Piotr Gramacki
A Vision for Geo-Temporal Deep Research Systems: Towards Comprehensive, Transparent, and Reproducible Geo-Temporal Information Synthesis
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has transformed information access, with current LLMs also powering deep research systems that can generate comprehensive report-style answers, through planned iterative search, retrieval, and reasoning. Still, current deep research systems lack the geo-temporal capabilities that are essential for answering context-rich questions involving geographic and/or temporal constraints, frequently occurring in domains like public health, environmental science, or socio-economic analysis. This paper reports our vision towards next generation systems, identifying important technical, infrastructural, and evaluative challenges in integrating geo-temporal reasoning into deep research pipelines. We argue for augmenting retrieval and synthesis processes with the ability to handle geo-temporal constraints, supported by open and reproducible infrastructures and rigorous evaluation protocols. Our vision outlines a path towards more advanced and geo-temporally aware deep research systems, of potential impact to the future of AI-driven information access.
Evaluation of Code LLMs on Geospatial Code Generation
Oct 06, 2024Abstract:Software development support tools have been studied for a long time, with recent approaches using Large Language Models (LLMs) for code generation. These models can generate Python code for data science and machine learning applications. LLMs are helpful for software engineers because they increase productivity in daily work. An LLM can also serve as a "mentor" for inexperienced software developers, and be a viable learning support. High-quality code generation with LLMs can also be beneficial in geospatial data science. However, this domain poses different challenges, and code generation LLMs are typically not evaluated on geospatial tasks. Here, we show how we constructed an evaluation benchmark for code generation models, based on a selection of geospatial tasks. We categorised geospatial tasks based on their complexity and required tools. Then, we created a dataset with tasks that test model capabilities in spatial reasoning, spatial data processing, and geospatial tools usage. The dataset consists of specific coding problems that were manually created for high quality. For every problem, we proposed a set of test scenarios that make it possible to automatically check the generated code for correctness. In addition, we tested a selection of existing code generation LLMs for code generation in the geospatial domain. We share our dataset and reproducible evaluation code on a public GitHub repository, arguing that this can serve as an evaluation benchmark for new LLMs in the future. Our dataset will hopefully contribute to the development new models capable of solving geospatial coding tasks with high accuracy. These models will enable the creation of coding assistants tailored for geospatial applications.
SRAI: Towards Standardization of Geospatial AI
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:Spatial Representations for Artificial Intelligence (srai) is a Python library for working with geospatial data. The library can download geospatial data, split a given area into micro-regions using multiple algorithms and train an embedding model using various architectures. It includes baseline models as well as more complex methods from published works. Those capabilities make it possible to use srai in a complete pipeline for geospatial task solving. The proposed library is the first step to standardize the geospatial AI domain toolset. It is fully open-source and published under Apache 2.0 licence.
Massively Multilingual Corpus of Sentiment Datasets and Multi-faceted Sentiment Classification Benchmark
Jun 13, 2023Abstract:Despite impressive advancements in multilingual corpora collection and model training, developing large-scale deployments of multilingual models still presents a significant challenge. This is particularly true for language tasks that are culture-dependent. One such example is the area of multilingual sentiment analysis, where affective markers can be subtle and deeply ensconced in culture. This work presents the most extensive open massively multilingual corpus of datasets for training sentiment models. The corpus consists of 79 manually selected datasets from over 350 datasets reported in the scientific literature based on strict quality criteria. The corpus covers 27 languages representing 6 language families. Datasets can be queried using several linguistic and functional features. In addition, we present a multi-faceted sentiment classification benchmark summarizing hundreds of experiments conducted on different base models, training objectives, dataset collections, and fine-tuning strategies.
Resources and Few-shot Learners for In-context Learning in Slavic Languages
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Despite the rapid recent progress in creating accurate and compact in-context learners, most recent work focuses on in-context learning (ICL) for tasks in English. However, the ability to interact with users of languages outside English presents a great potential for broadening the applicability of language technologies to non-English speakers. In this work, we collect the infrastructure necessary for training and evaluation of ICL in a selection of Slavic languages: Czech, Polish, and Russian. We link a diverse set of datasets and cast these into a unified instructional format through a set of transformations and newly-crafted templates written purely in target languages. Using the newly-curated dataset, we evaluate a set of the most recent in-context learners and compare their results to the supervised baselines. Finally, we train, evaluate and publish a set of in-context learning models that we train on the collected resources and compare their performance to previous work. We find that ICL models tuned in English are also able to learn some tasks from non-English contexts, but multilingual instruction fine-tuning consistently improves the ICL ability. We also find that the massive multitask training can be outperformed by single-task training in the target language, uncovering the potential for specializing in-context learners to the language(s) of their application.
Assessment of Massively Multilingual Sentiment Classifiers
Apr 11, 2022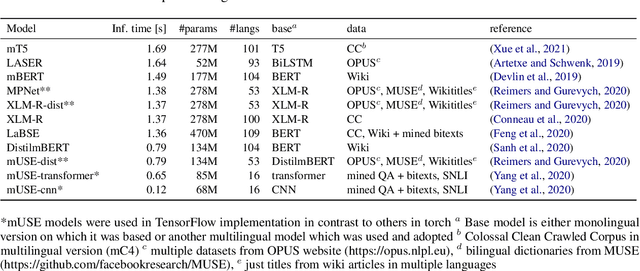
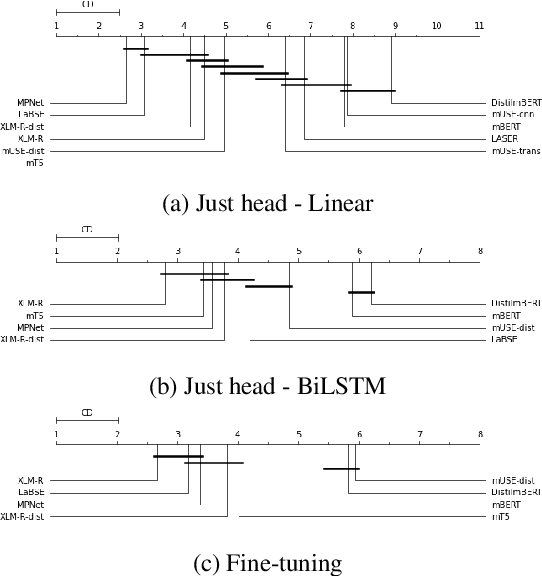
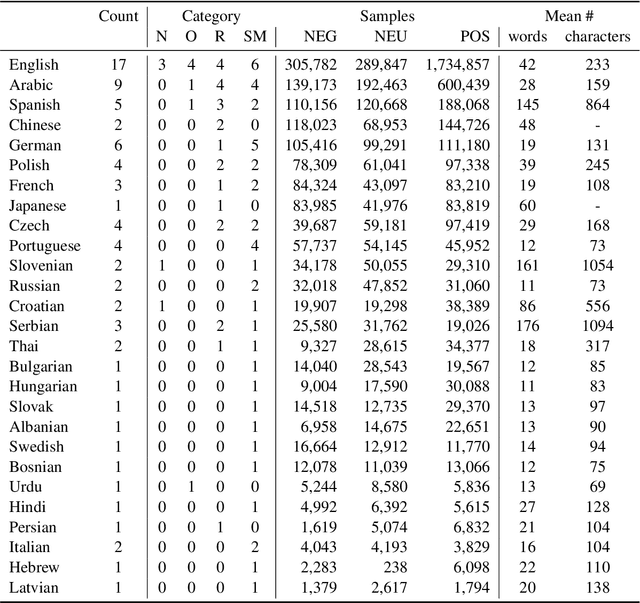
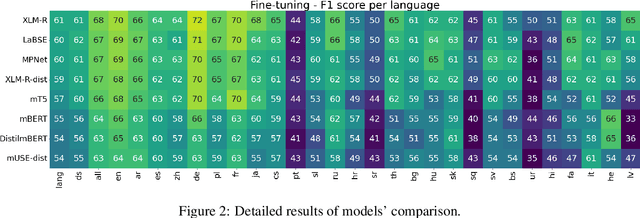
Abstract:Models are increasing in size and complexity in the hunt for SOTA. But what if those 2\% increase in performance does not make a difference in a production use case? Maybe benefits from a smaller, faster model outweigh those slight performance gains. Also, equally good performance across languages in multilingual tasks is more important than SOTA results on a single one. We present the biggest, unified, multilingual collection of sentiment analysis datasets. We use these to assess 11 models and 80 high-quality sentiment datasets (out of 342 raw datasets collected) in 27 languages and included results on the internally annotated datasets. We deeply evaluate multiple setups, including fine-tuning transformer-based models for measuring performance. We compare results in numerous dimensions addressing the imbalance in both languages coverage and dataset sizes. Finally, we present some best practices for working with such a massive collection of datasets and models from a multilingual perspective.
Unsupervised embedding and similarity detection of microregions using public transport schedules
Nov 03, 2021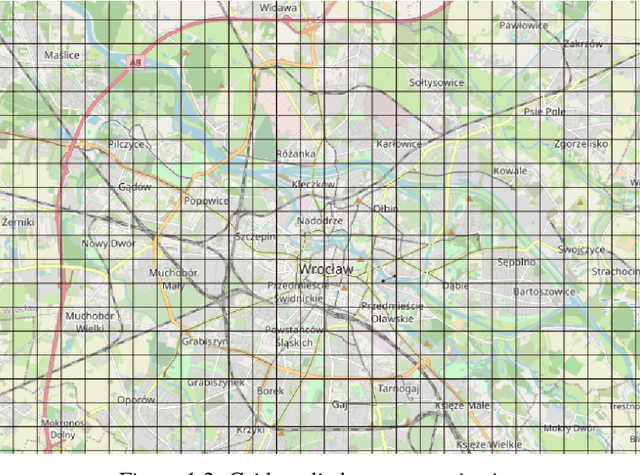
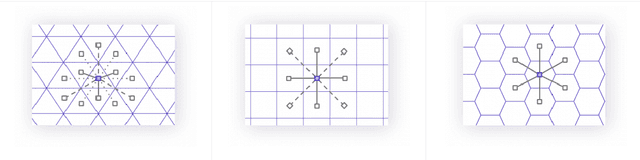
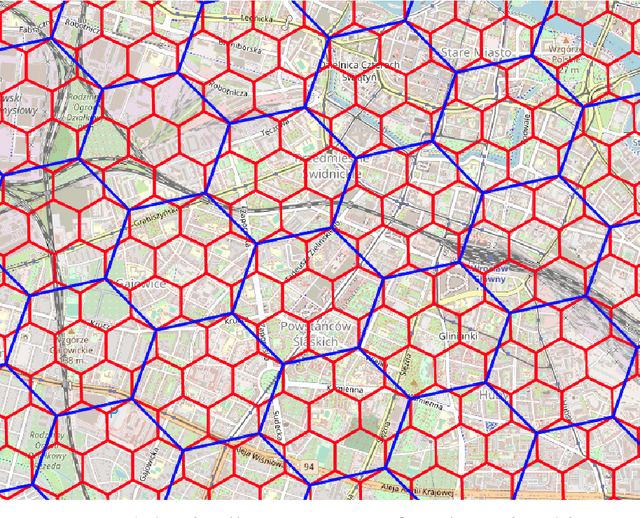
Abstract:The role of spatial data in tackling city-related tasks has been growing in recent years. To use them in machine learning models, it is often necessary to transform them into a vector representation, which has led to the development in the field of spatial data representation learning. There is also a growing variety of spatial data types for which representation learning methods are proposed. Public transport timetables have so far not been used in the task of learning representations of regions in a city. In this work, a method is developed to embed public transport availability information into vector space. To conduct experiments on its application, public transport timetables were collected from 48 European cities. Using the H3 spatial indexing method, they were divided into micro-regions. A method was also proposed to identify regions with similar characteristics of public transport offers. On its basis, a multi-level typology of public transport offers in the regions was defined. This thesis shows that the proposed representation method makes it possible to identify micro-regions with similar public transport characteristics between the cities, and can be used to evaluate the quality of public transport available in a city.
gtfs2vec -- Learning GTFS Embeddings for comparing Public Transport Offer in Microregions
Nov 02, 2021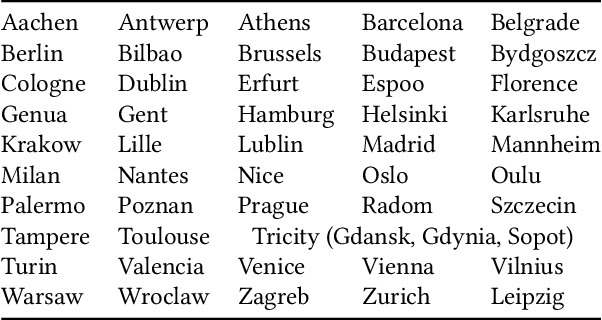

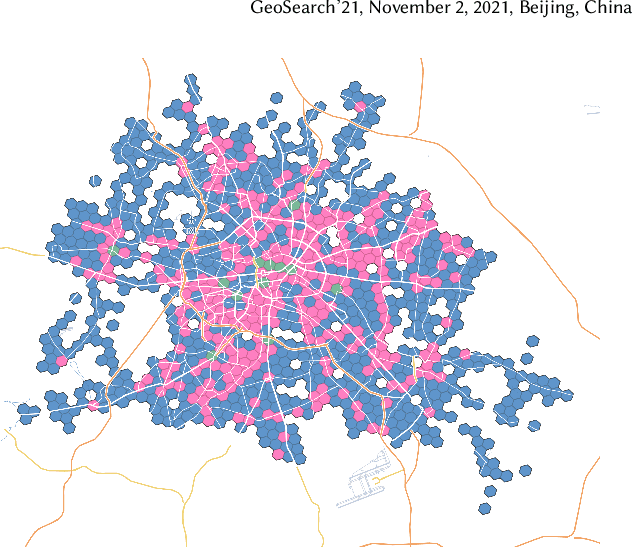
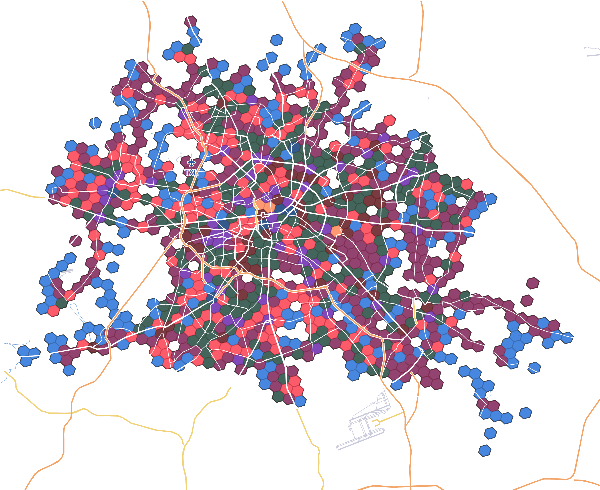
Abstract:We selected 48 European cities and gathered their public transport timetables in the GTFS format. We utilized Uber's H3 spatial index to divide each city into hexagonal micro-regions. Based on the timetables data we created certain features describing the quantity and variety of public transport availability in each region. Next, we trained an auto-associative deep neural network to embed each of the regions. Having such prepared representations, we then used a hierarchical clustering approach to identify similar regions. To do so, we utilized an agglomerative clustering algorithm with a euclidean distance between regions and Ward's method to minimize in-cluster variance. Finally, we analyzed the obtained clusters at different levels to identify some number of clusters that qualitatively describe public transport availability. We showed that our typology matches the characteristics of analyzed cities and allows succesful searching for areas with similar public transport schedule characteristics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge