To address this challenge, we develop DC-Gaussian based on the recent real-time neural rendering technique 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). Our approach includes an adaptive image decomposition module to model reflections and occlusions in a unified manner. Additionally, we introduce illumination-aware obstruction modeling to manage reflections and occlusions under varying lighting conditions. Lastly, we employ a geometry-guided Gaussian enhancement strategy to improve rendering details by incorporating additional geometry priors. Experiments on self-captured and public dash cam videos show that our method not only achieves state-of-the-art performance in novel view synthesis, but also accurately reconstructing captured scenes getting rid of obstructions.
Stock Movement and Volatility Prediction from Tweets, Macroeconomic Factors and Historical Prices
Dec 04, 2023



Abstract:Predicting stock market is vital for investors and policymakers, acting as a barometer of the economic health. We leverage social media data, a potent source of public sentiment, in tandem with macroeconomic indicators as government-compiled statistics, to refine stock market predictions. However, prior research using tweet data for stock market prediction faces three challenges. First, the quality of tweets varies widely. While many are filled with noise and irrelevant details, only a few genuinely mirror the actual market scenario. Second, solely focusing on the historical data of a particular stock without considering its sector can lead to oversight. Stocks within the same industry often exhibit correlated price behaviors. Lastly, simply forecasting the direction of price movement without assessing its magnitude is of limited value, as the extent of the rise or fall truly determines profitability. In this paper, diverging from the conventional methods, we pioneer an ECON. The framework has following advantages: First, ECON has an adept tweets filter that efficiently extracts and decodes the vast array of tweet data. Second, ECON discerns multi-level relationships among stocks, sectors, and macroeconomic factors through a self-aware mechanism in semantic space. Third, ECON offers enhanced accuracy in predicting substantial stock price fluctuations by capitalizing on stock price movement. We showcase the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed model using a dataset, specifically curated by us, for predicting stock market movements and volatility.
ALERTA-Net: A Temporal Distance-Aware Recurrent Networks for Stock Movement and Volatility Prediction
Oct 28, 2023Abstract:For both investors and policymakers, forecasting the stock market is essential as it serves as an indicator of economic well-being. To this end, we harness the power of social media data, a rich source of public sentiment, to enhance the accuracy of stock market predictions. Diverging from conventional methods, we pioneer an approach that integrates sentiment analysis, macroeconomic indicators, search engine data, and historical prices within a multi-attention deep learning model, masterfully decoding the complex patterns inherent in the data. We showcase the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed model using a dataset, specifically curated by us, for predicting stock market movements and volatility.
Self-Correlation and Cross-Correlation Learning for Few-Shot Remote Sensing Image Semantic Segmentation
Sep 15, 2023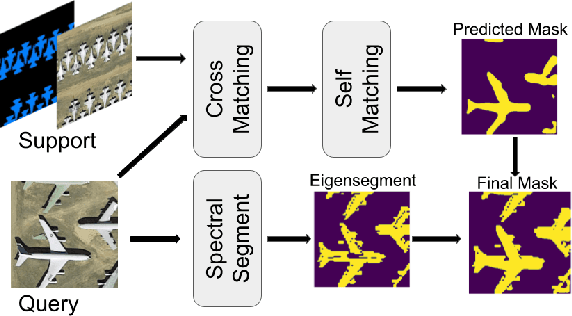

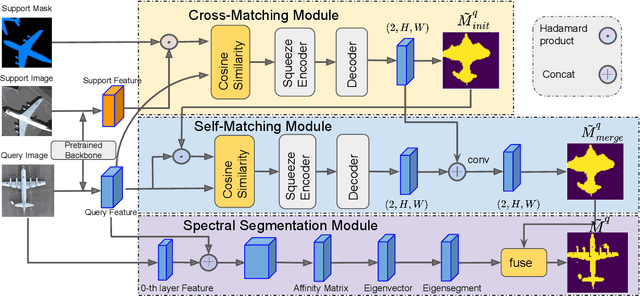

Abstract:Remote sensing image semantic segmentation is an important problem for remote sensing image interpretation. Although remarkable progress has been achieved, existing deep neural network methods suffer from the reliance on massive training data. Few-shot remote sensing semantic segmentation aims at learning to segment target objects from a query image using only a few annotated support images of the target class. Most existing few-shot learning methods stem primarily from their sole focus on extracting information from support images, thereby failing to effectively address the large variance in appearance and scales of geographic objects. To tackle these challenges, we propose a Self-Correlation and Cross-Correlation Learning Network for the few-shot remote sensing image semantic segmentation. Our model enhances the generalization by considering both self-correlation and cross-correlation between support and query images to make segmentation predictions. To further explore the self-correlation with the query image, we propose to adopt a classical spectral method to produce a class-agnostic segmentation mask based on the basic visual information of the image. Extensive experiments on two remote sensing image datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our model in few-shot remote sensing image semantic segmentation. Code and models will be accessed at https://github.com/linhanwang/SCCNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge