Iman Abbasnejad
SCONE-GAN: Semantic Contrastive learning-based Generative Adversarial Network for an end-to-end image translation
Nov 07, 2023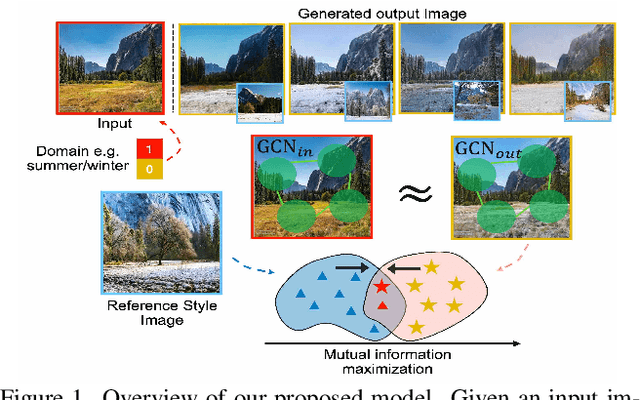
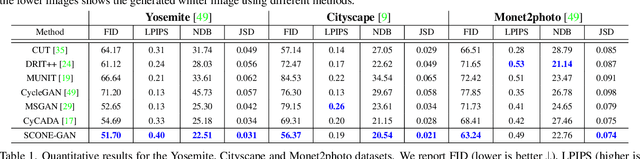
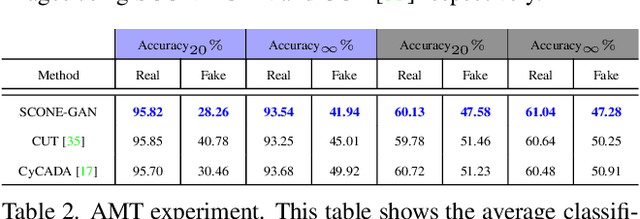

Abstract:SCONE-GAN presents an end-to-end image translation, which is shown to be effective for learning to generate realistic and diverse scenery images. Most current image-to-image translation approaches are devised as two mappings: a translation from the source to target domain and another to represent its inverse. While successful in many applications, these approaches may suffer from generating trivial solutions with limited diversity. That is because these methods learn more frequent associations rather than the scene structures. To mitigate the problem, we propose SCONE-GAN that utilises graph convolutional networks to learn the objects dependencies, maintain the image structure and preserve its semantics while transferring images into the target domain. For more realistic and diverse image generation we introduce style reference image. We enforce the model to maximize the mutual information between the style image and output. The proposed method explicitly maximizes the mutual information between the related patches, thus encouraging the generator to produce more diverse images. We validate the proposed algorithm for image-to-image translation and stylizing outdoor images. Both qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on four dataset.
Efficient Labelling of Affective Video Datasets via Few-Shot & Multi-Task Contrastive Learning
Aug 04, 2023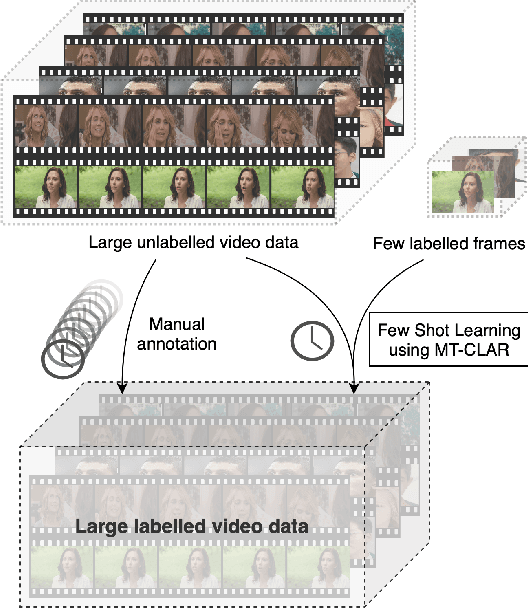
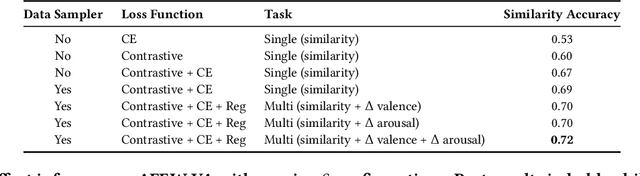
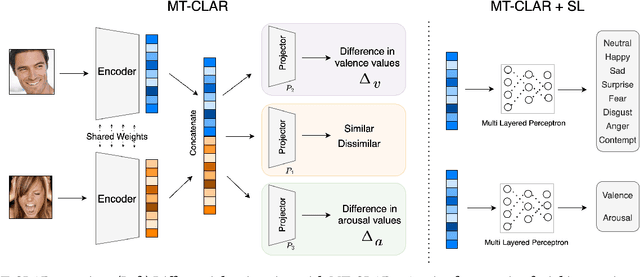
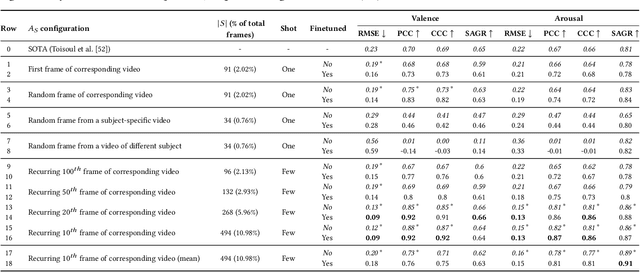
Abstract:Whilst deep learning techniques have achieved excellent emotion prediction, they still require large amounts of labelled training data, which are (a) onerous and tedious to compile, and (b) prone to errors and biases. We propose Multi-Task Contrastive Learning for Affect Representation (\textbf{MT-CLAR}) for few-shot affect inference. MT-CLAR combines multi-task learning with a Siamese network trained via contrastive learning to infer from a pair of expressive facial images (a) the (dis)similarity between the facial expressions, and (b) the difference in valence and arousal levels of the two faces. We further extend the image-based MT-CLAR framework for automated video labelling where, given one or a few labelled video frames (termed \textit{support-set}), MT-CLAR labels the remainder of the video for valence and arousal. Experiments are performed on the AFEW-VA dataset with multiple support-set configurations; moreover, supervised learning on representations learnt via MT-CLAR are used for valence, arousal and categorical emotion prediction on the AffectNet and AFEW-VA datasets. The results show that valence and arousal predictions via MT-CLAR are very comparable to the state-of-the-art (SOTA), and we significantly outperform SOTA with a support-set $\approx$6\% the size of the video dataset.
A Weakly Supervised Approach to Emotion-change Prediction and Improved Mood Inference
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:Whilst a majority of affective computing research focuses on inferring emotions, examining mood or understanding the \textit{mood-emotion interplay} has received significantly less attention. Building on prior work, we (a) deduce and incorporate emotion-change ($\Delta$) information for inferring mood, without resorting to annotated labels, and (b) attempt mood prediction for long duration video clips, in alignment with the characterisation of mood. We generate the emotion-change ($\Delta$) labels via metric learning from a pre-trained Siamese Network, and use these in addition to mood labels for mood classification. Experiments evaluating \textit{unimodal} (training only using mood labels) vs \textit{multimodal} (training using mood plus $\Delta$ labels) models show that mood prediction benefits from the incorporation of emotion-change information, emphasising the importance of modelling the mood-emotion interplay for effective mood inference.
An Active Information Seeking Model for Goal-oriented Vision-and-Language Tasks
Dec 16, 2018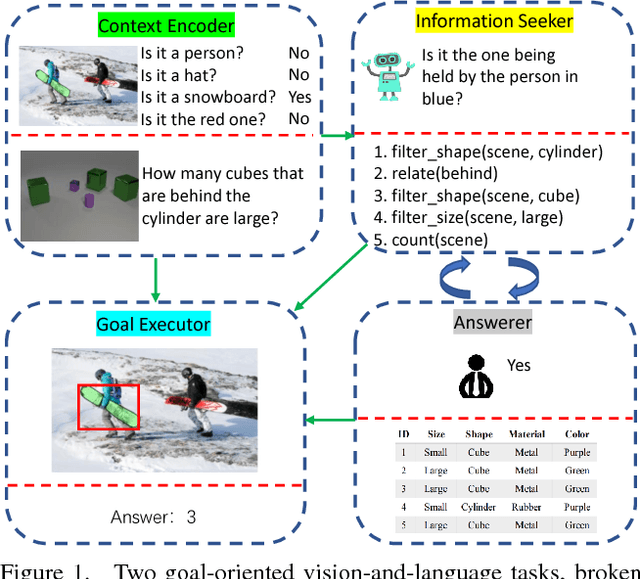
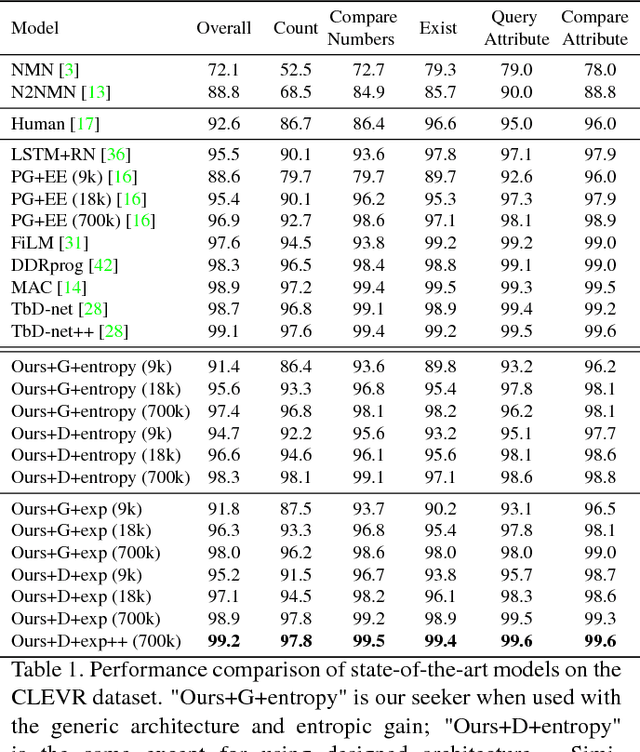
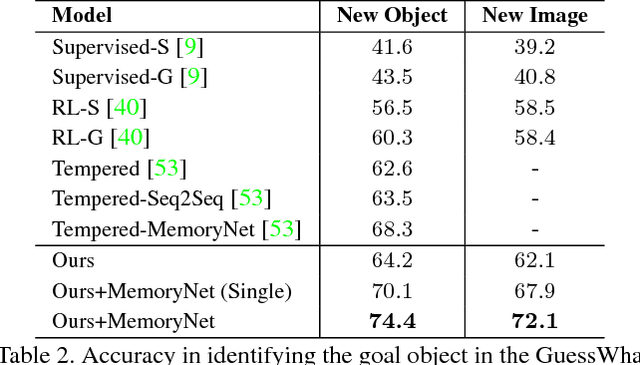
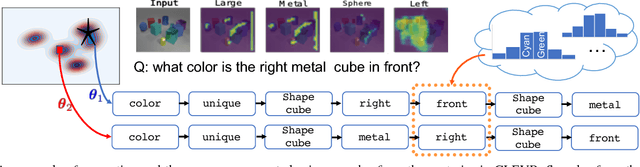
Abstract:As Computer Vision algorithms move from passive analysis of pixels to active reasoning over semantics, the breadth of information algorithms need to reason over has expanded significantly. One of the key challenges in this vein is the ability to identify the information required to make a decision, and select an action that will recover this information. We propose an reinforcement-learning approach that maintains an distribution over its internal information, thus explicitly representing the ambiguity in what it knows, and needs to know, towards achieving its goal. Potential actions are then generated according to particles sampled from this distribution. For each potential action a distribution of the expected answers is calculated, and the value of the information gained is obtained, as compared to the existing internal information. We demonstrate this approach applied to two vision-language problems that have attracted significant recent interest, visual dialogue and visual query generation. In both cases the method actively selects actions that will best reduce its internal uncertainty, and outperforms its competitors in achieving the goal of the challenge.
Meta Transfer Learning for Facial Emotion Recognition
May 25, 2018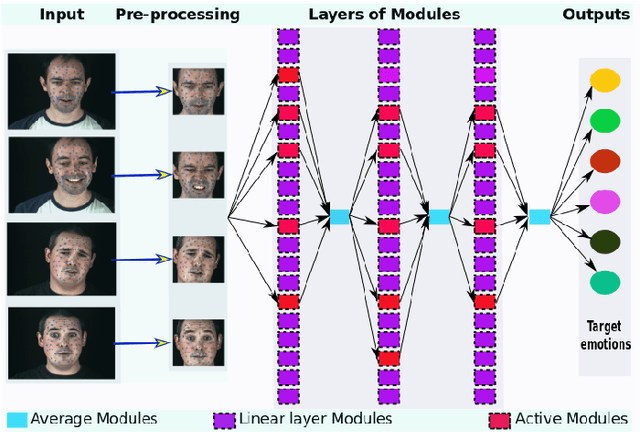
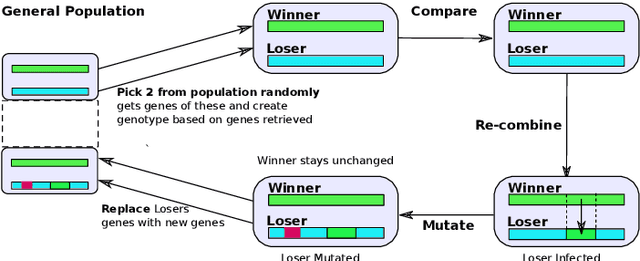
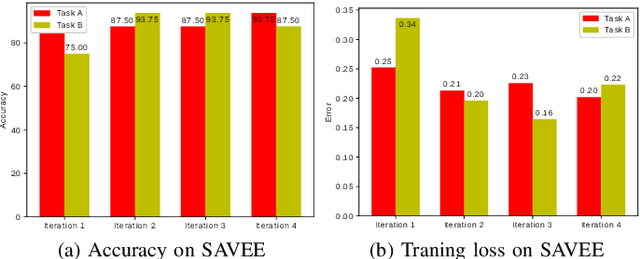
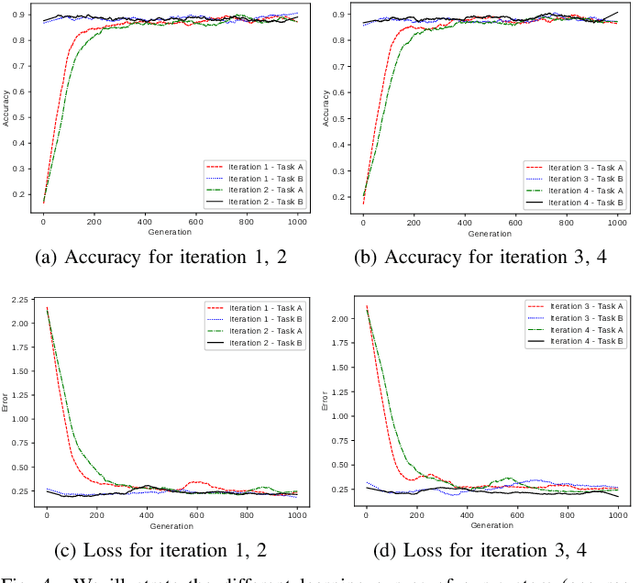
Abstract:The use of deep learning techniques for automatic facial expression recognition has recently attracted great interest but developed models are still unable to generalize well due to the lack of large emotion datasets for deep learning. To overcome this problem, in this paper, we propose utilizing a novel transfer learning approach relying on PathNet and investigate how knowledge can be accumulated within a given dataset and how the knowledge captured from one emotion dataset can be transferred into another in order to improve the overall performance. To evaluate the robustness of our system, we have conducted various sets of experiments on two emotion datasets: SAVEE and eNTERFACE. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed system leads to improvement in performance of emotion recognition and performs significantly better than the recent state-of-the-art schemes adopting fine-\ tuning/pre-trained approaches.
Bayesian Conditional Generative Adverserial Networks
Jun 17, 2017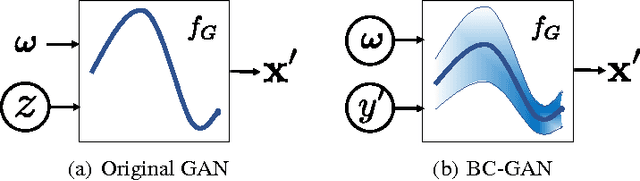
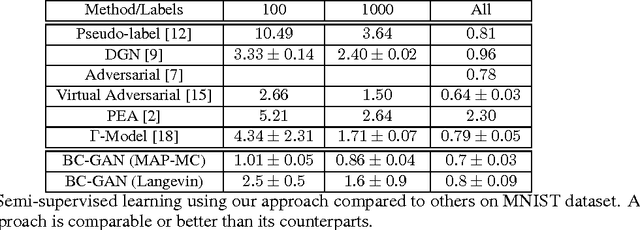
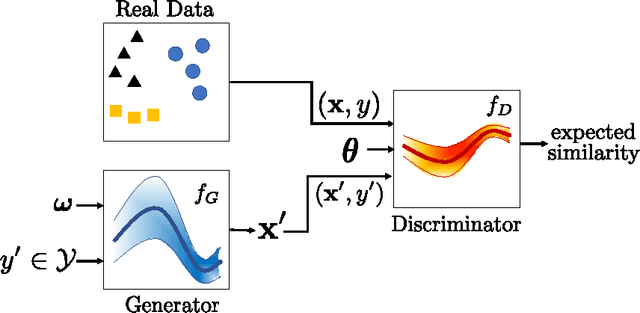
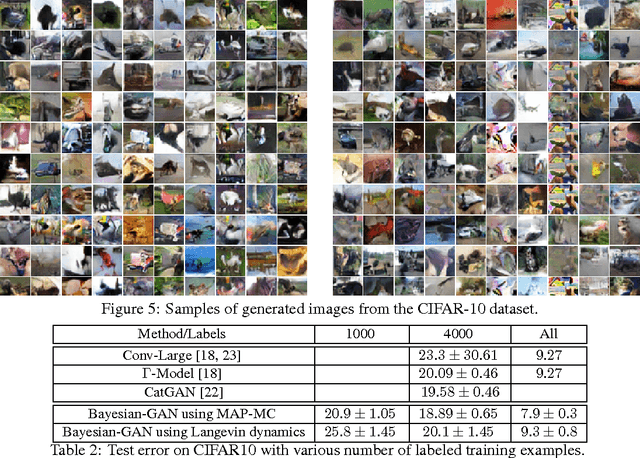
Abstract:Traditional GANs use a deterministic generator function (typically a neural network) to transform a random noise input $z$ to a sample $\mathbf{x}$ that the discriminator seeks to distinguish. We propose a new GAN called Bayesian Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (BC-GANs) that use a random generator function to transform a deterministic input $y'$ to a sample $\mathbf{x}$. Our BC-GANs extend traditional GANs to a Bayesian framework, and naturally handle unsupervised learning, supervised learning, and semi-supervised learning problems. Experiments show that the proposed BC-GANs outperforms the state-of-the-arts.
Joint Max Margin and Semantic Features for Continuous Event Detection in Complex Scenes
Jun 13, 2017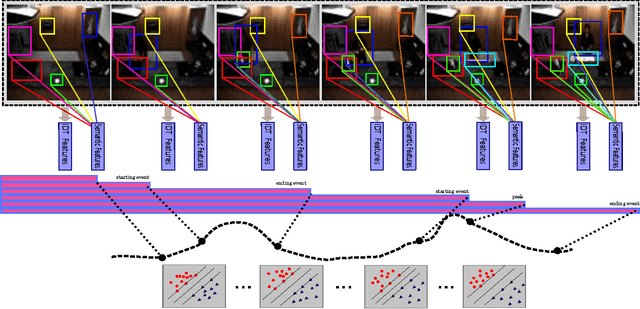
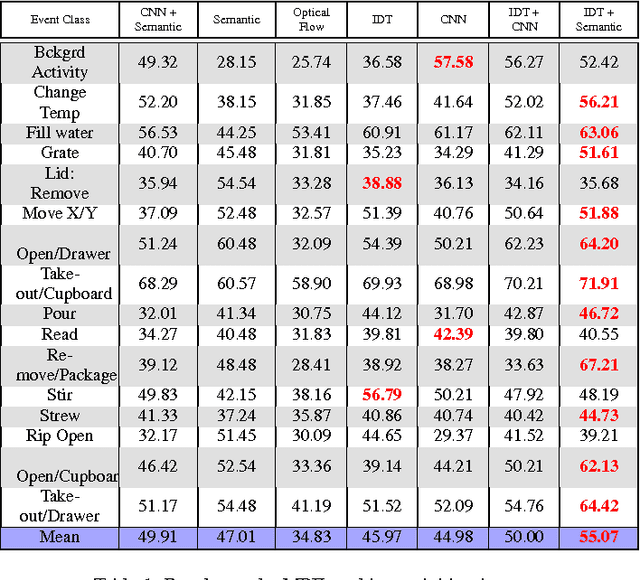
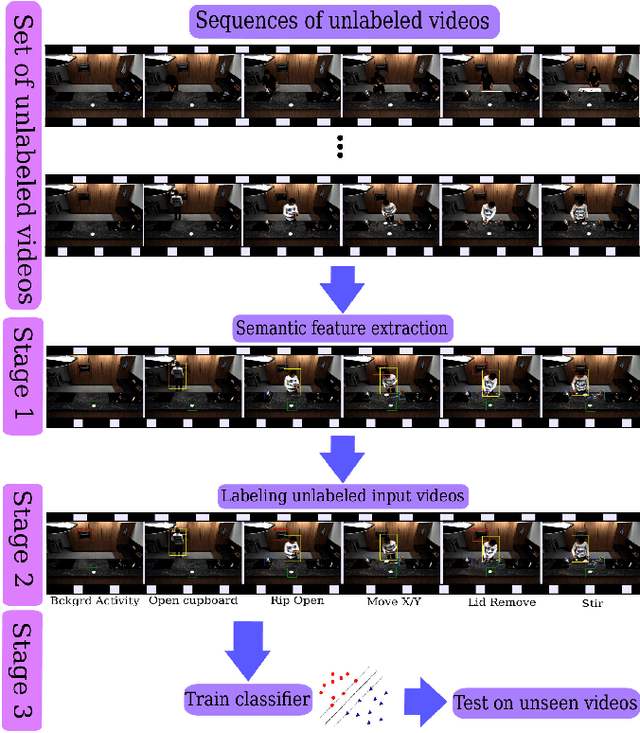
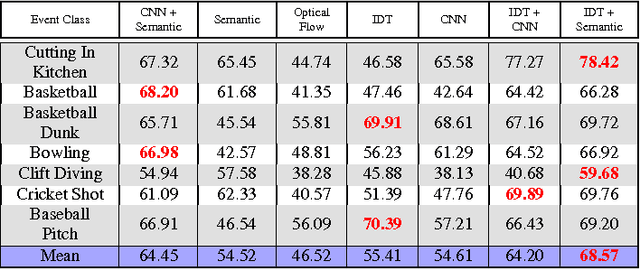
Abstract:In this paper the problem of complex event detection in the continuous domain (i.e. events with unknown starting and ending locations) is addressed. Existing event detection methods are limited to features that are extracted from the local spatial or spatio-temporal patches from the videos. However, this makes the model vulnerable to the events with similar concepts e.g. "Open drawer" and "Open cupboard". In this work, in order to address the aforementioned limitations we present a novel model based on the combination of semantic and temporal features extracted from video frames. We train a max-margin classifier on top of the extracted features in an adaptive framework that is able to detect the events with unknown starting and ending locations. Our model is based on the Bidirectional Region Neural Network and large margin Structural Output SVM. The generality of our model allows it to be simply applied to different labeled and unlabeled datasets. We finally test our algorithm on three challenging datasets, "UCF 101-Action Recognition", "MPII Cooking Activities" and "Hollywood", and we report state-of-the-art performance.
Incremental Real-Time Multibody VSLAM with Trajectory Optimization Using Stereo Camera
Aug 02, 2016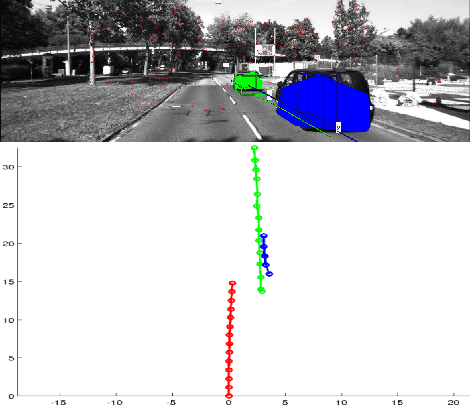
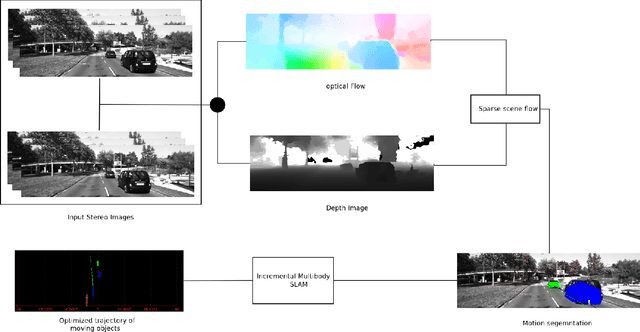
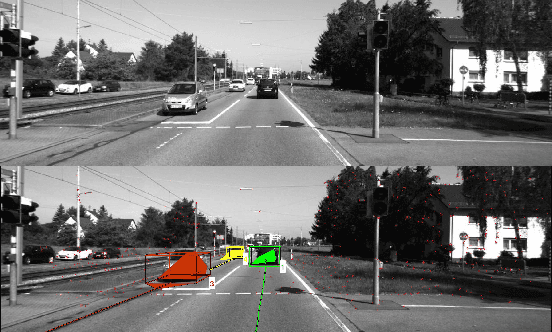
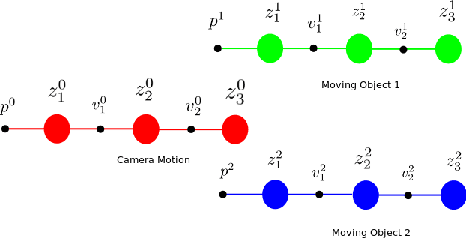
Abstract:Real time outdoor navigation in highly dynamic environments is an crucial problem. The recent literature on real time static SLAM don't scale up to dynamic outdoor environments. Most of these methods assume moving objects as outliers or discard the information provided by them. We propose an algorithm to jointly infer the camera trajectory and the moving object trajectory simultaneously. In this paper, we perform a sparse scene flow based motion segmentation using a stereo camera. The segmented objects motion models are used for accurate localization of the camera trajectory as well as the moving objects. We exploit the relationship between moving objects for improving the accuracy of the poses. We formulate the poses as a factor graph incorporating all the constraints. We achieve exact incremental solution by solving a full nonlinear optimization problem in real time. The evaluation is performed on the challenging KITTI dataset with multiple moving cars.Our method outperforms the previous baselines in outdoor navigation.
Learning Temporal Alignment Uncertainty for Efficient Event Detection
Sep 04, 2015

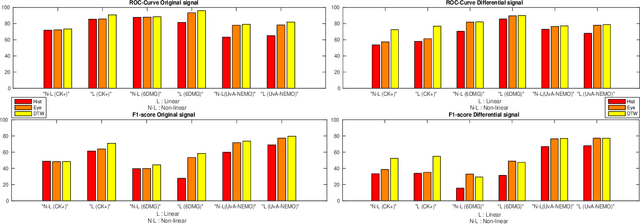
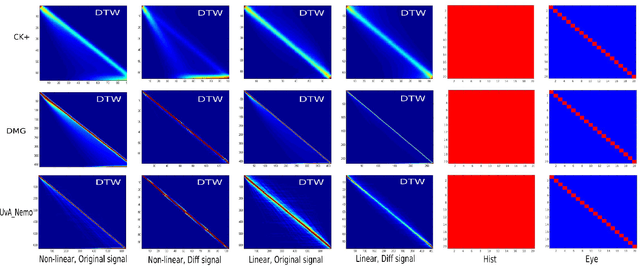
Abstract:In this paper we tackle the problem of efficient video event detection. We argue that linear detection functions should be preferred in this regard due to their scalability and efficiency during estimation and evaluation. A popular approach in this regard is to represent a sequence using a bag of words (BOW) representation due to its: (i) fixed dimensionality irrespective of the sequence length, and (ii) its ability to compactly model the statistics in the sequence. A drawback to the BOW representation, however, is the intrinsic destruction of the temporal ordering information. In this paper we propose a new representation that leverages the uncertainty in relative temporal alignments between pairs of sequences while not destroying temporal ordering. Our representation, like BOW, is of a fixed dimensionality making it easily integrated with a linear detection function. Extensive experiments on CK+, 6DMG, and UvA-NEMO databases show significant performance improvements across both isolated and continuous event detection tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge