Hongying Liu
FedMuon: Accelerating Federated Learning with Matrix Orthogonalization
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:The core bottleneck of Federated Learning (FL) lies in the communication rounds. That is, how to achieve more effective local updates is crucial for reducing communication rounds. Existing FL methods still primarily use element-wise local optimizers (Adam/SGD), neglecting the geometric structure of the weight matrices. This often leads to the amplification of pathological directions in the weights during local updates, leading deterioration in the condition number and slow convergence. Therefore, we introduce the Muon optimizer in local, which has matrix orthogonalization to optimize matrix-structured parameters. Experimental results show that, in IID setting, Local Muon significantly accelerates the convergence of FL and reduces communication rounds compared to Local SGD and Local AdamW. However, in non-IID setting, independent matrix orthogonalization based on the local distributions of each client induces strong client drift. Applying Muon in non-IID FL poses significant challenges: (1) client preconditioner leading to client drift; (2) moment reinitialization. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Federated Muon optimizer (FedMuon), which incorporates two key techniques: (1) momentum aggregation, where clients use the aggregated momentum for local initialization; (2) local-global alignment, where the local gradients are aligned with the global update direction to significantly reduce client drift. Theoretically, we prove that \texttt{FedMuon} achieves a linear speedup convergence rate without the heterogeneity assumption, where $S$ is the number of participating clients per round, $K$ is the number of local iterations, and $R$ is the total number of communication rounds. Empirically, we validate the effectiveness of FedMuon on language and vision models. Compared to several baselines, FedMuon significantly reduces communication rounds and improves test accuracy.
DP-FedPGN: Finding Global Flat Minima for Differentially Private Federated Learning via Penalizing Gradient Norm
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:To prevent inference attacks in Federated Learning (FL) and reduce the leakage of sensitive information, Client-level Differentially Private Federated Learning (CL-DPFL) is widely used. However, current CL-DPFL methods usually result in sharper loss landscapes, which leads to a decrease in model generalization after differential privacy protection. By using Sharpness Aware Minimization (SAM), the current popular federated learning methods are to find a local flat minimum value to alleviate this problem. However, the local flatness may not reflect the global flatness in CL-DPFL. Therefore, to address this issue and seek global flat minima of models, we propose a new CL-DPFL algorithm, DP-FedPGN, in which we introduce a global gradient norm penalty to the local loss to find the global flat minimum. Moreover, by using our global gradient norm penalty, we not only find a flatter global minimum but also reduce the locally updated norm, which means that we further reduce the error of gradient clipping. From a theoretical perspective, we analyze how DP-FedPGN mitigates the performance degradation caused by DP. Meanwhile, the proposed DP-FedPGN algorithm eliminates the impact of data heterogeneity and achieves fast convergence. We also use R\'enyi DP to provide strict privacy guarantees and provide sensitivity analysis for local updates. Finally, we conduct effectiveness tests on both ResNet and Transformer models, and achieve significant improvements in six visual and natural language processing tasks compared to existing state-of-the-art algorithms. The code is available at https://github.com/junkangLiu0/DP-FedPGN
FedAdamW: A Communication-Efficient Optimizer with Convergence and Generalization Guarantees for Federated Large Models
Oct 31, 2025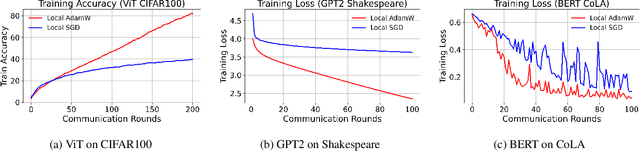
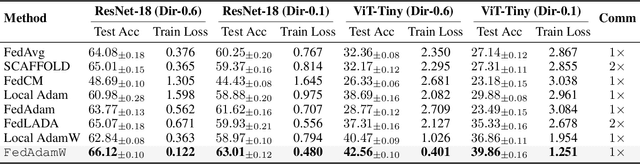
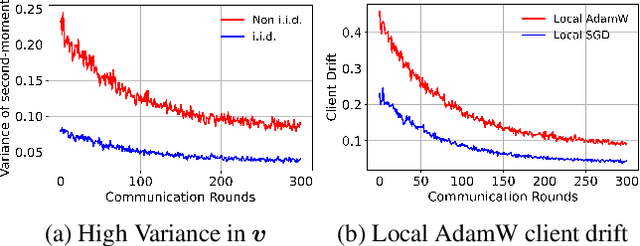
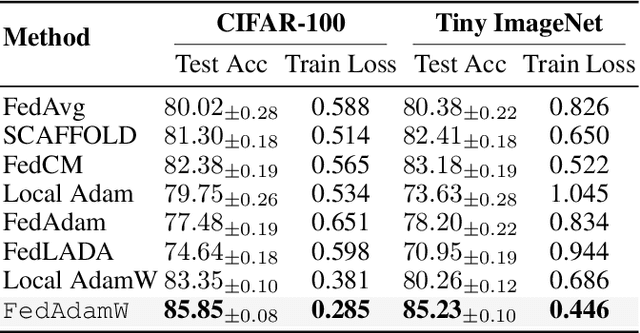
Abstract:AdamW has become one of the most effective optimizers for training large-scale models. We have also observed its effectiveness in the context of federated learning (FL). However, directly applying AdamW in federated learning settings poses significant challenges: (1) due to data heterogeneity, AdamW often yields high variance in the second-moment estimate $\boldsymbol{v}$; (2) the local overfitting of AdamW may cause client drift; and (3) Reinitializing moment estimates ($\boldsymbol{v}$, $\boldsymbol{m}$) at each round slows down convergence. To address these challenges, we propose the first \underline{Fed}erated \underline{AdamW} algorithm, called \texttt{FedAdamW}, for training and fine-tuning various large models. \texttt{FedAdamW} aligns local updates with the global update using both a \textbf{local correction mechanism} and decoupled weight decay to mitigate local overfitting. \texttt{FedAdamW} efficiently aggregates the \texttt{mean} of the second-moment estimates to reduce their variance and reinitialize them. Theoretically, we prove that \texttt{FedAdamW} achieves a linear speedup convergence rate of $\mathcal{O}(\sqrt{(L \Delta \sigma_l^2)/(S K R \epsilon^2)}+(L \Delta)/R)$ without \textbf{heterogeneity assumption}, where $S$ is the number of participating clients per round, $K$ is the number of local iterations, and $R$ is the total number of communication rounds. We also employ PAC-Bayesian generalization analysis to explain the effectiveness of decoupled weight decay in local training. Empirically, we validate the effectiveness of \texttt{FedAdamW} on language and vision Transformer models. Compared to several baselines, \texttt{FedAdamW} significantly reduces communication rounds and improves test accuracy. The code is available in https://github.com/junkangLiu0/FedAdamW.
Beyond Background Shift: Rethinking Instance Replay in Continual Semantic Segmentation
Mar 28, 2025



Abstract:In this work, we focus on continual semantic segmentation (CSS), where segmentation networks are required to continuously learn new classes without erasing knowledge of previously learned ones. Although storing images of old classes and directly incorporating them into the training of new models has proven effective in mitigating catastrophic forgetting in classification tasks, this strategy presents notable limitations in CSS. Specifically, the stored and new images with partial category annotations leads to confusion between unannotated categories and the background, complicating model fitting. To tackle this issue, this paper proposes a novel Enhanced Instance Replay (EIR) method, which not only preserves knowledge of old classes while simultaneously eliminating background confusion by instance storage of old classes, but also mitigates background shifts in the new images by integrating stored instances with new images. By effectively resolving background shifts in both stored and new images, EIR alleviates catastrophic forgetting in the CSS task, thereby enhancing the model's capacity for CSS. Experimental results validate the efficacy of our approach, which significantly outperforms state-of-the-art CSS methods.
Casual Inference via Style Bias Deconfounding for Domain Generalization
Mar 21, 2025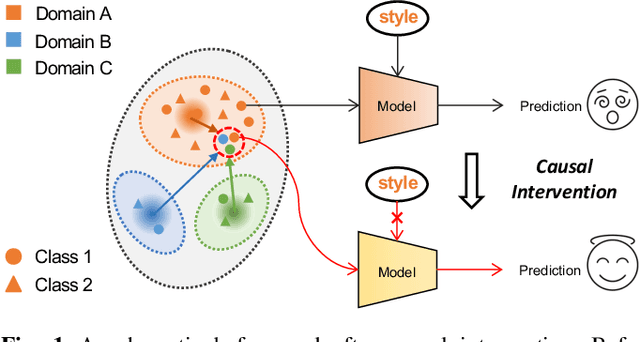
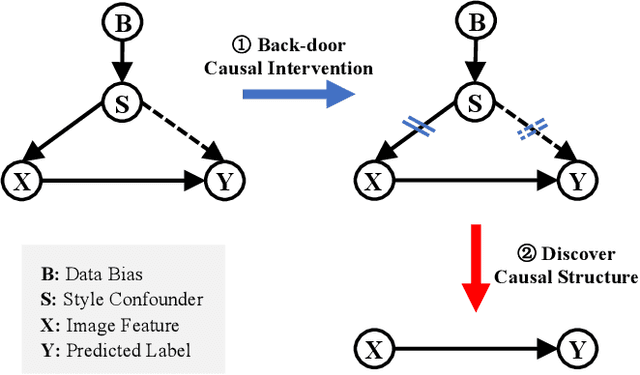
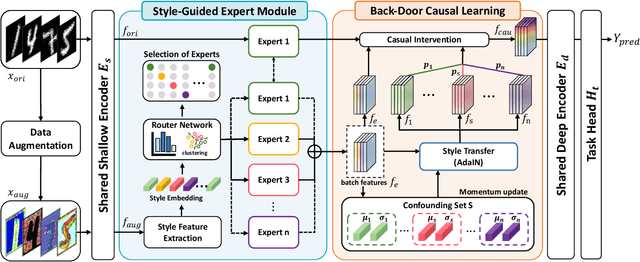
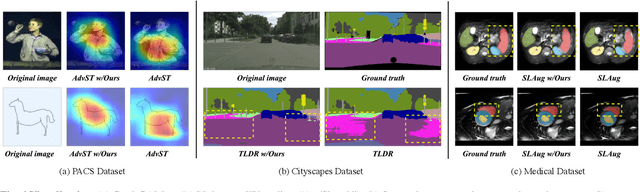
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) often struggle with out-of-distribution data, limiting their reliability in diverse realworld applications. To address this issue, domain generalization methods have been developed to learn domain-invariant features from single or multiple training domains, enabling generalization to unseen testing domains. However, existing approaches usually overlook the impact of style frequency within the training set. This oversight predisposes models to capture spurious visual correlations caused by style confounding factors, rather than learning truly causal representations, thereby undermining inference reliability. In this work, we introduce Style Deconfounding Causal Learning (SDCL), a novel causal inference-based framework designed to explicitly address style as a confounding factor. Our approaches begins with constructing a structural causal model (SCM) tailored to the domain generalization problem and applies a backdoor adjustment strategy to account for style influence. Building on this foundation, we design a style-guided expert module (SGEM) to adaptively clusters style distributions during training, capturing the global confounding style. Additionally, a back-door causal learning module (BDCL) performs causal interventions during feature extraction, ensuring fair integration of global confounding styles into sample predictions, effectively reducing style bias. The SDCL framework is highly versatile and can be seamlessly integrated with state-of-the-art data augmentation techniques. Extensive experiments across diverse natural and medical image recognition tasks validate its efficacy, demonstrating superior performance in both multi-domain and the more challenging single-domain generalization scenarios.
Towards Convexity in Anomaly Detection: A New Formulation of SSLM with Unique Optimal Solutions
Oct 31, 2024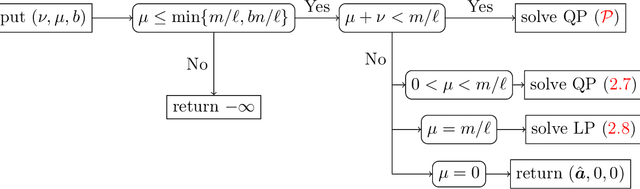
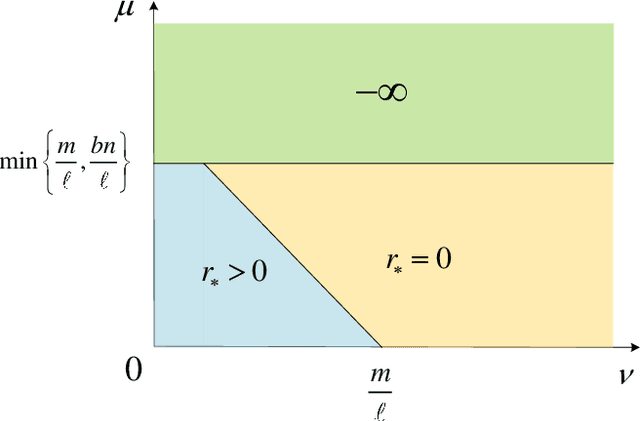
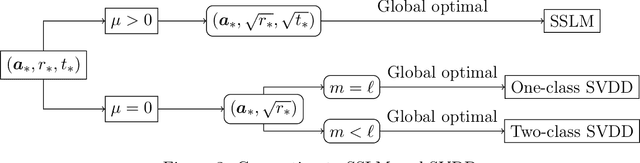
Abstract:An unsolved issue in widely used methods such as Support Vector Data Description (SVDD) and Small Sphere and Large Margin SVM (SSLM) for anomaly detection is their nonconvexity, which hampers the analysis of optimal solutions in a manner similar to SVMs and limits their applicability in large-scale scenarios. In this paper, we introduce a novel convex SSLM formulation which has been demonstrated to revert to a convex quadratic programming problem for hyperparameter values of interest. Leveraging the convexity of our method, we derive numerous results that are unattainable with traditional nonconvex approaches. We conduct a thorough analysis of how hyperparameters influence the optimal solution, pointing out scenarios where optimal solutions can be trivially found and identifying instances of ill-posedness. Most notably, we establish connections between our method and traditional approaches, providing a clear determination of when the optimal solution is unique -- a task unachievable with traditional nonconvex methods. We also derive the {\nu}-property to elucidate the interactions between hyperparameters and the fractions of support vectors and margin errors in both positive and negative classes.
Completed Feature Disentanglement Learning for Multimodal MRIs Analysis
Jul 06, 2024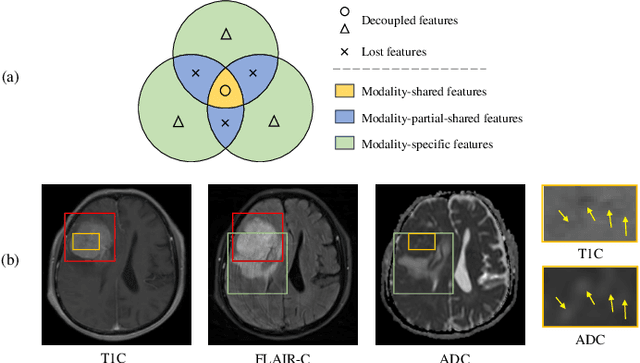
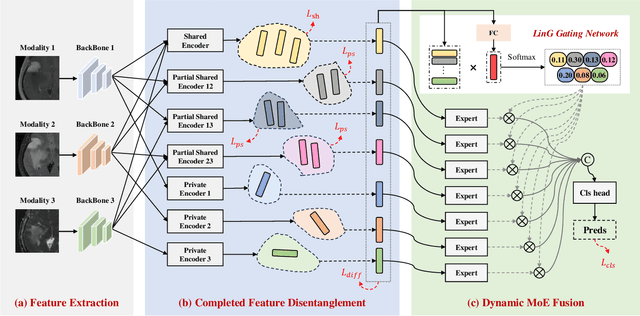
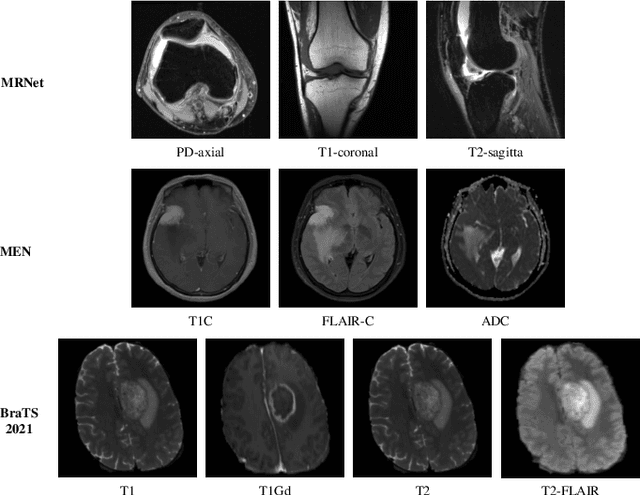
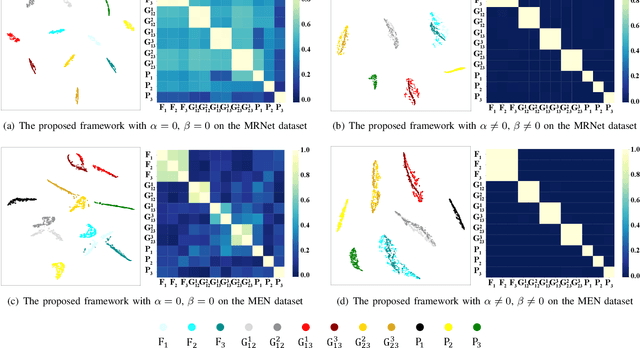
Abstract:Multimodal MRIs play a crucial role in clinical diagnosis and treatment. Feature disentanglement (FD)-based methods, aiming at learning superior feature representations for multimodal data analysis, have achieved significant success in multimodal learning (MML). Typically, existing FD-based methods separate multimodal data into modality-shared and modality-specific features, and employ concatenation or attention mechanisms to integrate these features. However, our preliminary experiments indicate that these methods could lead to a loss of shared information among subsets of modalities when the inputs contain more than two modalities, and such information is critical for prediction accuracy. Furthermore, these methods do not adequately interpret the relationships between the decoupled features at the fusion stage. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Complete Feature Disentanglement (CFD) strategy that recovers the lost information during feature decoupling. Specifically, the CFD strategy not only identifies modality-shared and modality-specific features, but also decouples shared features among subsets of multimodal inputs, termed as modality-partial-shared features. We further introduce a new Dynamic Mixture-of-Experts Fusion (DMF) module that dynamically integrates these decoupled features, by explicitly learning the local-global relationships among the features. The effectiveness of our approach is validated through classification tasks on three multimodal MRI datasets. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms other state-of-the-art MML methods with obvious margins, showcasing its superior performance.
Improving the Transferability of Adversarial Examples with Arbitrary Style Transfer
Aug 21, 2023
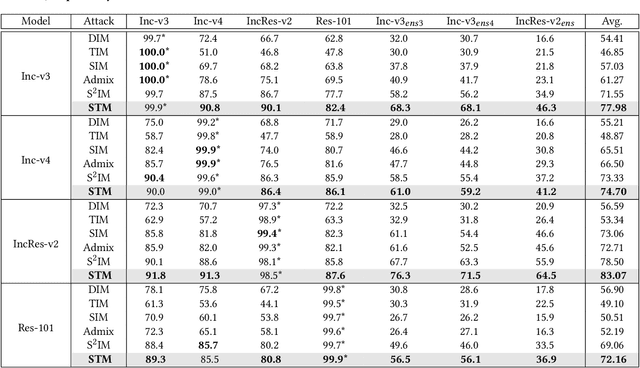
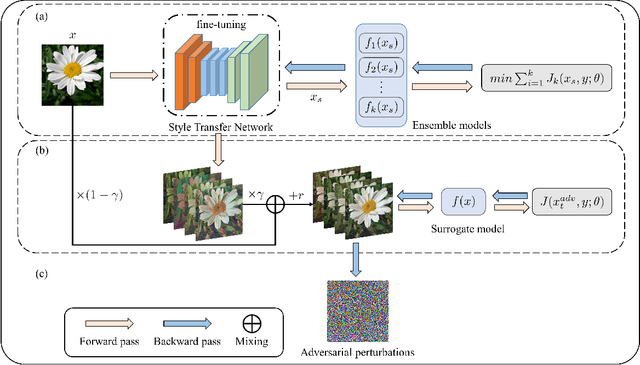

Abstract:Deep neural networks are vulnerable to adversarial examples crafted by applying human-imperceptible perturbations on clean inputs. Although many attack methods can achieve high success rates in the white-box setting, they also exhibit weak transferability in the black-box setting. Recently, various methods have been proposed to improve adversarial transferability, in which the input transformation is one of the most effective methods. In this work, we notice that existing input transformation-based works mainly adopt the transformed data in the same domain for augmentation. Inspired by domain generalization, we aim to further improve the transferability using the data augmented from different domains. Specifically, a style transfer network can alter the distribution of low-level visual features in an image while preserving semantic content for humans. Hence, we propose a novel attack method named Style Transfer Method (STM) that utilizes a proposed arbitrary style transfer network to transform the images into different domains. To avoid inconsistent semantic information of stylized images for the classification network, we fine-tune the style transfer network and mix up the generated images added by random noise with the original images to maintain semantic consistency and boost input diversity. Extensive experimental results on the ImageNet-compatible dataset show that our proposed method can significantly improve the adversarial transferability on either normally trained models or adversarially trained models than state-of-the-art input transformation-based attacks. Code is available at: https://github.com/Zhijin-Ge/STM.
Boosting Adversarial Transferability by Achieving Flat Local Maxima
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:Transfer-based attack adopts the adversarial examples generated on the surrogate model to attack various models, making it applicable in the physical world and attracting increasing interest. Recently, various adversarial attacks have emerged to boost adversarial transferability from different perspectives. In this work, inspired by the fact that flat local minima are correlated with good generalization, we assume and empirically validate that adversarial examples at a flat local region tend to have good transferability by introducing a penalized gradient norm to the original loss function. Since directly optimizing the gradient regularization norm is computationally expensive and intractable for generating adversarial examples, we propose an approximation optimization method to simplify the gradient update of the objective function. Specifically, we randomly sample an example and adopt the first-order gradient to approximate the second-order Hessian matrix, which makes computing more efficient by interpolating two Jacobian matrices. Meanwhile, in order to obtain a more stable gradient direction, we randomly sample multiple examples and average the gradients of these examples to reduce the variance due to random sampling during the iterative process. Extensive experimental results on the ImageNet-compatible dataset show that the proposed method can generate adversarial examples at flat local regions, and significantly improve the adversarial transferability on either normally trained models or adversarially trained models than the state-of-the-art attacks.
Constrained Optimization Involving Nonconvex $\ell_p$ Norms: Optimality Conditions, Algorithm and Convergence
Oct 27, 2021
Abstract:This paper investigates the optimality conditions for characterizing the local minimizers of the constrained optimization problems involving an $\ell_p$ norm ($0<p<1$) of the variables, which may appear in either the objective or the constraint. This kind of problems have strong applicability to a wide range of areas since usually the $\ell_p$ norm can promote sparse solutions. However, the nonsmooth and non-Lipschtiz nature of the $\ell_p$ norm often cause these problems difficult to analyze and solve. We provide the calculation of the subgradients of the $\ell_p$ norm and the normal cones of the $\ell_p$ ball. For both problems, we derive the first-order necessary conditions under various constraint qualifications. We also derive the sequential optimality conditions for both problems and study the conditions under which these conditions imply the first-order necessary conditions. We point out that the sequential optimality conditions can be easily satisfied for iteratively reweighted algorithms and show that the global convergence can be easily derived using sequential optimality conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge