Jan Kocoń
Shammie
Divide, Cache, Conquer: Dichotomic Prompting for Efficient Multi-Label LLM-Based Classification
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:We introduce a method for efficient multi-label text classification with large language models (LLMs), built on reformulating classification tasks as sequences of dichotomic (yes/no) decisions. Instead of generating all labels in a single structured response, each target dimension is queried independently, which, combined with a prefix caching mechanism, yields substantial efficiency gains for short-text inference without loss of accuracy. To demonstrate the approach, we focus on affective text analysis, covering 24 dimensions including emotions and sentiment. Using LLM-to-SLM distillation, a powerful annotator model (DeepSeek-V3) provides multiple annotations per text, which are aggregated to fine-tune smaller models (HerBERT-Large, CLARIN-1B, PLLuM-8B, Gemma3-1B). The fine-tuned models show significant improvements over zero-shot baselines, particularly on the dimensions seen during training. Our findings suggest that decomposing multi-label classification into dichotomic queries, combined with distillation and cache-aware inference, offers a scalable and effective framework for LLM-based classification. While we validate the method on affective states, the approach is general and applicable across domains.
PLLuM: A Family of Polish Large Language Models
Nov 05, 2025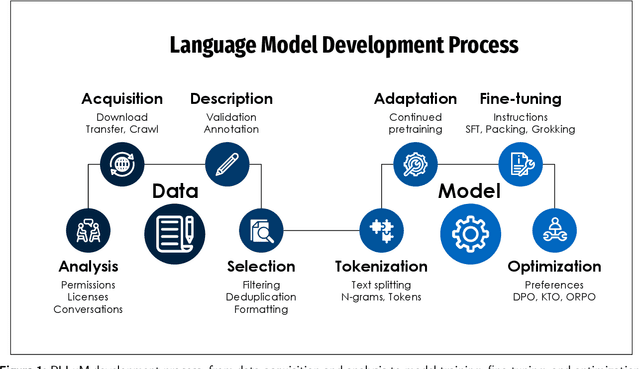
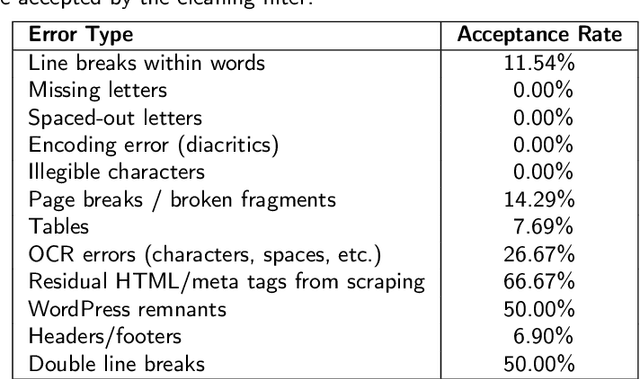
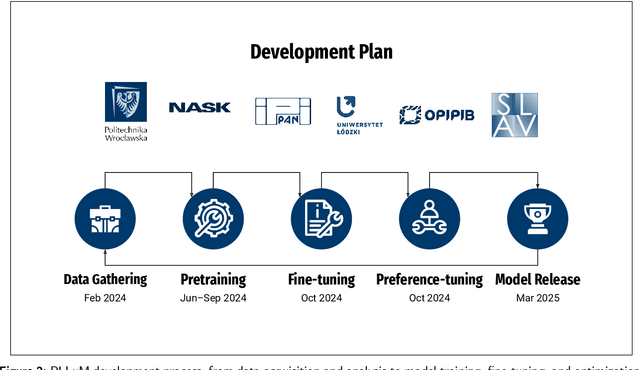
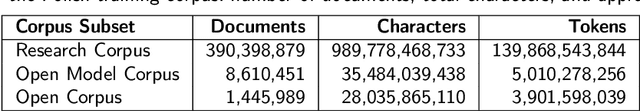
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) play a central role in modern artificial intelligence, yet their development has been primarily focused on English, resulting in limited support for other languages. We present PLLuM (Polish Large Language Model), the largest open-source family of foundation models tailored specifically for the Polish language. Developed by a consortium of major Polish research institutions, PLLuM addresses the need for high-quality, transparent, and culturally relevant language models beyond the English-centric commercial landscape. We describe the development process, including the construction of a new 140-billion-token Polish text corpus for pre-training, a 77k custom instructions dataset, and a 100k preference optimization dataset. A key component is a Responsible AI framework that incorporates strict data governance and a hybrid module for output correction and safety filtering. We detail the models' architecture, training procedures, and alignment techniques for both base and instruction-tuned variants, and demonstrate their utility in a downstream task within public administration. By releasing these models publicly, PLLuM aims to foster open research and strengthen sovereign AI technologies in Poland.
Enhancing AI Face Realism: Cost-Efficient Quality Improvement in Distilled Diffusion Models with a Fully Synthetic Dataset
May 04, 2025



Abstract:This study presents a novel approach to enhance the cost-to-quality ratio of image generation with diffusion models. We hypothesize that differences between distilled (e.g. FLUX.1-schnell) and baseline (e.g. FLUX.1-dev) models are consistent and, therefore, learnable within a specialized domain, like portrait generation. We generate a synthetic paired dataset and train a fast image-to-image translation head. Using two sets of low- and high-quality synthetic images, our model is trained to refine the output of a distilled generator (e.g., FLUX.1-schnell) to a level comparable to a baseline model like FLUX.1-dev, which is more computationally intensive. Our results show that the pipeline, which combines a distilled version of a large generative model with our enhancement layer, delivers similar photorealistic portraits to the baseline version with up to an 82% decrease in computational cost compared to FLUX.1-dev. This study demonstrates the potential for improving the efficiency of AI solutions involving large-scale image generation.
SupResDiffGAN a new approach for the Super-Resolution task
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present SupResDiffGAN, a novel hybrid architecture that combines the strengths of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models for super-resolution tasks. By leveraging latent space representations and reducing the number of diffusion steps, SupResDiffGAN achieves significantly faster inference times than other diffusion-based super-resolution models while maintaining competitive perceptual quality. To prevent discriminator overfitting, we propose adaptive noise corruption, ensuring a stable balance between the generator and the discriminator during training. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show that our approach outperforms traditional diffusion models such as SR3 and I$^2$SB in efficiency and image quality. This work bridges the performance gap between diffusion- and GAN-based methods, laying the foundation for real-time applications of diffusion models in high-resolution image generation.
Eagle and Finch: RWKV with Matrix-Valued States and Dynamic Recurrence
Apr 10, 2024



Abstract:We present Eagle (RWKV-5) and Finch (RWKV-6), sequence models improving upon the RWKV (RWKV-4) architecture. Our architectural design advancements include multi-headed matrix-valued states and a dynamic recurrence mechanism that improve expressivity while maintaining the inference efficiency characteristics of RNNs. We introduce a new multilingual corpus with 1.12 trillion tokens and a fast tokenizer based on greedy matching for enhanced multilinguality. We trained four Eagle models, ranging from 0.46 to 7.5 billion parameters, and two Finch models with 1.6 and 3.1 billion parameters and find that they achieve competitive performance across a wide variety of benchmarks. We release all our models on HuggingFace under the Apache 2.0 license. Models at: https://huggingface.co/RWKV Training code at: https://github.com/RWKV/RWKV-LM Inference code at: https://github.com/RWKV/ChatRWKV Time-parallel training code at: https://github.com/RWKV/RWKV-infctx-trainer
Personalized Large Language Models
Feb 14, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks in recent years. However, their universal nature poses limitations in scenarios requiring personalized responses, such as recommendation systems and chatbots. This paper investigates methods to personalize LLMs, comparing fine-tuning and zero-shot reasoning approaches on subjective tasks. Results demonstrate that personalized fine-tuning improves model reasoning compared to non-personalized models. Experiments on datasets for emotion recognition and hate speech detection show consistent performance gains with personalized methods across different LLM architectures. These findings underscore the importance of personalization for enhancing LLM capabilities in subjective text perception tasks.
Into the Unknown: Self-Learning Large Language Models
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:We address the main problem of self-learning LLM: the question of what to learn. We propose a self-learning LLM framework that enables an LLM to independently learn previously unknown knowledge through self-assessment of their own hallucinations. Using the hallucination score, we introduce a new concept of Points in The Unknown (PiUs), along with one extrinsic and three intrinsic methods for automatic PiUs identification. It facilitates the creation of a self-learning loop that focuses exclusively on the knowledge gap in Points in The Unknown, resulting in a reduced hallucination score. We also developed evaluation metrics for gauging an LLM's self-learning capability. Our experiments revealed that 7B-Mistral models that have been finetuned or aligned are capable of self-learning considerably well. Our self-learning concept allows more efficient LLM updates and opens new perspectives for knowledge exchange. It may also increase public trust in AI.
Modeling Uncertainty in Personalized Emotion Prediction with Normalizing Flows
Dec 10, 2023Abstract:Designing predictive models for subjective problems in natural language processing (NLP) remains challenging. This is mainly due to its non-deterministic nature and different perceptions of the content by different humans. It may be solved by Personalized Natural Language Processing (PNLP), where the model exploits additional information about the reader to make more accurate predictions. However, current approaches require complete information about the recipients to be straight embedded. Besides, the recent methods focus on deterministic inference or simple frequency-based estimations of the probabilities. In this work, we overcome this limitation by proposing a novel approach to capture the uncertainty of the forecast using conditional Normalizing Flows. This allows us to model complex multimodal distributions and to compare various models using negative log-likelihood (NLL). In addition, the new solution allows for various interpretations of possible reader perception thanks to the available sampling function. We validated our method on three challenging, subjective NLP tasks, including emotion recognition and hate speech. The comparative analysis of generalized and personalized approaches revealed that our personalized solutions significantly outperform the baseline and provide more precise uncertainty estimates. The impact on the text interpretability and uncertainty studies are presented as well. The information brought by the developed methods makes it possible to build hybrid models whose effectiveness surpasses classic solutions. In addition, an analysis and visualization of the probabilities of the given decisions for texts with high entropy of annotations and annotators with mixed views were carried out.
Deep Emotions Across Languages: A Novel Approach for Sentiment Propagation in Multilingual WordNets
Dec 07, 2023Abstract:Sentiment analysis involves using WordNets enriched with emotional metadata, which are valuable resources. However, manual annotation is time-consuming and expensive, resulting in only a few WordNet Lexical Units being annotated. This paper introduces two new techniques for automatically propagating sentiment annotations from a partially annotated WordNet to its entirety and to a WordNet in a different language: Multilingual Structured Synset Embeddings (MSSE) and Cross-Lingual Deep Neural Sentiment Propagation (CLDNS). We evaluated the proposed MSSE+CLDNS method extensively using Princeton WordNet and Polish WordNet, which have many inter-lingual relations. Our results show that the MSSE+CLDNS method outperforms existing propagation methods, indicating its effectiveness in enriching WordNets with emotional metadata across multiple languages. This work provides a solid foundation for large-scale, multilingual sentiment analysis and is valuable for academic research and practical applications.
From Big to Small Without Losing It All: Text Augmentation with ChatGPT for Efficient Sentiment Analysis
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:In the era of artificial intelligence, data is gold but costly to annotate. The paper demonstrates a groundbreaking solution to this dilemma using ChatGPT for text augmentation in sentiment analysis. We leverage ChatGPT's generative capabilities to create synthetic training data that significantly improves the performance of smaller models, making them competitive with, or even outperforming, their larger counterparts. This innovation enables models to be both efficient and effective, thereby reducing computational cost, inference time, and memory usage without compromising on quality. Our work marks a key advancement in the cost-effective development and deployment of robust sentiment analysis models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge