Jieji Ren
ExoGS: A 4D Real-to-Sim-to-Real Framework for Scalable Manipulation Data Collection
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Real-to-Sim-to-Real technique is gaining increasing interest for robotic manipulation, as it can generate scalable data in simulation while having narrower sim-to-real gap. However, previous methods mainly focused on environment-level visual real-to-sim transfer, ignoring the transfer of interactions, which could be challenging and inefficient to obtain purely in simulation especially for contact-rich tasks. We propose ExoGS, a robot-free 4D Real-to-Sim-to-Real framework that captures both static environments and dynamic interactions in the real world and transfers them seamlessly to a simulated environment. It provides a new solution for scalable manipulation data collection and policy learning. ExoGS employs a self-designed robot-isomorphic passive exoskeleton AirExo-3 to capture kinematically consistent trajectories with millimeter-level accuracy and synchronized RGB observations during direct human demonstrations. The robot, objects, and environment are reconstructed as editable 3D Gaussian Splatting assets, enabling geometry-consistent replay and large-scale data augmentation. Additionally, a lightweight Mask Adapter injects instance-level semantics into the policy to enhance robustness under visual domain shifts. Real-world experiments demonstrate that ExoGS significantly improves data efficiency and policy generalization compared to teleoperation-based baselines. Code and hardware files have been released on https://github.com/zaixiabalala/ExoGS.
Near-Light Color Photometric Stereo for mono-Chromaticity non-lambertian surface
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Color photometric stereo enables single-shot surface reconstruction, extending conventional photometric stereo that requires multiple images of a static scene under varying illumination to dynamic scenarios. However, most existing approaches assume ideal distant lighting and Lambertian reflectance, leaving more practical near-light conditions and non-Lambertian surfaces underexplored. To overcome this limitation, we propose a framework that leverages neural implicit representations for depth and BRDF modeling under the assumption of mono-chromaticity (uniform chromaticity and homogeneous material), which alleviates the inherent ill-posedness of color photometric stereo and allows for detailed surface recovery from just one image. Furthermore, we design a compact optical tactile sensor to validate our approach. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our method achieves accurate and robust surface reconstruction.
Adaptive Attention Distillation for Robust Few-Shot Segmentation under Environmental Perturbations
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Few-shot segmentation (FSS) aims to rapidly learn novel class concepts from limited examples to segment specific targets in unseen images, and has been widely applied in areas such as medical diagnosis and industrial inspection. However, existing studies largely overlook the complex environmental factors encountered in real world scenarios-such as illumination, background, and camera viewpoint-which can substantially increase the difficulty of test images. As a result, models trained under laboratory conditions often fall short of practical deployment requirements. To bridge this gap, in this paper, an environment-robust FSS setting is introduced that explicitly incorporates challenging test cases arising from complex environments-such as motion blur, small objects, and camouflaged targets-to enhance model's robustness under realistic, dynamic conditions. An environment robust FSS benchmark (ER-FSS) is established, covering eight datasets across multiple real world scenarios. In addition, an Adaptive Attention Distillation (AAD) method is proposed, which repeatedly contrasts and distills key shared semantics between known (support) and unknown (query) images to derive class-specific attention for novel categories. This strengthens the model's ability to focus on the correct targets in complex environments, thereby improving environmental robustness. Comparative experiments show that AAD improves mIoU by 3.3% - 8.5% across all datasets and settings, demonstrating superior performance and strong generalization. The source code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/guoqianyu-alberta/Adaptive-Attention-Distillation-for-FSS.
ForceVLA: Enhancing VLA Models with a Force-aware MoE for Contact-rich Manipulation
May 28, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have advanced general-purpose robotic manipulation by leveraging pretrained visual and linguistic representations. However, they struggle with contact-rich tasks that require fine-grained control involving force, especially under visual occlusion or dynamic uncertainty. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{ForceVLA}, a novel end-to-end manipulation framework that treats external force sensing as a first-class modality within VLA systems. ForceVLA introduces \textbf{FVLMoE}, a force-aware Mixture-of-Experts fusion module that dynamically integrates pretrained visual-language embeddings with real-time 6-axis force feedback during action decoding. This enables context-aware routing across modality-specific experts, enhancing the robot's ability to adapt to subtle contact dynamics. We also introduce \textbf{ForceVLA-Data}, a new dataset comprising synchronized vision, proprioception, and force-torque signals across five contact-rich manipulation tasks. ForceVLA improves average task success by 23.2\% over strong $\pi_0$-based baselines, achieving up to 80\% success in tasks such as plug insertion. Our approach highlights the importance of multimodal integration for dexterous manipulation and sets a new benchmark for physically intelligent robotic control. Code and data will be released at https://sites.google.com/view/forcevla2025.
Look-to-Touch: A Vision-Enhanced Proximity and Tactile Sensor for Distance and Geometry Perception in Robotic Manipulation
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Camera-based tactile sensors provide robots with a high-performance tactile sensing approach for environment perception and dexterous manipulation. However, achieving comprehensive environmental perception still requires cooperation with additional sensors, which makes the system bulky and limits its adaptability to unstructured environments. In this work, we present a vision-enhanced camera-based dual-modality sensor, which realizes full-scale distance sensing from 50 cm to -3 mm while simultaneously keeping ultra-high-resolution texture sensing and reconstruction capabilities. Unlike conventional designs with fixed opaque gel layers, our sensor features a partially transparent sliding window, enabling mechanical switching between tactile and visual modes. For each sensing mode, a dynamic distance sensing model and a contact geometry reconstruction model are proposed. Through integration with soft robotic fingers, we systematically evaluate the performance of each mode, as well as in their synergistic operation. Experimental results show robust distance tracking across various speeds, nanometer-scale roughness detection, and sub-millimeter 3D texture reconstruction. The combination of both modalities improves the robot's efficiency in executing grasping tasks. Furthermore, the embedded mechanical transmission in the sensor allows for fine-grained intra-hand adjustments and precise manipulation, unlocking new capabilities for soft robotic hands.
Reactive Diffusion Policy: Slow-Fast Visual-Tactile Policy Learning for Contact-Rich Manipulation
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Humans can accomplish complex contact-rich tasks using vision and touch, with highly reactive capabilities such as quick adjustments to environmental changes and adaptive control of contact forces; however, this remains challenging for robots. Existing visual imitation learning (IL) approaches rely on action chunking to model complex behaviors, which lacks the ability to respond instantly to real-time tactile feedback during the chunk execution. Furthermore, most teleoperation systems struggle to provide fine-grained tactile / force feedback, which limits the range of tasks that can be performed. To address these challenges, we introduce TactAR, a low-cost teleoperation system that provides real-time tactile feedback through Augmented Reality (AR), along with Reactive Diffusion Policy (RDP), a novel slow-fast visual-tactile imitation learning algorithm for learning contact-rich manipulation skills. RDP employs a two-level hierarchy: (1) a slow latent diffusion policy for predicting high-level action chunks in latent space at low frequency, (2) a fast asymmetric tokenizer for closed-loop tactile feedback control at high frequency. This design enables both complex trajectory modeling and quick reactive behavior within a unified framework. Through extensive evaluation across three challenging contact-rich tasks, RDP significantly improves performance compared to state-of-the-art visual IL baselines through rapid response to tactile / force feedback. Furthermore, experiments show that RDP is applicable across different tactile / force sensors. Code and videos are available on https://reactive-diffusion-policy.github.io/.
SymmeTac: Symmetric Color LED Driven Efficient Photometric Stereo Reconstruction Methods for Camera-based Tactile Sensors
Nov 10, 2024Abstract:Camera-based tactile sensors can provide high-density surface geometry and force information for robots in the interaction process with the target. However, most existing methods cannot achieve accurate reconstruction with high efficiency, impeding the applications in robots. To address these problems, we propose an efficient two-shot photometric stereo method based on symmetric color LED distribution. Specifically, based on the sensing response curve of CMOS channels, we design orthogonal red and blue LEDs as illumination to acquire four observation maps using channel-splitting in a two-shot manner. Subsequently, we develop a two-shot photometric stereo theory, which can estimate accurate surface normal and greatly reduce the computing overhead in magnitude. Finally, leveraging the characteristics of the camera-based tactile sensor, we optimize the algorithm to be a highly efficient, pure addition operation. Simulation and real-world experiments demonstrate the advantages of our approach. Further details are available on: https://github.com/Tacxels/SymmeTac.
TacIPC: Intersection- and Inversion-free FEM-based Elastomer Simulation For Optical Tactile Sensors
Nov 10, 2023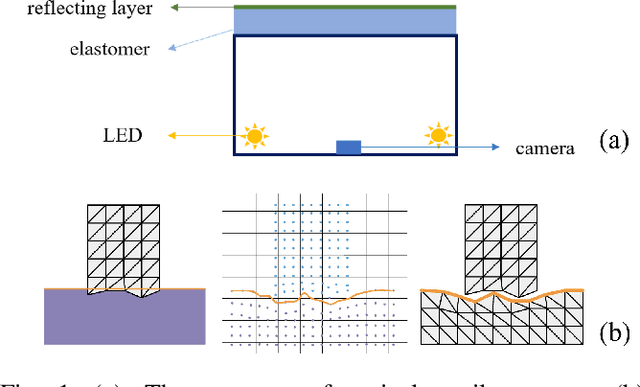
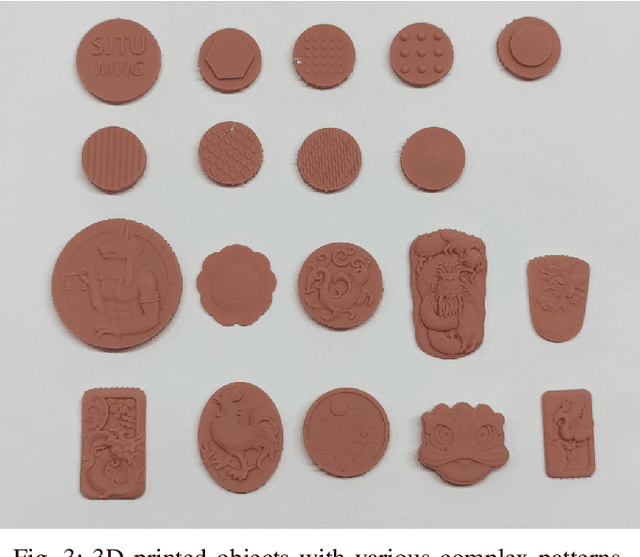
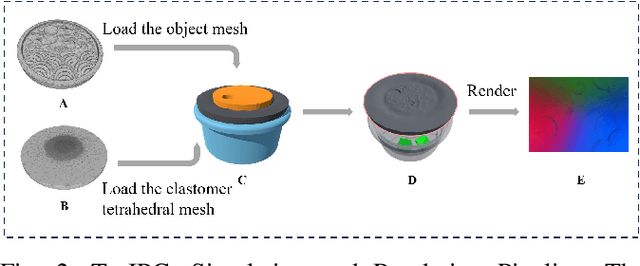

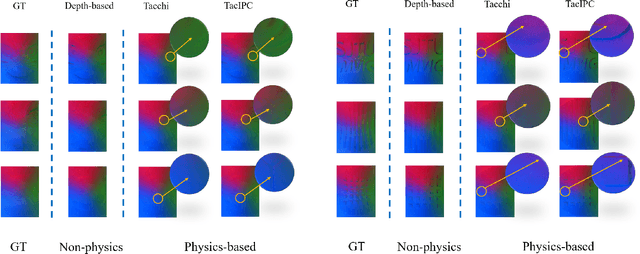
Abstract:Tactile perception stands as a critical sensory modality for human interaction with the environment. Among various tactile sensor techniques, optical sensor-based approaches have gained traction, notably for producing high-resolution tactile images. This work explores gel elastomer deformation simulation through a physics-based approach. While previous works in this direction usually adopt the explicit material point method (MPM), which has certain limitations in force simulation and rendering, we adopt the finite element method (FEM) and address the challenges in penetration and mesh distortion with incremental potential contact (IPC) method. As a result, we present a simulator named TacIPC, which can ensure numerically stable simulations while accommodating direct rendering and friction modeling. To evaluate TacIPC, we conduct three tasks: pseudo-image quality assessment, deformed geometry estimation, and marker displacement prediction. These tasks show its superior efficacy in reducing the sim-to-real gap. Our method can also seamlessly integrate with existing simulators. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/tac-ipc.
Differentiable Fluid Physics Parameter Identification Via Stirring
Nov 09, 2023
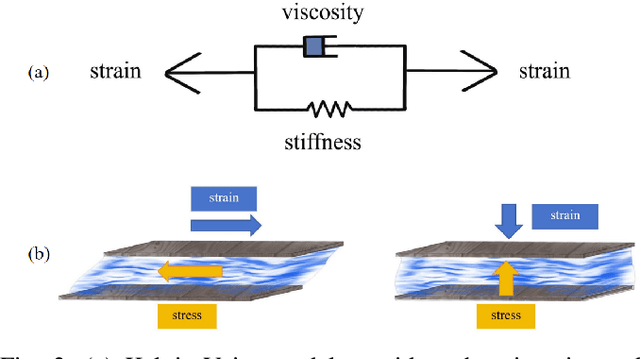


Abstract:Fluid interactions permeate daily human activities, with properties like density and viscosity playing pivotal roles in household tasks. While density estimation is straightforward through Archimedes' principle, viscosity poses a more intricate challenge, especially given the varied behaviors of Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. These fluids, which differ in their stress-strain relationships, are delineated by specific constitutive models such as the Carreau, Cross, and Herschel-Bulkley models, each possessing unique viscosity parameters. This study introduces a novel differentiable fitting framework, DiffStir, tailored to identify key physics parameters via the common daily operation of stirring. By employing a robotic arm for stirring and harnessing a differentiable Material Point Method (diffMPM)-based simulator, the framework can determine fluid parameters by matching observations from both the simulator and the real world. Recognizing the distinct preferences of the aforementioned constitutive models for specific fluids, an online strategy was adopted to adaptively select the most fitting model based on real-world data. Additionally, we propose a refining neural network to bridge the sim-to-real gap and mitigate sensor noise-induced inaccuracies. Comprehensive experiments were conducted to validate the efficacy of DiffStir, showcasing its precision in parameter estimation when benchmarked against reported literature values. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/diffstir.
Precise Robotic Needle-Threading with Tactile Perception and Reinforcement Learning
Nov 04, 2023Abstract:This work presents a novel tactile perception-based method, named T-NT, for performing the needle-threading task, an application of deformable linear object (DLO) manipulation. This task is divided into two main stages: Tail-end Finding and Tail-end Insertion. In the first stage, the agent traces the contour of the thread twice using vision-based tactile sensors mounted on the gripper fingers. The two-run tracing is to locate the tail-end of the thread. In the second stage, it employs a tactile-guided reinforcement learning (RL) model to drive the robot to insert the thread into the target needle eyelet. The RL model is trained in a Unity-based simulated environment. The simulation environment supports tactile rendering which can produce realistic tactile images and thread modeling. During insertion, the position of the poke point and the center of the eyelet are obtained through a pre-trained segmentation model, Grounded-SAM, which predicts the masks for both the needle eye and thread imprints. These positions are then fed into the reinforcement learning model, aiding in a smoother transition to real-world applications. Extensive experiments on real robots are conducted to demonstrate the efficacy of our method. More experiments and videos can be found in the supplementary materials and on the website: https://sites.google.com/view/tac-needlethreading.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge