Jason Rambach
When Anomalies Depend on Context: Learning Conditional Compatibility for Anomaly Detection
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Anomaly detection is often formulated under the assumption that abnormality is an intrinsic property of an observation, independent of context. This assumption breaks down in many real-world settings, where the same object or action may be normal or anomalous depending on latent contextual factors (e.g., running on a track versus on a highway). We revisit \emph{contextual anomaly detection}, classically defined as context-dependent abnormality, and operationalize it in the visual domain, where anomaly labels depend on subject--context compatibility rather than intrinsic appearance. To enable systematic study of this setting, we introduce CAAD-3K, a benchmark that isolates contextual anomalies by controlling subject identity while varying context. We further propose a conditional compatibility learning framework that leverages vision--language representations to model subject--context relationships under limited supervision. Our method substantially outperforms existing approaches on CAAD-3K and achieves state-of-the-art performance on MVTec-AD and VisA, demonstrating that modeling context dependence complements traditional structural anomaly detection. Our code and dataset will be publicly released.
PanoSAMic: Panoramic Image Segmentation from SAM Feature Encoding and Dual View Fusion
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Existing image foundation models are not optimized for spherical images having been trained primarily on perspective images. PanoSAMic integrates the pre-trained Segment Anything (SAM) encoder to make use of its extensive training and integrate it into a semantic segmentation model for panoramic images using multiple modalities. We modify the SAM encoder to output multi-stage features and introduce a novel spatio-modal fusion module that allows the model to select the relevant modalities and best features from each modality for different areas of the input. Furthermore, our semantic decoder uses spherical attention and dual view fusion to overcome the distortions and edge discontinuity often associated with panoramic images. PanoSAMic achieves state-of-the-art (SotA) results on Stanford2D3DS for RGB, RGB-D, and RGB-D-N modalities and on Matterport3D for RGB and RGB-D modalities. https://github.com/dfki-av/PanoSAMic
IMKD: Intensity-Aware Multi-Level Knowledge Distillation for Camera-Radar Fusion
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:High-performance Radar-Camera 3D object detection can be achieved by leveraging knowledge distillation without using LiDAR at inference time. However, existing distillation methods typically transfer modality-specific features directly to each sensor, which can distort their unique characteristics and degrade their individual strengths. To address this, we introduce IMKD, a radar-camera fusion framework based on multi-level knowledge distillation that preserves each sensor's intrinsic characteristics while amplifying their complementary strengths. IMKD applies a three-stage, intensity-aware distillation strategy to enrich the fused representation across the architecture: (1) LiDAR-to-Radar intensity-aware feature distillation to enhance radar representations with fine-grained structural cues, (2) LiDAR-to-Fused feature intensity-guided distillation to selectively highlight useful geometry and depth information at the fusion level, fostering complementarity between the modalities rather than forcing them to align, and (3) Camera-Radar intensity-guided fusion mechanism that facilitates effective feature alignment and calibration. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes benchmark show that IMKD reaches 67.0% NDS and 61.0% mAP, outperforming all prior distillation-based radar-camera fusion methods. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/dfki-av/IMKD/.
DriverGaze360: OmniDirectional Driver Attention with Object-Level Guidance
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Predicting driver attention is a critical problem for developing explainable autonomous driving systems and understanding driver behavior in mixed human-autonomous vehicle traffic scenarios. Although significant progress has been made through large-scale driver attention datasets and deep learning architectures, existing works are constrained by narrow frontal field-of-view and limited driving diversity. Consequently, they fail to capture the full spatial context of driving environments, especially during lane changes, turns, and interactions involving peripheral objects such as pedestrians or cyclists. In this paper, we introduce DriverGaze360, a large-scale 360$^\circ$ field of view driver attention dataset, containing $\sim$1 million gaze-labeled frames collected from 19 human drivers, enabling comprehensive omnidirectional modeling of driver gaze behavior. Moreover, our panoramic attention prediction approach, DriverGaze360-Net, jointly learns attention maps and attended objects by employing an auxiliary semantic segmentation head. This improves spatial awareness and attention prediction across wide panoramic inputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DriverGaze360-Net achieves state-of-the-art attention prediction performance on multiple metrics on panoramic driving images. Dataset and method available at https://av.dfki.de/drivergaze360.
JENGA: Object selection and pose estimation for robotic grasping from a stack
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Vision-based robotic object grasping is typically investigated in the context of isolated objects or unstructured object sets in bin picking scenarios. However, there are several settings, such as construction or warehouse automation, where a robot needs to interact with a structured object formation such as a stack. In this context, we define the problem of selecting suitable objects for grasping along with estimating an accurate 6DoF pose of these objects. To address this problem, we propose a camera-IMU based approach that prioritizes unobstructed objects on the higher layers of stacks and introduce a dataset for benchmarking and evaluation, along with a suitable evaluation metric that combines object selection with pose accuracy. Experimental results show that although our method can perform quite well, this is a challenging problem if a completely error-free solution is needed. Finally, we show results from the deployment of our method for a brick-picking application in a construction scenario.
SynRailObs: A Synthetic Dataset for Obstacle Detection in Railway Scenarios
May 16, 2025Abstract:Detecting potential obstacles in railway environments is critical for preventing serious accidents. Identifying a broad range of obstacle categories under complex conditions requires large-scale datasets with precisely annotated, high-quality images. However, existing publicly available datasets fail to meet these requirements, thereby hindering progress in railway safety research. To address this gap, we introduce SynRailObs, a high-fidelity synthetic dataset designed to represent a diverse range of weather conditions and geographical features. Furthermore, diffusion models are employed to generate rare and difficult-to-capture obstacles that are typically challenging to obtain in real-world scenarios. To evaluate the effectiveness of SynRailObs, we perform experiments in real-world railway environments, testing on both ballasted and ballastless tracks across various weather conditions. The results demonstrate that SynRailObs holds substantial potential for advancing obstacle detection in railway safety applications. Models trained on this dataset show consistent performance across different distances and environmental conditions. Moreover, the model trained on SynRailObs exhibits zero-shot capabilities, which are essential for applications in security-sensitive domains. The data is available in https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/qiushi910/synrailobs.
Resolving Symmetry Ambiguity in Correspondence-based Methods for Instance-level Object Pose Estimation
May 17, 2024Abstract:Estimating the 6D pose of an object from a single RGB image is a critical task that becomes additionally challenging when dealing with symmetric objects. Recent approaches typically establish one-to-one correspondences between image pixels and 3D object surface vertices. However, the utilization of one-to-one correspondences introduces ambiguity for symmetric objects. To address this, we propose SymCode, a symmetry-aware surface encoding that encodes the object surface vertices based on one-to-many correspondences, eliminating the problem of one-to-one correspondence ambiguity. We also introduce SymNet, a fast end-to-end network that directly regresses the 6D pose parameters without solving a PnP problem. We demonstrate faster runtime and comparable accuracy achieved by our method on the T-LESS and IC-BIN benchmarks of mostly symmetric objects. Our source code will be released upon acceptance.
HiPose: Hierarchical Binary Surface Encoding and Correspondence Pruning for RGB-D 6DoF Object Pose Estimation
Nov 21, 2023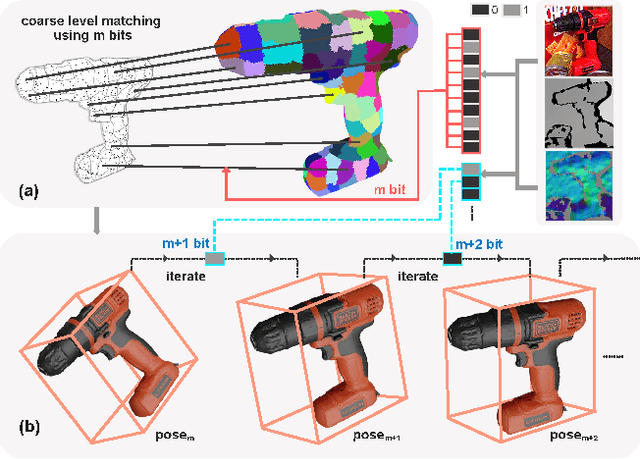

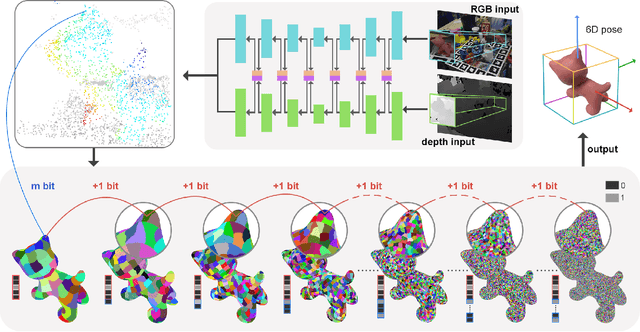
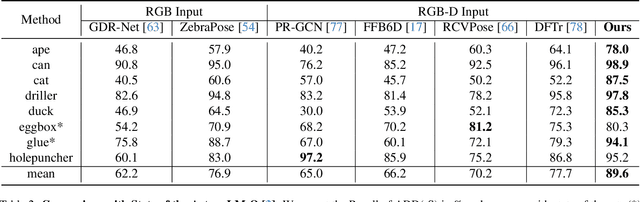
Abstract:In this work, we present a novel dense-correspondence method for 6DoF object pose estimation from a single RGB-D image. While many existing data-driven methods achieve impressive performance, they tend to be time-consuming due to their reliance on rendering-based refinement approaches. To circumvent this limitation, we present HiPose, which establishes 3D-3D correspondences in a coarse-to-fine manner with a hierarchical binary surface encoding. Unlike previous dense-correspondence methods, we estimate the correspondence surface by employing point-to-surface matching and iteratively constricting the surface until it becomes a correspondence point while gradually removing outliers. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks LM-O, YCB-V, and T-Less demonstrate that our method surpasses all refinement-free methods and is even on par with expensive refinement-based approaches. Crucially, our approach is computationally efficient and enables real-time critical applications with high accuracy requirements. Code and models will be released.
Cross-Dataset Experimental Study of Radar-Camera Fusion in Bird's-Eye View
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:By exploiting complementary sensor information, radar and camera fusion systems have the potential to provide a highly robust and reliable perception system for advanced driver assistance systems and automated driving functions. Recent advances in camera-based object detection offer new radar-camera fusion possibilities with bird's eye view feature maps. In this work, we propose a novel and flexible fusion network and evaluate its performance on two datasets: nuScenes and View-of-Delft. Our experiments reveal that while the camera branch needs large and diverse training data, the radar branch benefits more from a high-performance radar. Using transfer learning, we improve the camera's performance on the smaller dataset. Our results further demonstrate that the radar-camera fusion approach significantly outperforms the camera-only and radar-only baselines.
Single Frame Semantic Segmentation Using Multi-Modal Spherical Images
Aug 18, 2023Abstract:In recent years, the research community has shown a lot of interest to panoramic images that offer a 360-degree directional perspective. Multiple data modalities can be fed, and complimentary characteristics can be utilized for more robust and rich scene interpretation based on semantic segmentation, to fully realize the potential. Existing research, however, mostly concentrated on pinhole RGB-X semantic segmentation. In this study, we propose a transformer-based cross-modal fusion architecture to bridge the gap between multi-modal fusion and omnidirectional scene perception. We employ distortion-aware modules to address extreme object deformations and panorama distortions that result from equirectangular representation. Additionally, we conduct cross-modal interactions for feature rectification and information exchange before merging the features in order to communicate long-range contexts for bi-modal and tri-modal feature streams. In thorough tests using combinations of four different modality types in three indoor panoramic-view datasets, our technique achieved state-of-the-art mIoU performance: 60.60% on Stanford2D3DS (RGB-HHA), 71.97% Structured3D (RGB-D-N), and 35.92% Matterport3D (RGB-D). We plan to release all codes and trained models soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge