Huaijie Wang
EKPC: Elastic Knowledge Preservation and Compensation for Class-Incremental Learning
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) aims to enable AI models to continuously learn from sequentially arriving data of different classes over time while retaining previously acquired knowledge. Recently, Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods, like prompt pool-based approaches and adapter tuning, have shown great attraction in CIL. However, these methods either introduce additional parameters that increase memory usage, or rely on rigid regularization techniques which reduce forgetting but compromise model flexibility. To overcome these limitations, we propose the Elastic Knowledge Preservation and Compensation (EKPC) method, integrating Importance-aware Parameter Regularization (IPR) and Trainable Semantic Drift Compensation (TSDC) for CIL. Specifically, the IPR method assesses the sensitivity of network parameters to prior tasks using a novel parameter-importance algorithm. It then selectively constrains updates within the shared adapter according to these importance values, thereby preserving previously acquired knowledge while maintaining the model's flexibility. However, it still exhibits slight semantic differences in previous knowledge to accommodate new incremental tasks, leading to decision boundaries confusion in classifier. To eliminate this confusion, TSDC trains a unified classifier by compensating prototypes with trainable semantic drift. Extensive experiments on five CIL benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, showing superior performances to existing state-of-the-art methods.
StPR: Spatiotemporal Preservation and Routing for Exemplar-Free Video Class-Incremental Learning
May 20, 2025Abstract:Video Class-Incremental Learning (VCIL) seeks to develop models that continuously learn new action categories over time without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. Unlike traditional Class-Incremental Learning (CIL), VCIL introduces the added complexity of spatiotemporal structures, making it particularly challenging to mitigate catastrophic forgetting while effectively capturing both frame-shared semantics and temporal dynamics. Existing approaches either rely on exemplar rehearsal, raising concerns over memory and privacy, or adapt static image-based methods that neglect temporal modeling. To address these limitations, we propose Spatiotemporal Preservation and Routing (StPR), a unified and exemplar-free VCIL framework that explicitly disentangles and preserves spatiotemporal information. First, we introduce Frame-Shared Semantics Distillation (FSSD), which identifies semantically stable and meaningful channels by jointly considering semantic sensitivity and classification contribution. These important semantic channels are selectively regularized to maintain prior knowledge while allowing for adaptation. Second, we design a Temporal Decomposition-based Mixture-of-Experts (TD-MoE), which dynamically routes task-specific experts based on their temporal dynamics, enabling inference without task ID or stored exemplars. Together, StPR effectively leverages spatial semantics and temporal dynamics, achieving a unified, exemplar-free VCIL framework. Extensive experiments on UCF101, HMDB51, and Kinetics400 show that our method outperforms existing baselines while offering improved interpretability and efficiency in VCIL. Code is available in the supplementary materials.
Offline Reinforcement Learning for LLM Multi-Step Reasoning
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Improving the multi-step reasoning ability of large language models (LLMs) with offline reinforcement learning (RL) is essential for quickly adapting them to complex tasks. While Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has shown promise in aligning LLMs with human preferences, it is less suitable for multi-step reasoning tasks because (1) DPO relies on paired preference data, which is not readily available for multi-step reasoning tasks, and (2) it treats all tokens uniformly, making it ineffective for credit assignment in multi-step reasoning tasks, which often come with sparse reward. In this work, we propose OREO (Offline Reasoning Optimization), an offline RL method for enhancing LLM multi-step reasoning. Building on insights from previous works of maximum entropy reinforcement learning, it jointly learns a policy model and value function by optimizing the soft Bellman Equation. We show in principle that it reduces the need to collect pairwise data and enables better credit assignment. Empirically, OREO surpasses existing offline learning methods on multi-step reasoning benchmarks, including mathematical reasoning tasks (GSM8K, MATH) and embodied agent control (ALFWorld). The approach can be extended to a multi-iteration framework when additional resources are available. Furthermore, the learned value function can be leveraged to guide the tree search for free, which can further boost performance during test time.
BitNet: Scaling 1-bit Transformers for Large Language Models
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:The increasing size of large language models has posed challenges for deployment and raised concerns about environmental impact due to high energy consumption. In this work, we introduce BitNet, a scalable and stable 1-bit Transformer architecture designed for large language models. Specifically, we introduce BitLinear as a drop-in replacement of the nn.Linear layer in order to train 1-bit weights from scratch. Experimental results on language modeling show that BitNet achieves competitive performance while substantially reducing memory footprint and energy consumption, compared to state-of-the-art 8-bit quantization methods and FP16 Transformer baselines. Furthermore, BitNet exhibits a scaling law akin to full-precision Transformers, suggesting its potential for effective scaling to even larger language models while maintaining efficiency and performance benefits.
Language-Guided Generation of Physically Realistic Robot Motion and Control
Jun 18, 2023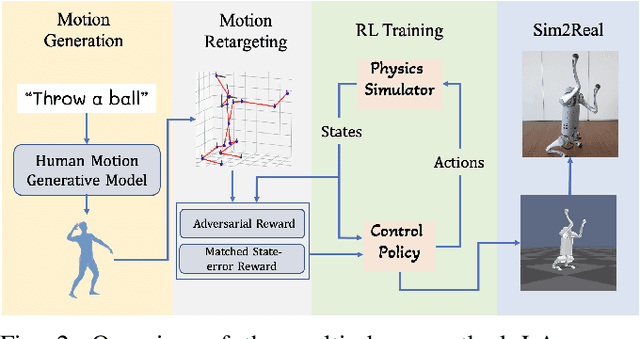
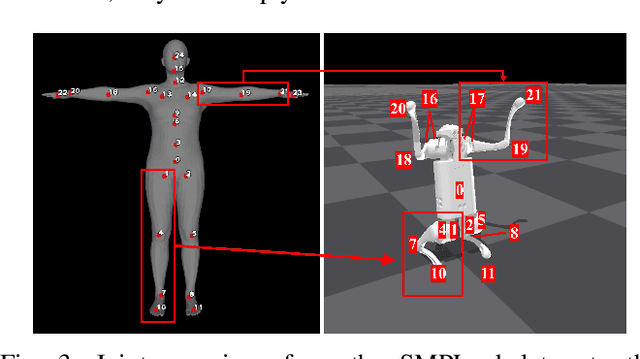
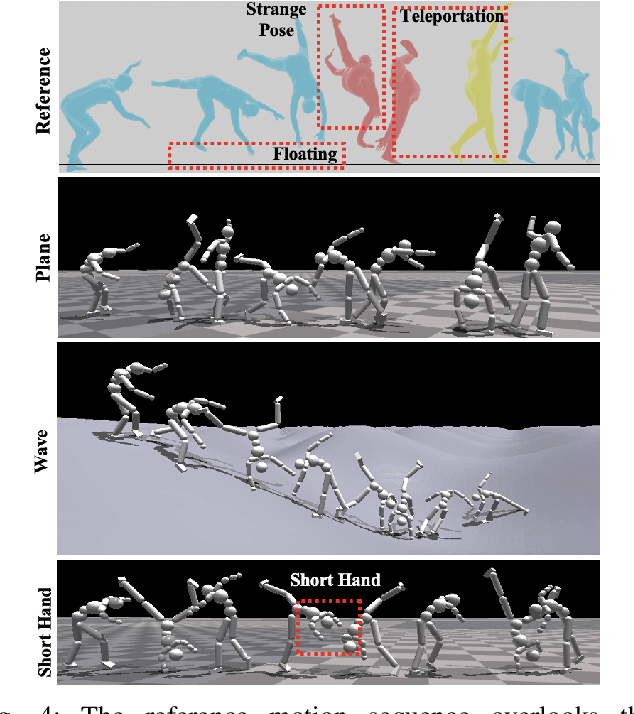
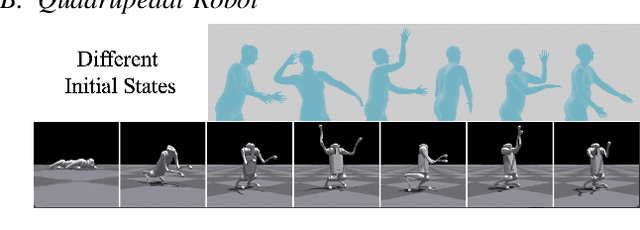
Abstract:We aim to control a robot to physically behave in the real world following any high-level language command like "cartwheel" or "kick. " Although human motion datasets exist, this task remains particularly challenging since generative models can produce physically unrealistic motions, which will be more severe for robots due to different body structures and physical properties. In addition, to control a physical robot to perform a desired motion, a control policy must be learned. We develop LAnguage-Guided mOtion cONtrol (LAGOON), a multi-phase method to generate physically realistic robot motions under language commands. LAGOON first leverages a pre-trained model to generate human motion from a language command. Then an RL phase is adopted to train a control policy in simulation to mimic the generated human motion. Finally, with domain randomization, we show that our learned policy can be successfully deployed to a quadrupedal robot, leading to a robot dog that can stand up and wave its front legs in the real world to mimic the behavior of a hand-waving human.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge