Jihwan Bang
Think Straight, Stop Smart: Structured Reasoning for Efficient Multi-Hop RAG
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Multi-hop retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a promising strategy for complex reasoning, yet existing iterative prompting approaches remain inefficient. They often regenerate predictable token sequences at every step and rely on stochastic stopping, leading to excessive token usage and unstable termination. We propose TSSS (Think Straight, Stop Smart), a structured multi-hop RAG framework designed for efficiency. TSSS introduces (i) a template-based reasoning that caches recurring prefixes and anchors sub-queries to the main question, reducing token generation cost while promoting stable reasoning, and (ii) a retriever-based terminator, which deterministically halts reasoning once additional sub-queries collapse into repetition. This separation of structured reasoning and termination control enables both faster inference and more reliable answers. On HotpotQA, 2WikiMultiHop, and MuSiQue, TSSS achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and competitive efficiency among RAG-CoT approaches, highlighting its effectiveness in efficiency-constrained scenarios such as on-device inference.
References Indeed Matter? Reference-Free Preference Optimization for Conversational Query Reformulation
May 10, 2025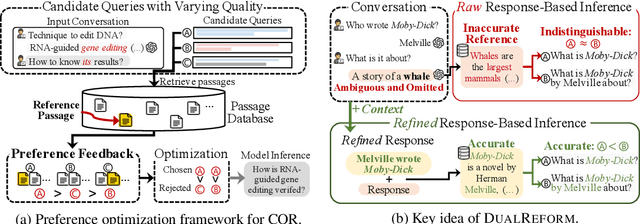
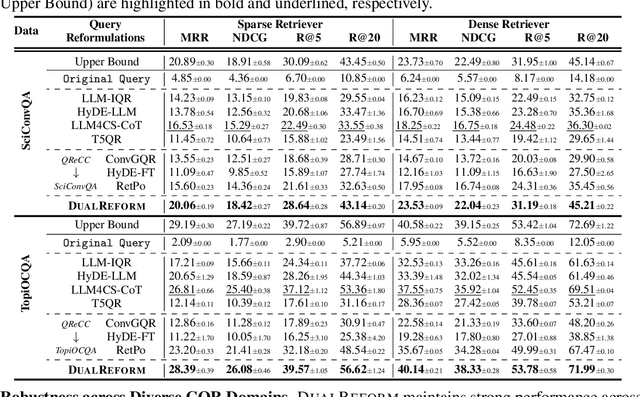
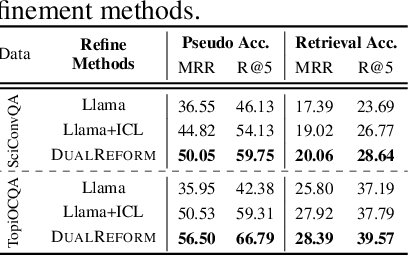
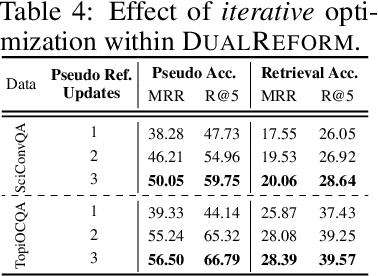
Abstract:Conversational query reformulation (CQR) has become indispensable for improving retrieval in dialogue-based applications. However, existing approaches typically rely on reference passages for optimization, which are impractical to acquire in real-world scenarios. To address this limitation, we introduce a novel reference-free preference optimization framework DualReform that generates pseudo reference passages from commonly-encountered conversational datasets containing only queries and responses. DualReform attains this goal through two key innovations: (1) response-based inference, where responses serve as proxies to infer pseudo reference passages, and (2) response refinement via the dual-role of CQR, where a CQR model refines responses based on the shared objectives between response refinement and CQR. Despite not relying on reference passages, DualReform achieves 96.9--99.1% of the retrieval accuracy attainable only with reference passages and surpasses the state-of-the-art method by up to 31.6%.
ReFeed: Multi-dimensional Summarization Refinement with Reflective Reasoning on Feedback
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Summarization refinement faces challenges when extending to multi-dimension. In this paper, we introduce ReFeed, a powerful summarization refinement pipeline that enhances multiple dimensions through reflective reasoning on feedback. To achieve this, we release SumFeed-CoT, a large-scale Long-CoT-based dataset optimized for training a lightweight model with reflective reasoning. Our experiments reveal how the number of dimensions, feedback exposure, and reasoning policy influence refinement performance, highlighting reflective reasoning and simultaneously addressing multiple feedback is crucial to mitigate trade-off between dimensions. Furthermore, ReFeed is robust to noisy feedback and feedback order. Lastly, our finding emphasizes that creating data with a proper goal and guideline constitutes a fundamental pillar of effective reasoning. The dataset and model will be released.
Chain-of-Rank: Enhancing Large Language Models for Domain-Specific RAG in Edge Device
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) with large language models (LLMs) is especially valuable in specialized domains, where precision is critical. To more specialize the LLMs into a target domain, domain-specific RAG has recently been developed by allowing the LLM to access the target domain early via finetuning. The domain-specific RAG makes more sense in resource-constrained environments like edge devices, as they should perform a specific task (e.g. personalization) reliably using only small-scale LLMs. While the domain-specific RAG is well-aligned with edge devices in this respect, it often relies on widely-used reasoning techniques like chain-of-thought (CoT). The reasoning step is useful to understand the given external knowledge, and yet it is computationally expensive and difficult for small-scale LLMs to learn it. Tackling this, we propose the Chain of Rank (CoR) which shifts the focus from intricate lengthy reasoning to simple ranking of the reliability of input external documents. Then, CoR reduces computational complexity while maintaining high accuracy, making it particularly suited for resource-constrained environments. We attain the state-of-the-art (SOTA) results in benchmarks, and analyze its efficacy.
Crayon: Customized On-Device LLM via Instant Adapter Blending and Edge-Server Hybrid Inference
Jun 11, 2024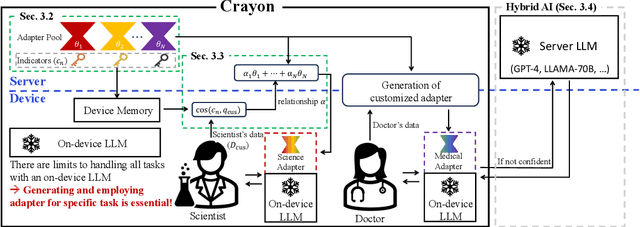
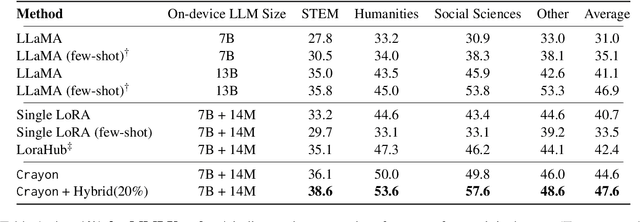
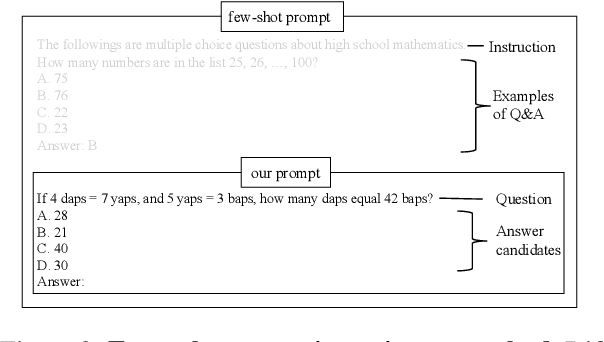
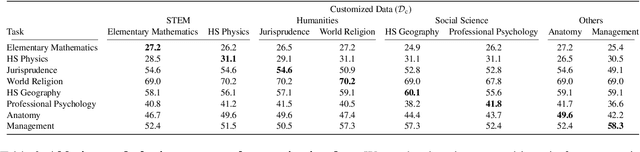
Abstract:The customization of large language models (LLMs) for user-specified tasks gets important. However, maintaining all the customized LLMs on cloud servers incurs substantial memory and computational overheads, and uploading user data can also lead to privacy concerns. On-device LLMs can offer a promising solution by mitigating these issues. Yet, the performance of on-device LLMs is inherently constrained by the limitations of small-scaled models. To overcome these restrictions, we first propose Crayon, a novel approach for on-device LLM customization. Crayon begins by constructing a pool of diverse base adapters, and then we instantly blend them into a customized adapter without extra training. In addition, we develop a device-server hybrid inference strategy, which deftly allocates more demanding queries or non-customized tasks to a larger, more capable LLM on a server. This ensures optimal performance without sacrificing the benefits of on-device customization. We carefully craft a novel benchmark from multiple question-answer datasets, and show the efficacy of our method in the LLM customization.
Adaptive Shortcut Debiasing for Online Continual Learning
Dec 14, 2023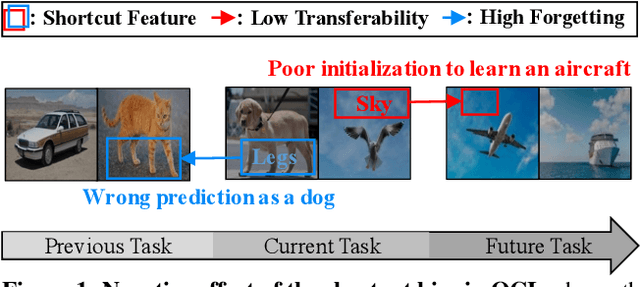
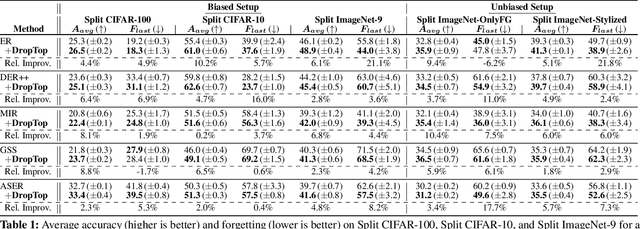
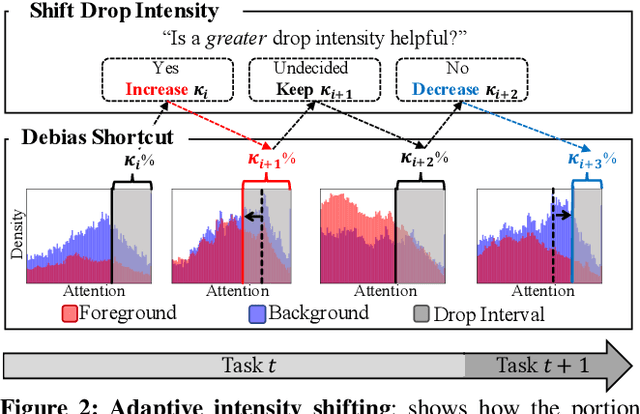
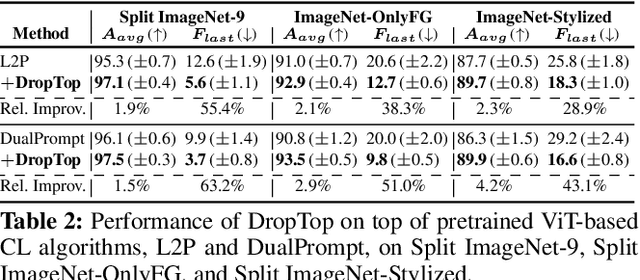
Abstract:We propose a novel framework DropTop that suppresses the shortcut bias in online continual learning (OCL) while being adaptive to the varying degree of the shortcut bias incurred by continuously changing environment. By the observed high-attention property of the shortcut bias, highly-activated features are considered candidates for debiasing. More importantly, resolving the limitation of the online environment where prior knowledge and auxiliary data are not ready, two novel techniques -- feature map fusion and adaptive intensity shifting -- enable us to automatically determine the appropriate level and proportion of the candidate shortcut features to be dropped. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets demonstrate that, when combined with various OCL algorithms, DropTop increases the average accuracy by up to 10.4% and decreases the forgetting by up to 63.2%.
Active Prompt Learning in Vision Language Models
Nov 27, 2023



Abstract:Pre-trained Vision Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated notable progress in various zero-shot tasks, such as classification and retrieval. Despite their performance, because improving performance on new tasks requires task-specific knowledge, their adaptation is essential. While labels are needed for the adaptation, acquiring them is typically expensive. To overcome this challenge, active learning, a method of achieving a high performance by obtaining labels for a small number of samples from experts, has been studied. Active learning primarily focuses on selecting unlabeled samples for labeling and leveraging them to train models. In this study, we pose the question, "how can the pre-trained VLMs be adapted under the active learning framework?" In response to this inquiry, we observe that (1) simply applying a conventional active learning framework to pre-trained VLMs even may degrade performance compared to random selection because of the class imbalance in labeling candidates, and (2) the knowledge of VLMs can provide hints for achieving the balance before labeling. Based on these observations, we devise a novel active learning framework for VLMs, denoted as PCB. To assess the effectiveness of our approach, we conduct experiments on seven different real-world datasets, and the results demonstrate that PCB surpasses conventional active learning and random sampling methods.
One Size Fits All for Semantic Shifts: Adaptive Prompt Tuning for Continual Learning
Nov 18, 2023



Abstract:In real-world continual learning scenarios, tasks often exhibit intricate and unpredictable semantic shifts, posing challenges for fixed prompt management strategies. We identify the inadequacy of universal and specific prompting in handling these dynamic shifts. Universal prompting is ineffective for tasks with abrupt semantic changes, while specific prompting struggles with overfitting under mild semantic shifts. To overcome these limitations, we propose an adaptive prompting approach that tailors minimal yet sufficient prompts based on the task semantics. Our methodology, SemPrompt, incorporates a two-level semantic grouping process: macroscopic semantic assignment and microscopic semantic refinement. This process ensures optimal prompt utilization for varying task semantics, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of learning in real-world CL settings. Our experimental results demonstrate that SemPrompt consistently outperforms existing methods in adapting to diverse semantic shifts in tasks.
Prompt-Guided Transformers for End-to-End Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Mar 25, 2023Abstract:Prompt-OVD is an efficient and effective framework for open-vocabulary object detection that utilizes class embeddings from CLIP as prompts, guiding the Transformer decoder to detect objects in both base and novel classes. Additionally, our novel RoI-based masked attention and RoI pruning techniques help leverage the zero-shot classification ability of the Vision Transformer-based CLIP, resulting in improved detection performance at minimal computational cost. Our experiments on the OV-COCO and OVLVIS datasets demonstrate that Prompt-OVD achieves an impressive 21.2 times faster inference speed than the first end-to-end open-vocabulary detection method (OV-DETR), while also achieving higher APs than four two-stage-based methods operating within similar inference time ranges. Code will be made available soon.
Meta-Query-Net: Resolving Purity-Informativeness Dilemma in Open-set Active Learning
Oct 13, 2022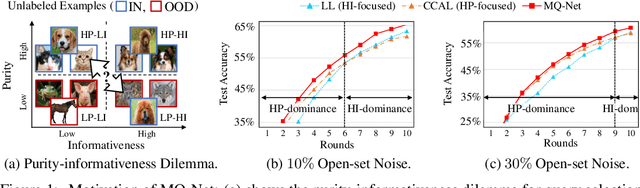
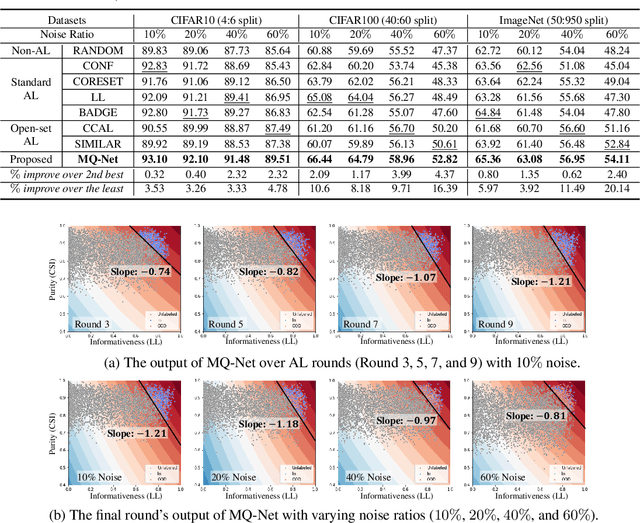
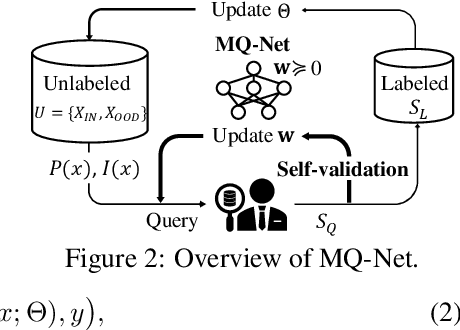
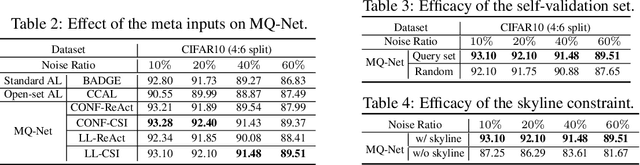
Abstract:Unlabeled data examples awaiting annotations contain open-set noise inevitably. A few active learning studies have attempted to deal with this open-set noise for sample selection by filtering out the noisy examples. However, because focusing on the purity of examples in a query set leads to overlooking the informativeness of the examples, the best balancing of purity and informativeness remains an important question. In this paper, to solve this purity-informativeness dilemma in open-set active learning, we propose a novel Meta-Query-Net,(MQ-Net) that adaptively finds the best balancing between the two factors. Specifically, by leveraging the multi-round property of active learning, we train MQ-Net using a query set without an additional validation set. Furthermore, a clear dominance relationship between unlabeled examples is effectively captured by MQ-Net through a novel skyline regularization. Extensive experiments on multiple open-set active learning scenarios demonstrate that the proposed MQ-Net achieves 20.14% improvement in terms of accuracy, compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge