Marcin Gruza
Towards Model-Based Data Acquisition for Subjective Multi-Task NLP Problems
Dec 13, 2023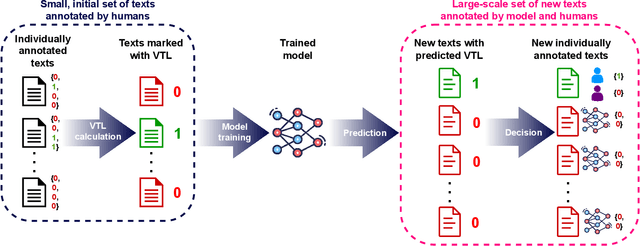
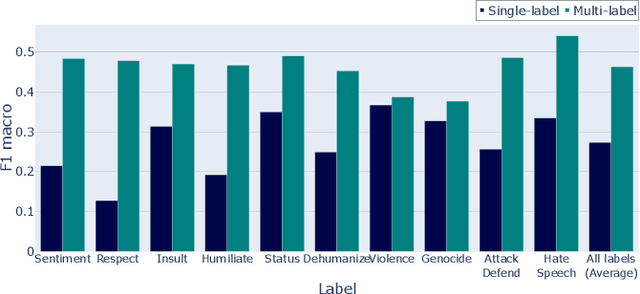
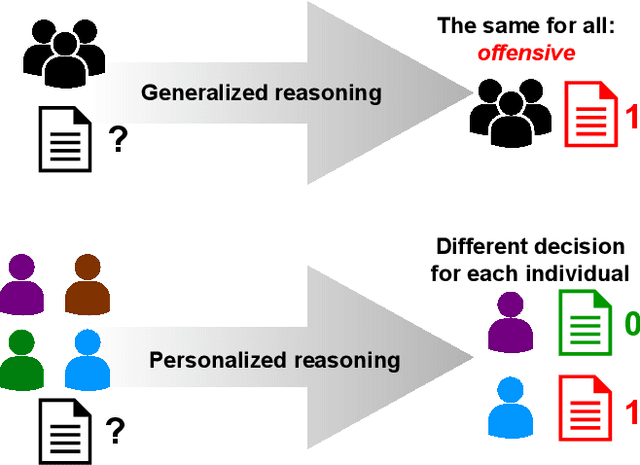
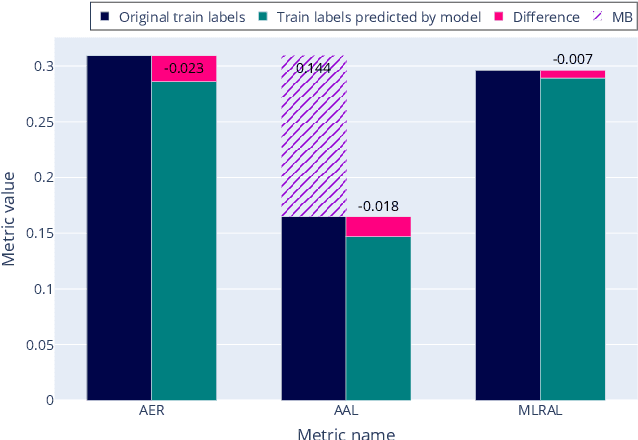
Abstract:Data annotated by humans is a source of knowledge by describing the peculiarities of the problem and therefore fueling the decision process of the trained model. Unfortunately, the annotation process for subjective natural language processing (NLP) problems like offensiveness or emotion detection is often very expensive and time-consuming. One of the inevitable risks is to spend some of the funds and annotator effort on annotations that do not provide any additional knowledge about the specific task. To minimize these costs, we propose a new model-based approach that allows the selection of tasks annotated individually for each text in a multi-task scenario. The experiments carried out on three datasets, dozens of NLP tasks, and thousands of annotations show that our method allows up to 40% reduction in the number of annotations with negligible loss of knowledge. The results also emphasize the need to collect a diverse amount of data required to efficiently train a model, depending on the subjectivity of the annotation task. We also focused on measuring the relation between subjective tasks by evaluating the model in single-task and multi-task scenarios. Moreover, for some datasets, training only on the labels predicted by our model improved the efficiency of task selection as a self-supervised learning regularization technique.
Massively Multilingual Corpus of Sentiment Datasets and Multi-faceted Sentiment Classification Benchmark
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Despite impressive advancements in multilingual corpora collection and model training, developing large-scale deployments of multilingual models still presents a significant challenge. This is particularly true for language tasks that are culture-dependent. One such example is the area of multilingual sentiment analysis, where affective markers can be subtle and deeply ensconced in culture. This work presents the most extensive open massively multilingual corpus of datasets for training sentiment models. The corpus consists of 79 manually selected datasets from over 350 datasets reported in the scientific literature based on strict quality criteria. The corpus covers 27 languages representing 6 language families. Datasets can be queried using several linguistic and functional features. In addition, we present a multi-faceted sentiment classification benchmark summarizing hundreds of experiments conducted on different base models, training objectives, dataset collections, and fine-tuning strategies.
ChatGPT: Jack of all trades, master of none
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:OpenAI has released the Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer (ChatGPT) and revolutionized the approach in artificial intelligence to human-model interaction. The first contact with the chatbot reveals its ability to provide detailed and precise answers in various areas. There are several publications on ChatGPT evaluation, testing its effectiveness on well-known natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, the existing studies are mostly non-automated and tested on a very limited scale. In this work, we examined ChatGPT's capabilities on 25 diverse analytical NLP tasks, most of them subjective even to humans, such as sentiment analysis, emotion recognition, offensiveness and stance detection, natural language inference, word sense disambiguation, linguistic acceptability and question answering. We automated ChatGPT's querying process and analyzed more than 38k responses. Our comparison of its results with available State-of-the-Art (SOTA) solutions showed that the average loss in quality of the ChatGPT model was about 25% for zero-shot and few-shot evaluation. We showed that the more difficult the task (lower SOTA performance), the higher the ChatGPT loss. It especially refers to pragmatic NLP problems like emotion recognition. We also tested the ability of personalizing ChatGPT responses for selected subjective tasks via Random Contextual Few-Shot Personalization, and we obtained significantly better user-based predictions. Additional qualitative analysis revealed a ChatGPT bias, most likely due to the rules imposed on human trainers by OpenAI. Our results provide the basis for a fundamental discussion of whether the high quality of recent predictive NLP models can indicate a tool's usefulness to society and how the learning and validation procedures for such systems should be established.
Assessment of Massively Multilingual Sentiment Classifiers
Apr 11, 2022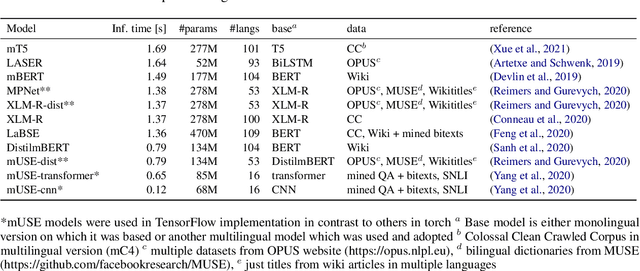
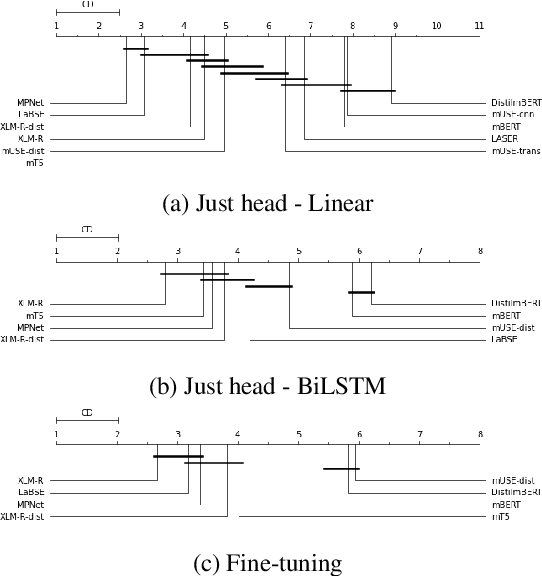
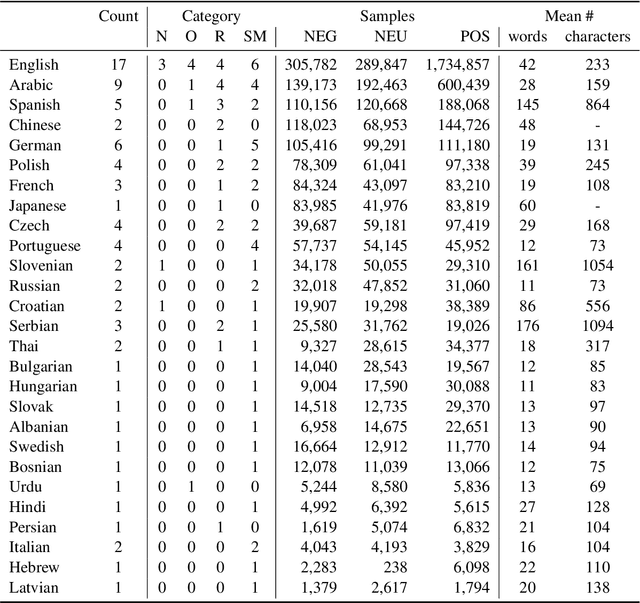
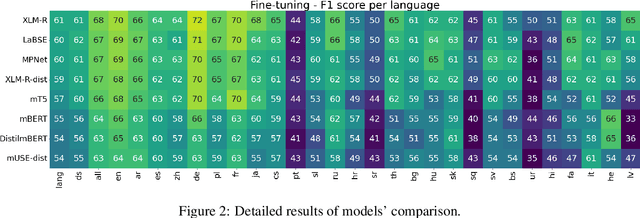
Abstract:Models are increasing in size and complexity in the hunt for SOTA. But what if those 2\% increase in performance does not make a difference in a production use case? Maybe benefits from a smaller, faster model outweigh those slight performance gains. Also, equally good performance across languages in multilingual tasks is more important than SOTA results on a single one. We present the biggest, unified, multilingual collection of sentiment analysis datasets. We use these to assess 11 models and 80 high-quality sentiment datasets (out of 342 raw datasets collected) in 27 languages and included results on the internally annotated datasets. We deeply evaluate multiple setups, including fine-tuning transformer-based models for measuring performance. We compare results in numerous dimensions addressing the imbalance in both languages coverage and dataset sizes. Finally, we present some best practices for working with such a massive collection of datasets and models from a multilingual perspective.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge