Jianhao Yan
BAPO: Boundary-Aware Policy Optimization for Reliable Agentic Search
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:RL-based agentic search enables LLMs to solve complex questions via dynamic planning and external search. While this approach significantly enhances accuracy with agent policies optimized via large-scale reinforcement learning, we identify a critical gap in reliability: these agents fail to recognize their reasoning boundaries and rarely admit ``I DON'T KNOW'' (IDK) even when evidence is insufficient or reasoning reaches its limit. The lack of reliability often leads to plausible but unreliable answers, introducing significant risks in many real-world scenarios. To this end, we propose Boundary-Aware Policy Optimization (BAPO), a novel RL framework designed to cultivate reliable boundary awareness without compromising accuracy. BAPO introduces two key components: (i) a group-based boundary-aware reward that encourages an IDK response only when the reasoning reaches its limit, and (ii) an adaptive reward modulator that strategically suspends this reward during early exploration, preventing the model from exploiting IDK as a shortcut. Extensive experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that BAPO substantially enhances the overall reliability of agentic search.
Learning to Reason under Off-Policy Guidance
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large reasoning models (LRMs) demonstrate that sophisticated behaviors such as multi-step reasoning and self-reflection can emerge via reinforcement learning (RL) with simple rule-based rewards. However, existing zero-RL approaches are inherently ``on-policy'', limiting learning to a model's own outputs and failing to acquire reasoning abilities beyond its initial capabilities. We introduce LUFFY (Learning to reason Under oFF-policY guidance), a framework that augments zero-RL with off-policy reasoning traces. LUFFY dynamically balances imitation and exploration by combining off-policy demonstrations with on-policy rollouts during training. Notably, we propose policy shaping via regularized importance sampling to avoid superficial and rigid imitation during mixed-policy training. Remarkably, LUFFY achieves an over +7.0 average gain across six math benchmarks and an advantage of over +6.2 points in out-of-distribution tasks. It also substantially surpasses imitation-based supervised fine-tuning (SFT), particularly in generalization. Analysis shows LUFFY not only imitates effectively but also explores beyond demonstrations, offering a scalable path to train generalizable reasoning models with off-policy guidance.
A Survey of Efficient Reasoning for Large Reasoning Models: Language, Multimodality, and Beyond
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Recent Large Reasoning Models (LRMs), such as DeepSeek-R1 and OpenAI o1, have demonstrated strong performance gains by scaling up the length of Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning during inference. However, a growing concern lies in their tendency to produce excessively long reasoning traces, which are often filled with redundant content (e.g., repeated definitions), over-analysis of simple problems, and superficial exploration of multiple reasoning paths for harder tasks. This inefficiency introduces significant challenges for training, inference, and real-world deployment (e.g., in agent-based systems), where token economy is critical. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive overview of recent efforts aimed at improving reasoning efficiency in LRMs, with a particular focus on the unique challenges that arise in this new paradigm. We identify common patterns of inefficiency, examine methods proposed across the LRM lifecycle, i.e., from pretraining to inference, and discuss promising future directions for research. To support ongoing development, we also maintain a real-time GitHub repository tracking recent progress in the field. We hope this survey serves as a foundation for further exploration and inspires innovation in this rapidly evolving area.
RefuteBench 2.0 -- Agentic Benchmark for Dynamic Evaluation of LLM Responses to Refutation Instruction
Feb 25, 2025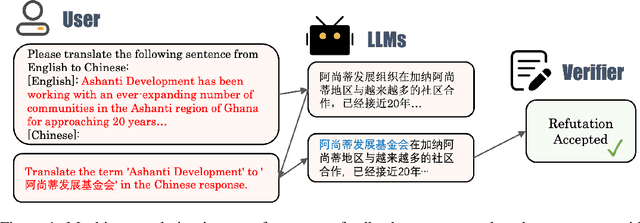
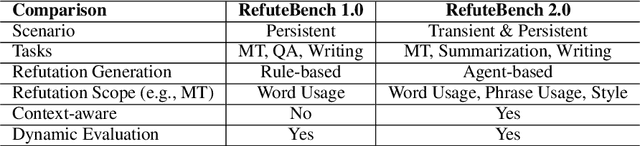
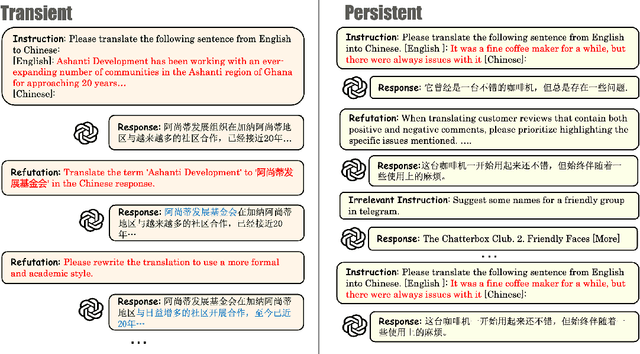
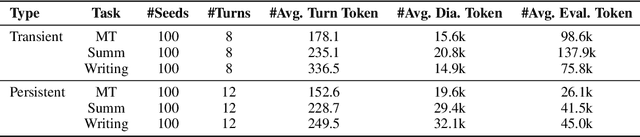
Abstract:In the multi-turn interaction schema, large language models (LLMs) can leverage user feedback to enhance the quality and relevance of their responses. However, evaluating an LLM's ability to incorporate user refutation feedback is crucial yet challenging. In this study, we introduce RefuteBench 2.0, which significantly extends the original RefuteBench by incorporating LLM agents as refuters and evaluators, which allows for flexible and comprehensive assessment. We design both transient and persistent refutation instructions with different validity periods. Meta-evaluation shows that the LLM-based refuter could generate more human-like refutations and the evaluators could assign scores with high correlation with humans. Experimental results of various LLMs show that current models could effectively satisfy the refutation but fail to memorize the refutation information. Interestingly, we also observe that the performance of the initial task decreases as the refutations increase. Analysis of the attention scores further shows a potential weakness of current LLMs: they struggle to retain and correctly use previous information during long context dialogues. https://github.com/ElliottYan/RefuteBench-2.0
Unveiling Attractor Cycles in Large Language Models: A Dynamical Systems View of Successive Paraphrasing
Feb 21, 2025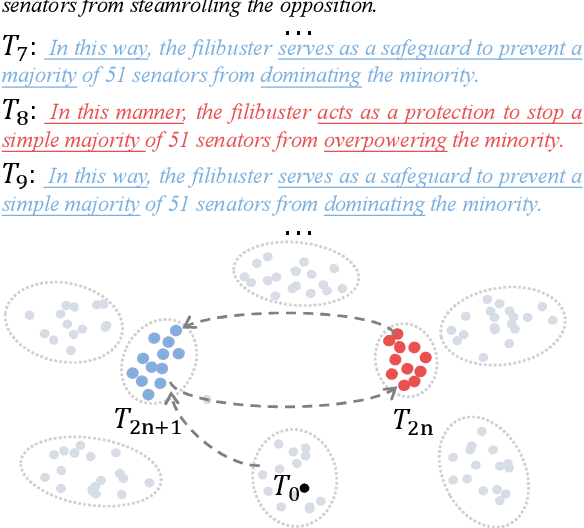
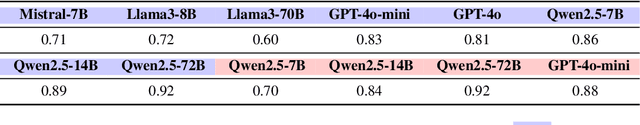
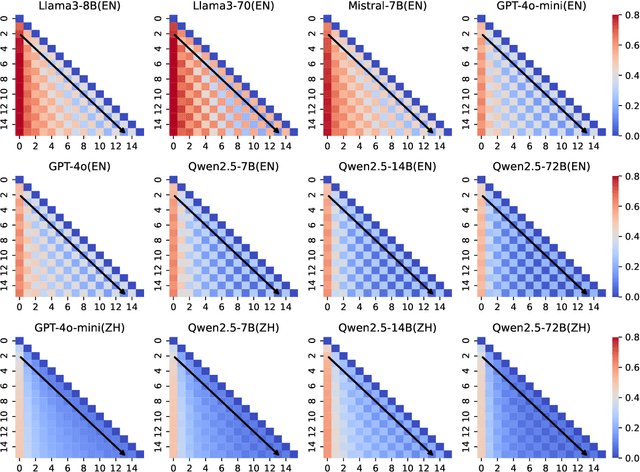
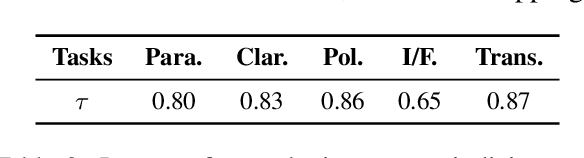
Abstract:Dynamical systems theory provides a framework for analyzing iterative processes and evolution over time. Within such systems, repetitive transformations can lead to stable configurations, known as attractors, including fixed points and limit cycles. Applying this perspective to large language models (LLMs), which iteratively map input text to output text, provides a principled approach to characterizing long-term behaviors. Successive paraphrasing serves as a compelling testbed for exploring such dynamics, as paraphrases re-express the same underlying meaning with linguistic variation. Although LLMs are expected to explore a diverse set of paraphrases in the text space, our study reveals that successive paraphrasing converges to stable periodic states, such as 2-period attractor cycles, limiting linguistic diversity. This phenomenon is attributed to the self-reinforcing nature of LLMs, as they iteratively favour and amplify certain textual forms over others. This pattern persists with increasing generation randomness or alternating prompts and LLMs. These findings underscore inherent constraints in LLM generative capability, while offering a novel dynamical systems perspective for studying their expressive potential.
Benchmarking GPT-4 against Human Translators: A Comprehensive Evaluation Across Languages, Domains, and Expertise Levels
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:This study presents a comprehensive evaluation of GPT-4's translation capabilities compared to human translators of varying expertise levels. Through systematic human evaluation using the MQM schema, we assess translations across three language pairs (Chinese$\longleftrightarrow$English, Russian$\longleftrightarrow$English, and Chinese$\longleftrightarrow$Hindi) and three domains (News, Technology, and Biomedical). Our findings reveal that GPT-4 achieves performance comparable to junior-level translators in terms of total errors, while still lagging behind senior translators. Unlike traditional Neural Machine Translation systems, which show significant performance degradation in resource-poor language directions, GPT-4 maintains consistent translation quality across all evaluated language pairs. Through qualitative analysis, we identify distinctive patterns in translation approaches: GPT-4 tends toward overly literal translations and exhibits lexical inconsistency, while human translators sometimes over-interpret context and introduce hallucinations. This study represents the first systematic comparison between LLM and human translators across different proficiency levels, providing valuable insights into the current capabilities and limitations of LLM-based translation systems.
Keys to Robust Edits: from Theoretical Insights to Practical Advances
Oct 12, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized knowledge storage and retrieval, but face challenges with conflicting and outdated information. Knowledge editing techniques have been proposed to address these issues, yet they struggle with robustness tests involving long contexts, paraphrased subjects, and continuous edits. This work investigates the cause of these failures in locate-and-edit methods, offering theoretical insights into their key-value modeling and deriving mathematical bounds for robust and specific edits, leading to a novel 'group discussion' conceptual model for locate-and-edit methods. Empirical analysis reveals that keys used by current methods fail to meet robustness and specificity requirements. To address this, we propose a Robust Edit Pathway (REP) that disentangles editing keys from LLMs' inner representations. Evaluations on LLaMA2-7B and Mistral-7B using the CounterFact dataset show that REP significantly improves robustness across various metrics, both in-domain and out-of-domain, with minimal trade-offs in success rate and locality. Our findings advance the development of reliable and flexible knowledge updating in LLMs.
ELICIT: LLM Augmentation via External In-Context Capability
Oct 12, 2024
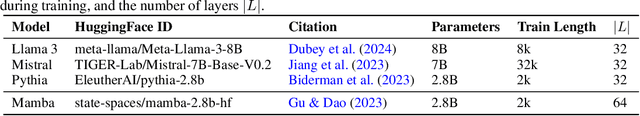

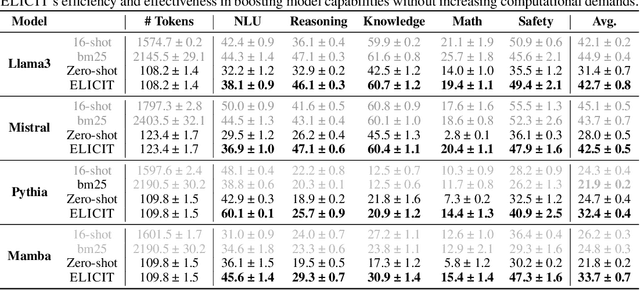
Abstract:Enhancing the adaptive capabilities of large language models is a critical pursuit in both research and application. Traditional fine-tuning methods require substantial data and computational resources, especially for enhancing specific capabilities, while in-context learning is limited by the need for appropriate demonstrations and efficient token usage. Inspired by the expression of in-context learned capabilities through task vectors and the concept of modularization, we propose \alg, a framework consisting of two modules designed to effectively store and reuse task vectors to elicit the diverse capabilities of models without additional training or inference tokens. Our comprehensive experiments and analysis demonstrate that our pipeline is highly transferable across different input formats, tasks, and model architectures. ELICIT serves as a plug-and-play performance booster to enable adaptive elicitation of model capabilities. By externally storing and reusing vectors that represent in-context learned capabilities, \alg not only demonstrates the potential to operate modular capabilities but also significantly enhances the performance, versatility, adaptability, and scalability of large language models. Our code will be publicly available at https://github.com/LINs-lab/ELICIT.
See What LLMs Cannot Answer: A Self-Challenge Framework for Uncovering LLM Weaknesses
Aug 16, 2024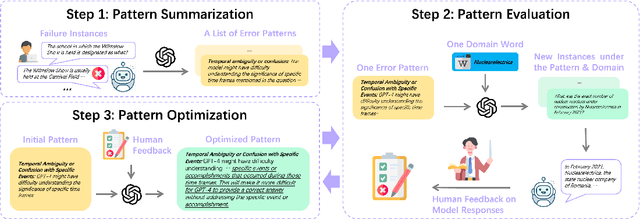
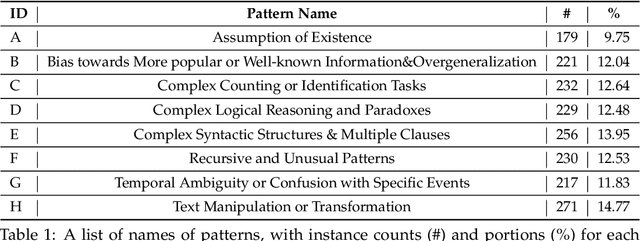

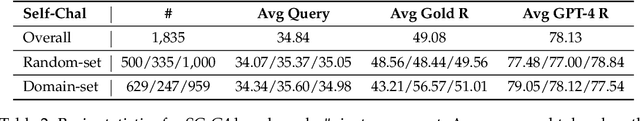
Abstract:The impressive performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) has consistently surpassed numerous human-designed benchmarks, presenting new challenges in assessing the shortcomings of LLMs. Designing tasks and finding LLMs' limitations are becoming increasingly important. In this paper, we investigate the question of whether an LLM can discover its own limitations from the errors it makes. To this end, we propose a Self-Challenge evaluation framework with human-in-the-loop. Starting from seed instances that GPT-4 fails to answer, we prompt GPT-4 to summarize error patterns that can be used to generate new instances and incorporate human feedback on them to refine these patterns for generating more challenging data, iteratively. We end up with 8 diverse patterns, such as text manipulation and questions with assumptions. We then build a benchmark, SC-G4, consisting of 1,835 instances generated by GPT-4 using these patterns, with human-annotated gold responses. The SC-G4 serves as a challenging benchmark that allows for a detailed assessment of LLMs' abilities. Our results show that only 44.96\% of instances in SC-G4 can be answered correctly by GPT-4. Interestingly, our pilot study indicates that these error patterns also challenge other LLMs, such as Claude-3 and Llama-3, and cannot be fully resolved through fine-tuning. Our work takes the first step to demonstrate that LLMs can autonomously identify their inherent flaws and provide insights for future dynamic and automatic evaluation.
GPT-4 vs. Human Translators: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Translation Quality Across Languages, Domains, and Expertise Levels
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:This study comprehensively evaluates the translation quality of Large Language Models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4, against human translators of varying expertise levels across multiple language pairs and domains. Through carefully designed annotation rounds, we find that GPT-4 performs comparably to junior translators in terms of total errors made but lags behind medium and senior translators. We also observe the imbalanced performance across different languages and domains, with GPT-4's translation capability gradually weakening from resource-rich to resource-poor directions. In addition, we qualitatively study the translation given by GPT-4 and human translators, and find that GPT-4 translator suffers from literal translations, but human translators sometimes overthink the background information. To our knowledge, this study is the first to evaluate LLMs against human translators and analyze the systematic differences between their outputs, providing valuable insights into the current state of LLM-based translation and its potential limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge