Jianlin Liu
Toward Multi-class Anomaly Detection: Exploring Class-aware Unified Model against Inter-class Interference
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:In the context of high usability in single-class anomaly detection models, recent academic research has become concerned about the more complex multi-class anomaly detection. Although several papers have designed unified models for this task, they often overlook the utility of class labels, a potent tool for mitigating inter-class interference. To address this issue, we introduce a Multi-class Implicit Neural representation Transformer for unified Anomaly Detection (MINT-AD), which leverages the fine-grained category information in the training stage. By learning the multi-class distributions, the model generates class-aware query embeddings for the transformer decoder, mitigating inter-class interference within the reconstruction model. Utilizing such an implicit neural representation network, MINT-AD can project category and position information into a feature embedding space, further supervised by classification and prior probability loss functions. Experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that MINT-AD outperforms existing unified training models.
SoftPatch: Unsupervised Anomaly Detection with Noisy Data
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:Although mainstream unsupervised anomaly detection (AD) algorithms perform well in academic datasets, their performance is limited in practical application due to the ideal experimental setting of clean training data. Training with noisy data is an inevitable problem in real-world anomaly detection but is seldom discussed. This paper considers label-level noise in image sensory anomaly detection for the first time. To solve this problem, we proposed a memory-based unsupervised AD method, SoftPatch, which efficiently denoises the data at the patch level. Noise discriminators are utilized to generate outlier scores for patch-level noise elimination before coreset construction. The scores are then stored in the memory bank to soften the anomaly detection boundary. Compared with existing methods, SoftPatch maintains a strong modeling ability of normal data and alleviates the overconfidence problem in coreset. Comprehensive experiments in various noise scenes demonstrate that SoftPatch outperforms the state-of-the-art AD methods on the MVTecAD and BTAD benchmarks and is comparable to those methods under the setting without noise.
* 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems
FusionDepth: Complement Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation with Cost Volume
May 10, 2023Abstract:Multi-view stereo depth estimation based on cost volume usually works better than self-supervised monocular depth estimation except for moving objects and low-textured surfaces. So in this paper, we propose a multi-frame depth estimation framework which monocular depth can be refined continuously by multi-frame sequential constraints, leveraging a Bayesian fusion layer within several iterations. Both monocular and multi-view networks can be trained with no depth supervision. Our method also enhances the interpretability when combining monocular estimation with multi-view cost volume. Detailed experiments show that our method surpasses state-of-the-art unsupervised methods utilizing single or multiple frames at test time on KITTI benchmark.
NeRF-Loc: Visual Localization with Conditional Neural Radiance Field
Apr 17, 2023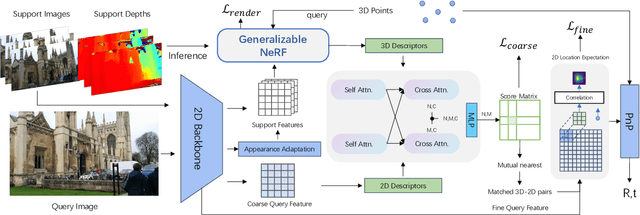
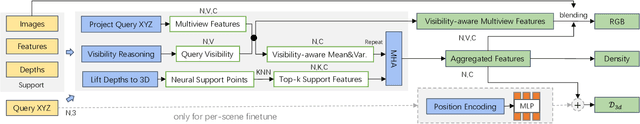
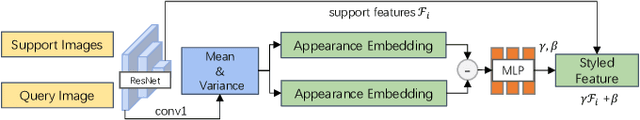
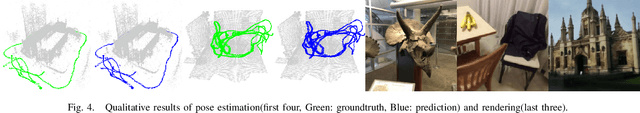
Abstract:We propose a novel visual re-localization method based on direct matching between the implicit 3D descriptors and the 2D image with transformer. A conditional neural radiance field(NeRF) is chosen as the 3D scene representation in our pipeline, which supports continuous 3D descriptors generation and neural rendering. By unifying the feature matching and the scene coordinate regression to the same framework, our model learns both generalizable knowledge and scene prior respectively during two training stages. Furthermore, to improve the localization robustness when domain gap exists between training and testing phases, we propose an appearance adaptation layer to explicitly align styles between the 3D model and the query image. Experiments show that our method achieves higher localization accuracy than other learning-based approaches on multiple benchmarks. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/JenningsL/nerf-loc}.
G2PTL: A Pre-trained Model for Delivery Address and its Applications in Logistics System
Apr 04, 2023



Abstract:Text-based delivery addresses, as the data foundation for logistics systems, contain abundant and crucial location information. How to effectively encode the delivery address is a core task to boost the performance of downstream tasks in the logistics system. Pre-trained Models (PTMs) designed for Natural Language Process (NLP) have emerged as the dominant tools for encoding semantic information in text. Though promising, those NLP-based PTMs fall short of encoding geographic knowledge in the delivery address, which considerably trims down the performance of delivery-related tasks in logistic systems such as Cainiao. To tackle the above problem, we propose a domain-specific pre-trained model, named G2PTL, a Geography-Graph Pre-trained model for delivery address in Logistics field. G2PTL combines the semantic learning capabilities of text pre-training with the geographical-relationship encoding abilities of graph modeling. Specifically, we first utilize real-world logistics delivery data to construct a large-scale heterogeneous graph of delivery addresses, which contains abundant geographic knowledge and delivery information. Then, G2PTL is pre-trained with subgraphs sampled from the heterogeneous graph. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of G2PTL through four downstream tasks in logistics systems on real-world datasets. G2PTL has been deployed in production in Cainiao's logistics system, which significantly improves the performance of delivery-related tasks.
Rethinking Dimensionality Reduction in Grid-based 3D Object Detection
Sep 24, 2022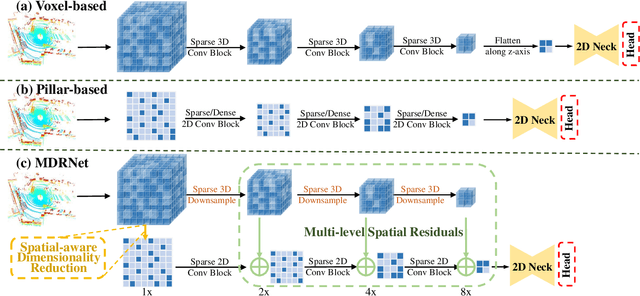
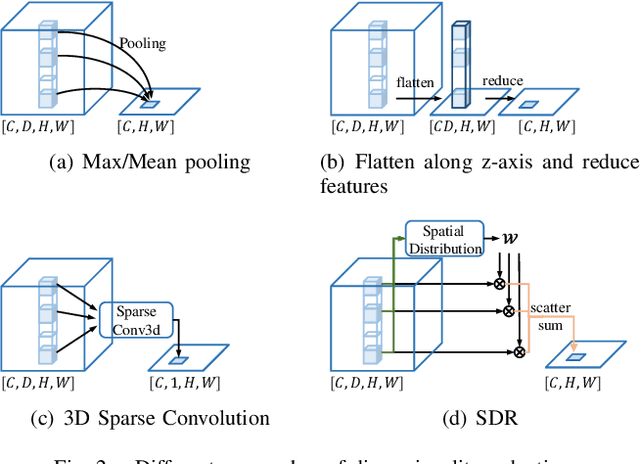
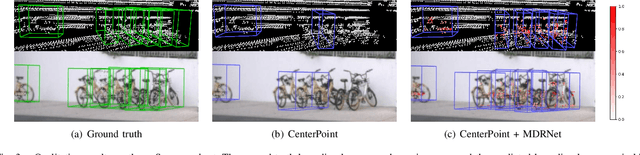
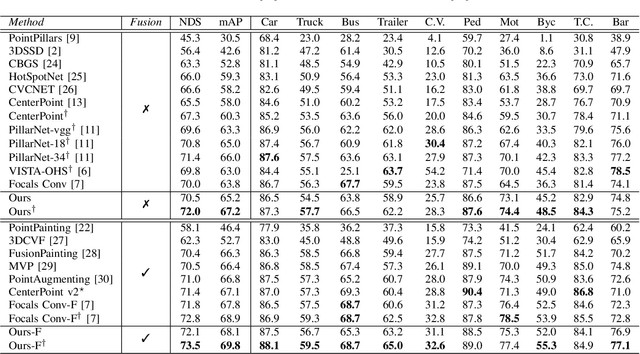
Abstract:Bird's eye view (BEV) is widely adopted by most of the current point cloud detectors due to the applicability of well-explored 2D detection techniques. However, existing methods obtain BEV features by simply collapsing voxel or point features along the height dimension, which causes the heavy loss of 3D spatial information. To alleviate the information loss, we propose a novel point cloud detection network based on a Multi-level feature dimensionality reduction strategy, called MDRNet. In MDRNet, the Spatial-aware Dimensionality Reduction (SDR) is designed to dynamically focus on the valuable parts of the object during voxel-to-BEV feature transformation. Furthermore, the Multi-level Spatial Residuals (MSR) is proposed to fuse the multi-level spatial information in the BEV feature maps. Extensive experiments on nuScenes show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. The code will be available upon publication.
Scatter Points in Space: 3D Detection from Multi-view Monocular Images
Aug 31, 2022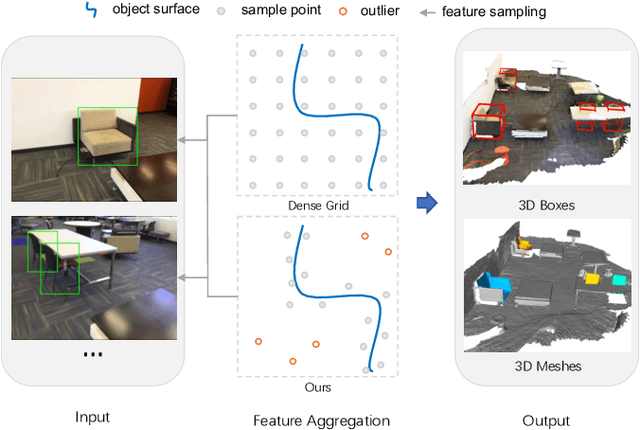
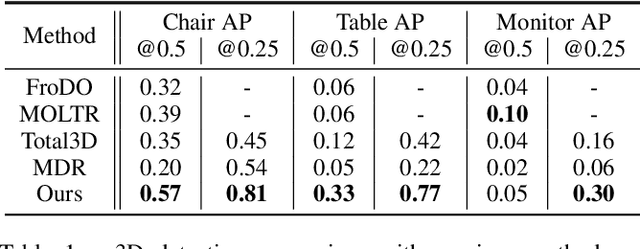
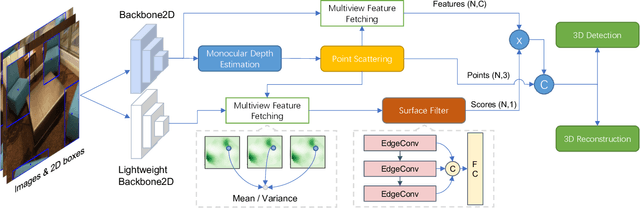
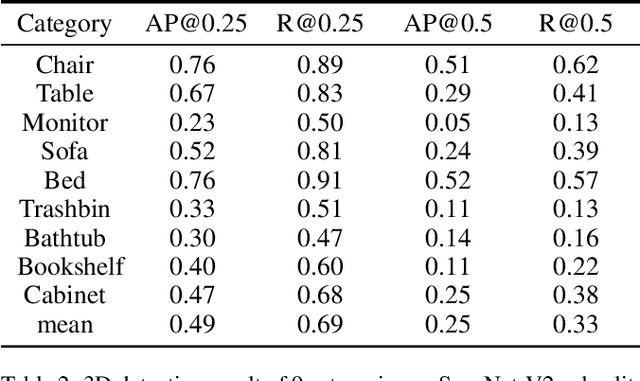
Abstract:3D object detection from monocular image(s) is a challenging and long-standing problem of computer vision. To combine information from different perspectives without troublesome 2D instance tracking, recent methods tend to aggregate multiview feature by sampling regular 3D grid densely in space, which is inefficient. In this paper, we attempt to improve multi-view feature aggregation by proposing a learnable keypoints sampling method, which scatters pseudo surface points in 3D space, in order to keep data sparsity. The scattered points augmented by multi-view geometric constraints and visual features are then employed to infer objects location and shape in the scene. To make up the limitations of single frame and model multi-view geometry explicitly, we further propose a surface filter module for noise suppression. Experimental results show that our method achieves significantly better performance than previous works in terms of 3D detection (more than 0.1 AP improvement on some categories of ScanNet). The code will be publicly available.
Guide Local Feature Matching by Overlap Estimation
Feb 23, 2022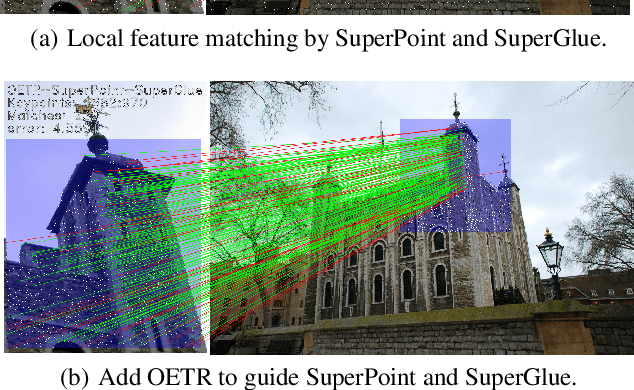
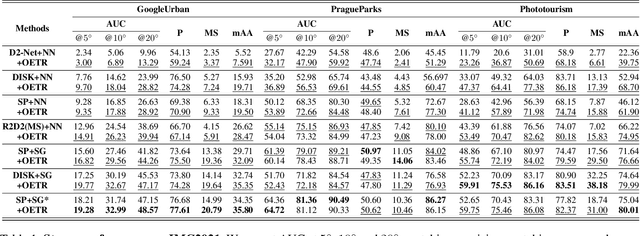
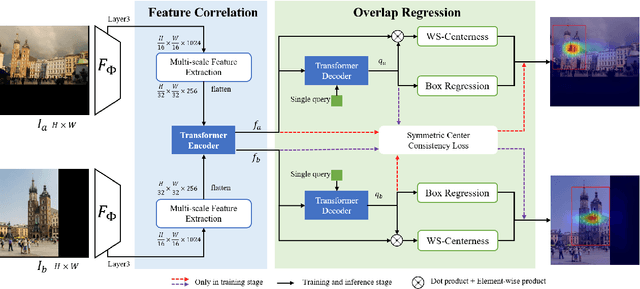
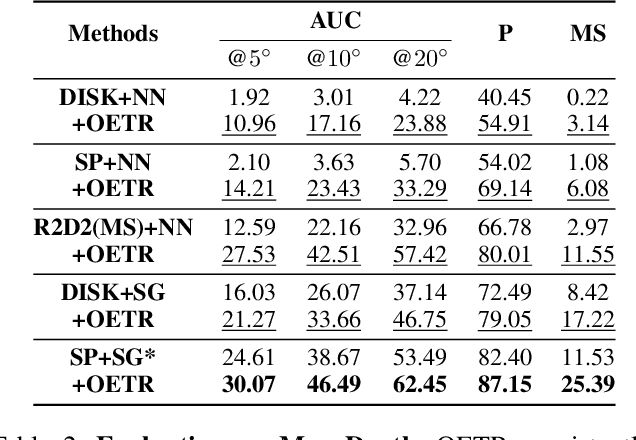
Abstract:Local image feature matching under large appearance, viewpoint, and distance changes is challenging yet important. Conventional methods detect and match tentative local features across the whole images, with heuristic consistency checks to guarantee reliable matches. In this paper, we introduce a novel Overlap Estimation method conditioned on image pairs with TRansformer, named OETR, to constrain local feature matching in the commonly visible region. OETR performs overlap estimation in a two-step process of feature correlation and then overlap regression. As a preprocessing module, OETR can be plugged into any existing local feature detection and matching pipeline, to mitigate potential view angle or scale variance. Intensive experiments show that OETR can boost state-of-the-art local feature matching performance substantially, especially for image pairs with small shared regions. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/AbyssGaze/OETR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge