What Have We Achieved on Non-autoregressive Translation?
Paper and Code
May 21, 2024
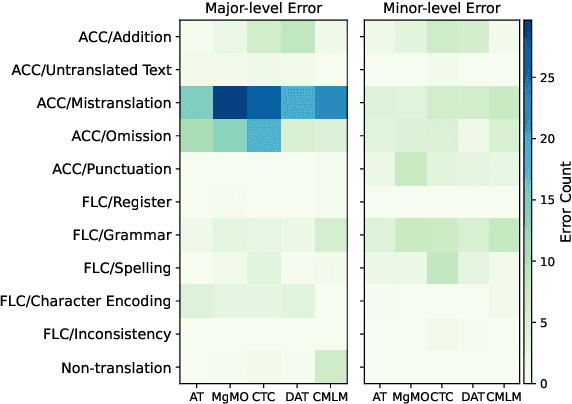


Recent advances have made non-autoregressive (NAT) translation comparable to autoregressive methods (AT). However, their evaluation using BLEU has been shown to weakly correlate with human annotations. Limited research compares non-autoregressive translation and autoregressive translation comprehensively, leaving uncertainty about the true proximity of NAT to AT. To address this gap, we systematically evaluate four representative NAT methods across various dimensions, including human evaluation. Our empirical results demonstrate that despite narrowing the performance gap, state-of-the-art NAT still underperforms AT under more reliable evaluation metrics. Furthermore, we discover that explicitly modeling dependencies is crucial for generating natural language and generalizing to out-of-distribution sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge