Jianliang Gao
GraphPAS: Parallel Architecture Search for Graph Neural Networks
Dec 07, 2021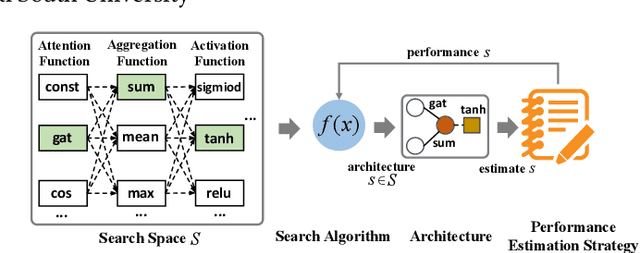
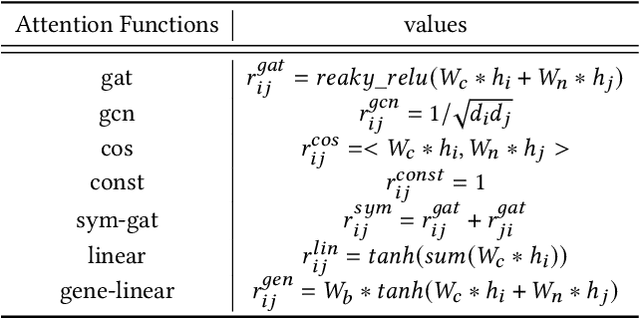
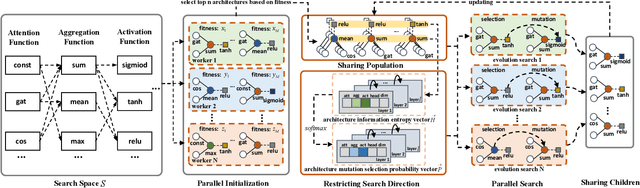
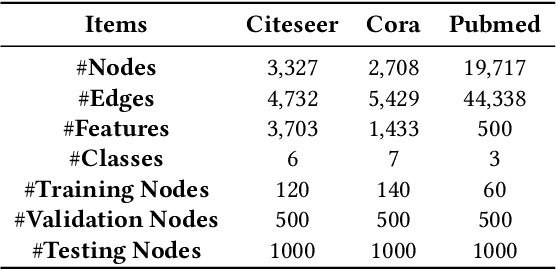
Abstract:Graph neural architecture search has received a lot of attention as Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) has been successfully applied on the non-Euclidean data recently. However, exploring all possible GNNs architectures in the huge search space is too time-consuming or impossible for big graph data. In this paper, we propose a parallel graph architecture search (GraphPAS) framework for graph neural networks. In GraphPAS, we explore the search space in parallel by designing a sharing-based evolution learning, which can improve the search efficiency without losing the accuracy. Additionally, architecture information entropy is adopted dynamically for mutation selection probability, which can reduce space exploration. The experimental result shows that GraphPAS outperforms state-of-art models with efficiency and accuracy simultaneously.
Cyclic Label Propagation for Graph Semi-supervised Learning
Nov 24, 2020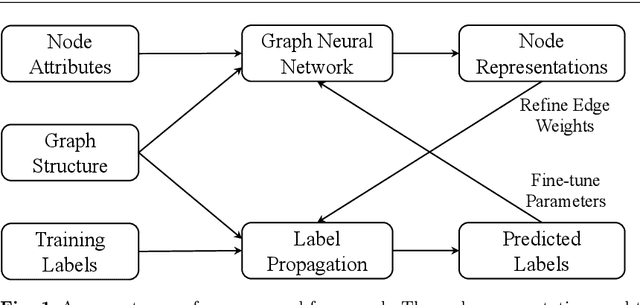
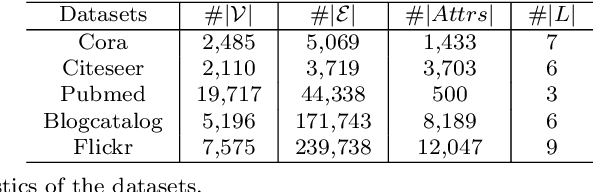
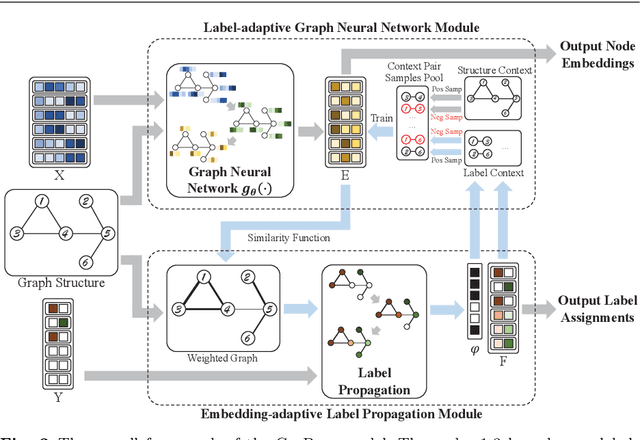
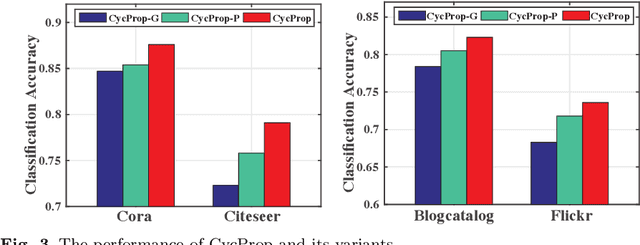
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) have emerged as effective approaches for graph analysis, especially in the scenario of semi-supervised learning. Despite its success, GNN often suffers from over-smoothing and over-fitting problems, which affects its performance on node classification tasks. We analyze that an alternative method, the label propagation algorithm (LPA), avoids the aforementioned problems thus it is a promising choice for graph semi-supervised learning. Nevertheless, the intrinsic limitations of LPA on feature exploitation and relation modeling make propagating labels become less effective. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel framework for graph semi-supervised learning termed as Cyclic Label Propagation (CycProp for abbreviation), which integrates GNNs into the process of label propagation in a cyclic and mutually reinforcing manner to exploit the advantages of both GNNs and LPA. In particular, our proposed CycProp updates the node embeddings learned by GNN module with the augmented information by label propagation, while fine-tunes the weighted graph of label propagation with the help of node embedding in turn. After the model converges, reliably predicted labels and informative node embeddings are obtained with the LPA and GNN modules respectively. Extensive experiments on various real-world datasets are conducted, and the experimental results empirically demonstrate that the proposed CycProp model can achieve relatively significant gains over the state-of-the-art methods.
Distant Supervision for E-commerce Query Segmentation via Attention Network
Nov 09, 2020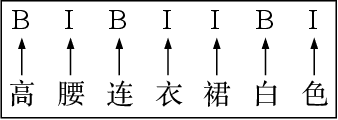
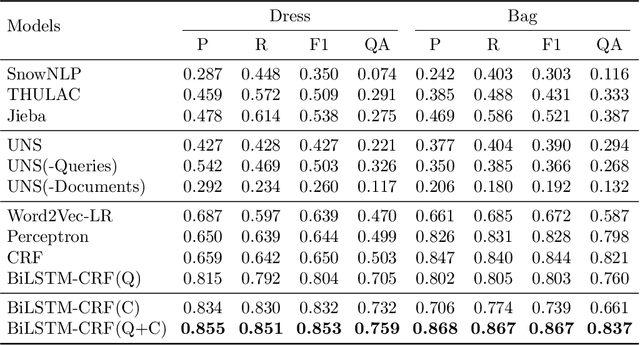
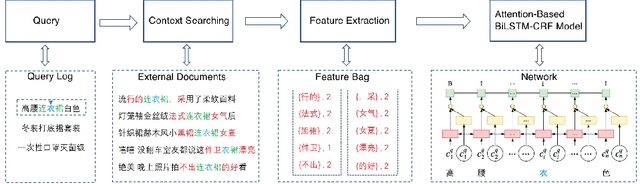
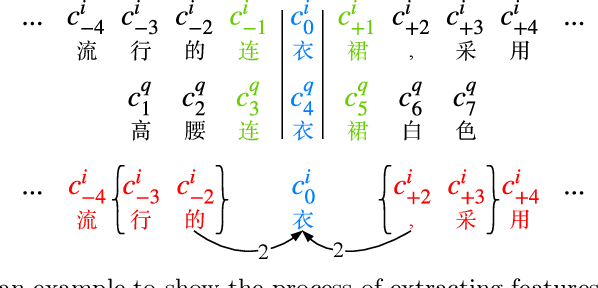
Abstract:The booming online e-commerce platforms demand highly accurate approaches to segment queries that carry the product requirements of consumers. Recent works have shown that the supervised methods, especially those based on deep learning, are attractive for achieving better performance on the problem of query segmentation. However, the lack of labeled data is still a big challenge for training a deep segmentation network, and the problem of Out-of-Vocabulary (OOV) also adversely impacts the performance of query segmentation. Different from query segmentation task in an open domain, e-commerce scenario can provide external documents that are closely related to these queries. Thus, to deal with the two challenges, we employ the idea of distant supervision and design a novel method to find contexts in external documents and extract features from these contexts. In this work, we propose a BiLSTM-CRF based model with an attention module to encode external features, such that external contexts information, which can be utilized naturally and effectively to help query segmentation. Experiments on two datasets show the effectiveness of our approach compared with several kinds of baselines.
Method and Dataset Entity Mining in Scientific Literature: A CNN + Bi-LSTM Model with Self-attention
Oct 26, 2020



Abstract:Literature analysis facilitates researchers to acquire a good understanding of the development of science and technology. The traditional literature analysis focuses largely on the literature metadata such as topics, authors, abstracts, keywords, references, etc., and little attention was paid to the main content of papers. In many scientific domains such as science, computing, engineering, etc., the methods and datasets involved in the scientific papers published in those domains carry important information and are quite useful for domain analysis as well as algorithm and dataset recommendation. In this paper, we propose a novel entity recognition model, called MDER, which is able to effectively extract the method and dataset entities from the main textual content of scientific papers. The model utilizes rule embedding and adopts a parallel structure of CNN and Bi-LSTM with the self-attention mechanism. We evaluate the proposed model on datasets which are constructed from the published papers of four research areas in computer science, i.e., NLP, CV, Data Mining and AI. The experimental results demonstrate that our model performs well in all the four areas and it features a good learning capacity for cross-area learning and recognition. We also conduct experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of different building modules within our model which indicate that the importance of different building modules in collectively contributing to the good entity recognition performance as a whole. The data augmentation experiments on our model demonstrated that data augmentation positively contributes to model training, making our model much more robust in dealing with the scenarios where only small number of training samples are available. We finally apply our model on PAKDD papers published from 2009-2019 to mine insightful results from scientific papers published in a longer time span.
Fast Botnet Detection From Streaming Logs Using Online Lanczos Method
Dec 19, 2018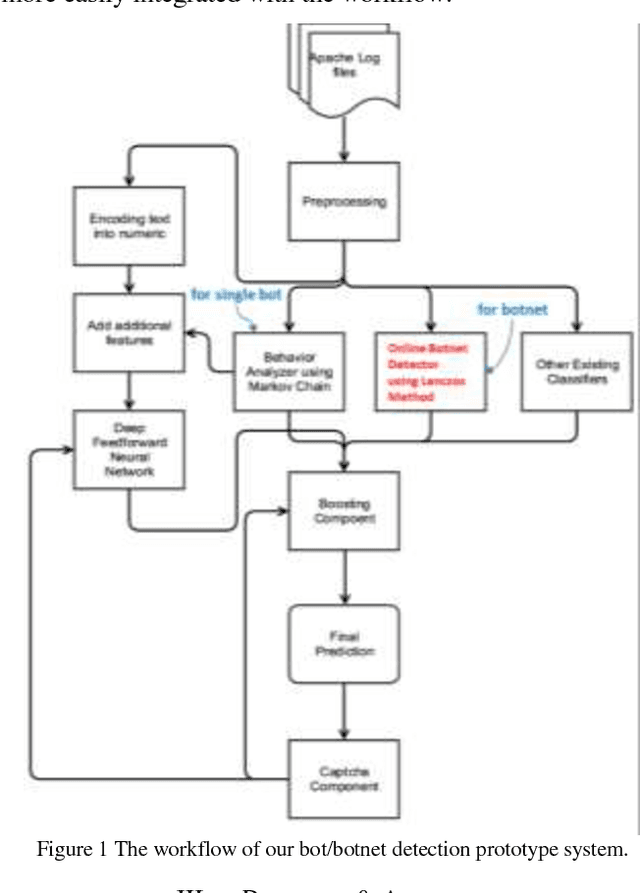
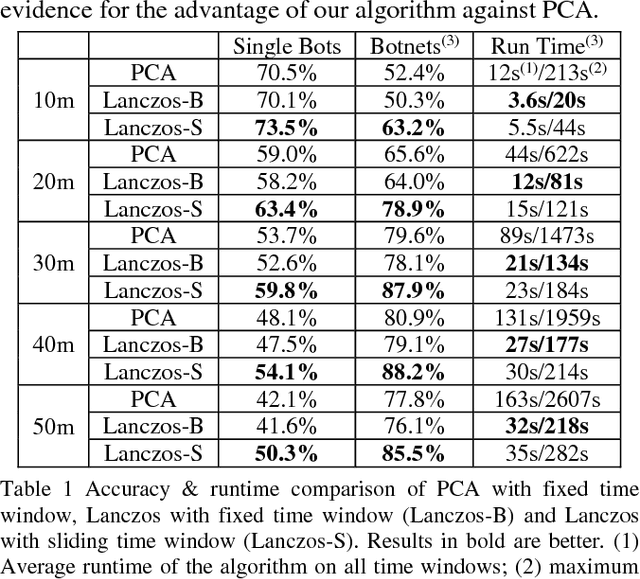
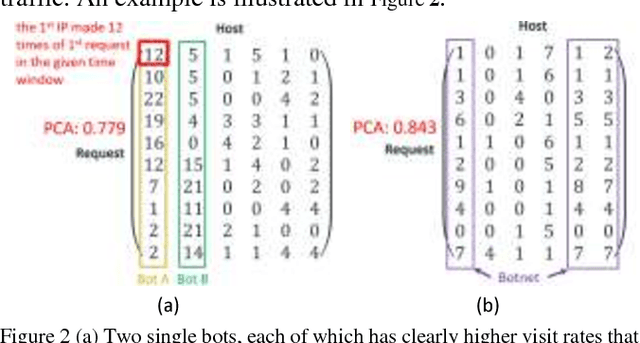
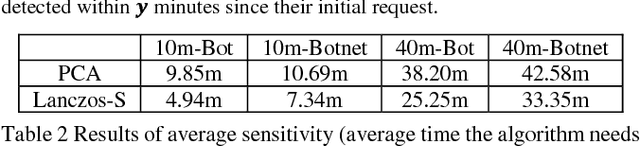
Abstract:Botnet, a group of coordinated bots, is becoming the main platform of malicious Internet activities like DDOS, click fraud, web scraping, spam/rumor distribution, etc. This paper focuses on design and experiment of a new approach for botnet detection from streaming web server logs, motivated by its wide applicability, real-time protection capability, ease of use and better security of sensitive data. Our algorithm is inspired by a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to capture correlation in data, and we are first to recognize and adapt Lanczos method to improve the time complexity of PCA-based botnet detection from cubic to sub-cubic, which enables us to more accurately and sensitively detect botnets with sliding time windows rather than fixed time windows. We contribute a generalized online correlation matrix update formula, and a new termination condition for Lanczos iteration for our purpose based on error bound and non-decreasing eigenvalues of symmetric matrices. On our dataset of an ecommerce website logs, experiments show the time cost of Lanczos method with different time windows are consistently only 20% to 25% of PCA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge