David Dean
Meta Transfer Learning for Emotion Recognition
Jun 23, 2020



Abstract:Deep learning has been widely adopted in automatic emotion recognition and has lead to significant progress in the field. However, due to insufficient annotated emotion datasets, pre-trained models are limited in their generalization capability and thus lead to poor performance on novel test sets. To mitigate this challenge, transfer learning performing fine-tuning on pre-trained models has been applied. However, the fine-tuned knowledge may overwrite and/or discard important knowledge learned from pre-trained models. In this paper, we address this issue by proposing a PathNet-based transfer learning method that is able to transfer emotional knowledge learned from one visual/audio emotion domain to another visual/audio emotion domain, and transfer the emotional knowledge learned from multiple audio emotion domains into one another to improve overall emotion recognition accuracy. To show the robustness of our proposed system, various sets of experiments for facial expression recognition and speech emotion recognition task on three emotion datasets: SAVEE, EMODB, and eNTERFACE have been carried out. The experimental results indicate that our proposed system is capable of improving the performance of emotion recognition, making its performance substantially superior to the recent proposed fine-tuning/pre-trained models based transfer learning methods.
Meta Transfer Learning for Facial Emotion Recognition
May 25, 2018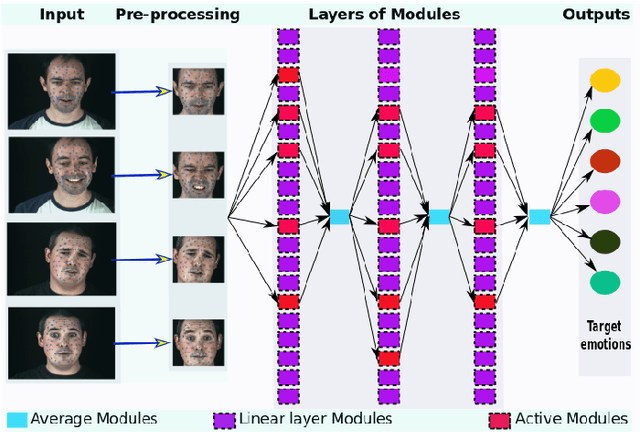
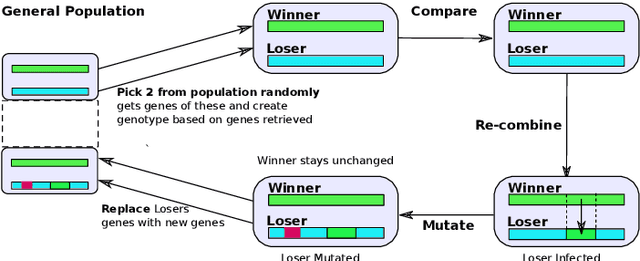
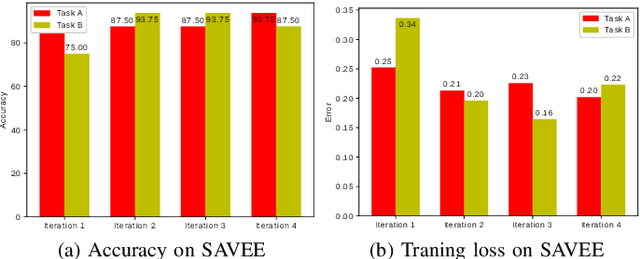
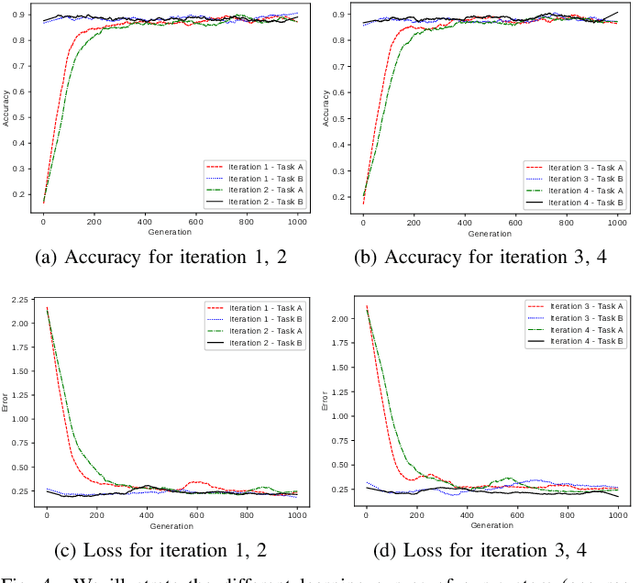
Abstract:The use of deep learning techniques for automatic facial expression recognition has recently attracted great interest but developed models are still unable to generalize well due to the lack of large emotion datasets for deep learning. To overcome this problem, in this paper, we propose utilizing a novel transfer learning approach relying on PathNet and investigate how knowledge can be accumulated within a given dataset and how the knowledge captured from one emotion dataset can be transferred into another in order to improve the overall performance. To evaluate the robustness of our system, we have conducted various sets of experiments on two emotion datasets: SAVEE and eNTERFACE. The experimental results demonstrate that our proposed system leads to improvement in performance of emotion recognition and performs significantly better than the recent state-of-the-art schemes adopting fine-\ tuning/pre-trained approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge