Towards Model-Based Data Acquisition for Subjective Multi-Task NLP Problems
Paper and Code
Dec 13, 2023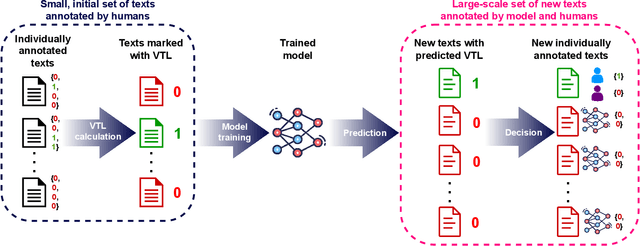
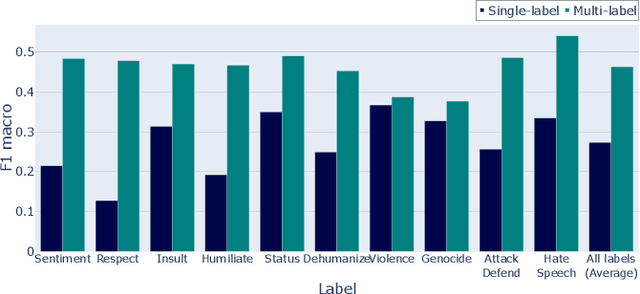
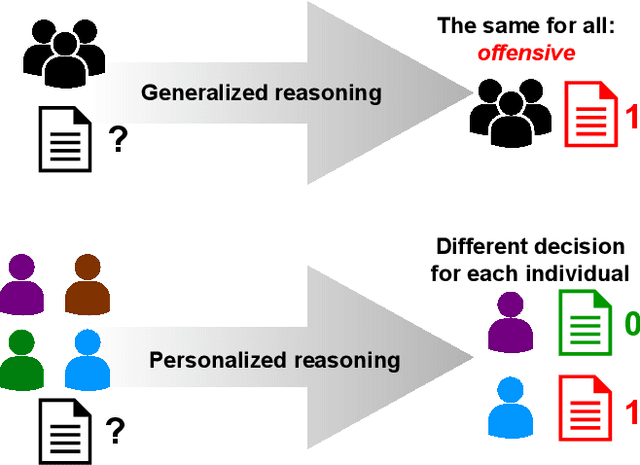
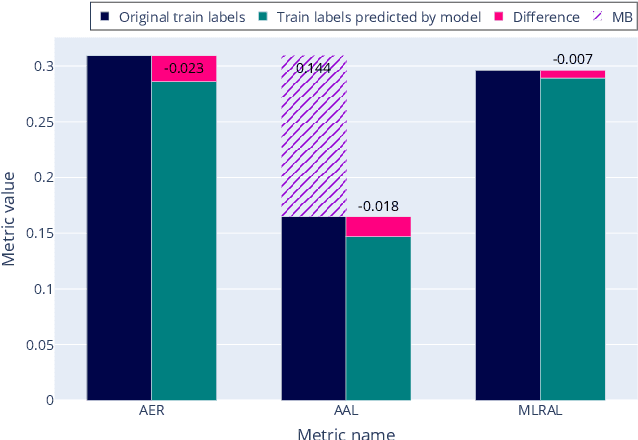
Data annotated by humans is a source of knowledge by describing the peculiarities of the problem and therefore fueling the decision process of the trained model. Unfortunately, the annotation process for subjective natural language processing (NLP) problems like offensiveness or emotion detection is often very expensive and time-consuming. One of the inevitable risks is to spend some of the funds and annotator effort on annotations that do not provide any additional knowledge about the specific task. To minimize these costs, we propose a new model-based approach that allows the selection of tasks annotated individually for each text in a multi-task scenario. The experiments carried out on three datasets, dozens of NLP tasks, and thousands of annotations show that our method allows up to 40% reduction in the number of annotations with negligible loss of knowledge. The results also emphasize the need to collect a diverse amount of data required to efficiently train a model, depending on the subjectivity of the annotation task. We also focused on measuring the relation between subjective tasks by evaluating the model in single-task and multi-task scenarios. Moreover, for some datasets, training only on the labels predicted by our model improved the efficiency of task selection as a self-supervised learning regularization technique.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge