Hoan Nguyen
RoboDesign1M: A Large-scale Dataset for Robot Design Understanding
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Robot design is a complex and time-consuming process that requires specialized expertise. Gaining a deeper understanding of robot design data can enable various applications, including automated design generation, retrieving example designs from text, and developing AI-powered design assistants. While recent advancements in foundation models present promising approaches to addressing these challenges, progress in this field is hindered by the lack of large-scale design datasets. In this paper, we introduce RoboDesign1M, a large-scale dataset comprising 1 million samples. Our dataset features multimodal data collected from scientific literature, covering various robotics domains. We propose a semi-automated data collection pipeline, enabling efficient and diverse data acquisition. To assess the effectiveness of RoboDesign1M, we conduct extensive experiments across multiple tasks, including design image generation, visual question answering about designs, and design image retrieval. The results demonstrate that our dataset serves as a challenging new benchmark for design understanding tasks and has the potential to advance research in this field. RoboDesign1M will be released to support further developments in AI-driven robotic design automation.
Large Language Model Critics for Execution-Free Evaluation of Code Changes
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) offer a promising way forward for automating software engineering tasks, such as bug fixes, feature additions, etc., via multi-step LLM-based agentic workflows. However, existing metrics for evaluating such workflows, mainly build status and occasionally log analysis, are too sparse and limited in providing the information needed to assess the quality of changes made. In this work, we designed LLM-based critics to derive well-structured and rigorous intermediate/step-level, execution-free evaluation proxies for repo-level code changes. Importantly, we assume access to the gold test patch for the problem (i.e., reference-aware) to assess both semantics and executability of generated patches. With the gold test patch as a reference, we predict executability of all editing locations with an F1 score of 91.6%, aggregating which, we can predict the build status in 84.8% of the instances in SWE-bench. In particular, such an execution-focused LLM critic outperforms other reference-free and reference-aware LLM critics by 38.9% to 72.5%. Moreover, we demonstrate the usefulness of such a reference-aware framework in comparing patches generated by different agentic workflows. Finally, we open-source the library developed for this project, which allows further usage for either other agentic workflows or other benchmarks. The source code is available at https://github.com/amazon-science/code-agent-eval.
SplineFormer: An Explainable Transformer-Based Approach for Autonomous Endovascular Navigation
Jan 08, 2025Abstract:Endovascular navigation is a crucial aspect of minimally invasive procedures, where precise control of curvilinear instruments like guidewires is critical for successful interventions. A key challenge in this task is accurately predicting the evolving shape of the guidewire as it navigates through the vasculature, which presents complex deformations due to interactions with the vessel walls. Traditional segmentation methods often fail to provide accurate real-time shape predictions, limiting their effectiveness in highly dynamic environments. To address this, we propose SplineFormer, a new transformer-based architecture, designed specifically to predict the continuous, smooth shape of the guidewire in an explainable way. By leveraging the transformer's ability, our network effectively captures the intricate bending and twisting of the guidewire, representing it as a spline for greater accuracy and smoothness. We integrate our SplineFormer into an end-to-end robot navigation system by leveraging the condensed information. The experimental results demonstrate that our SplineFormer is able to perform endovascular navigation autonomously and achieves a 50% success rate when cannulating the brachiocephalic artery on the real robot.
Guide3D: A Bi-planar X-ray Dataset for 3D Shape Reconstruction
Oct 29, 2024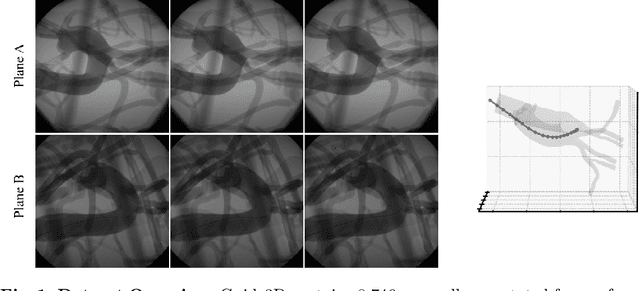
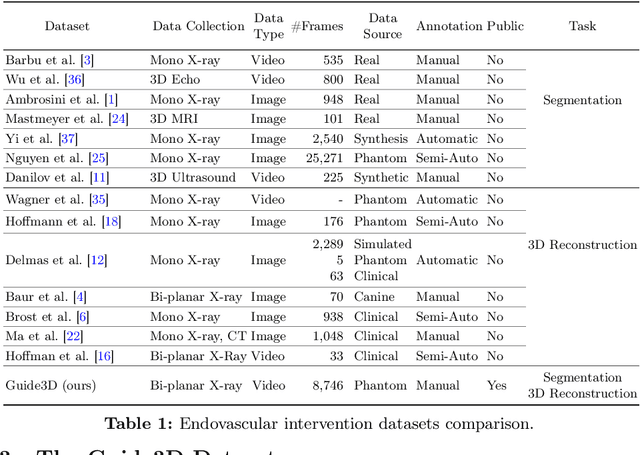
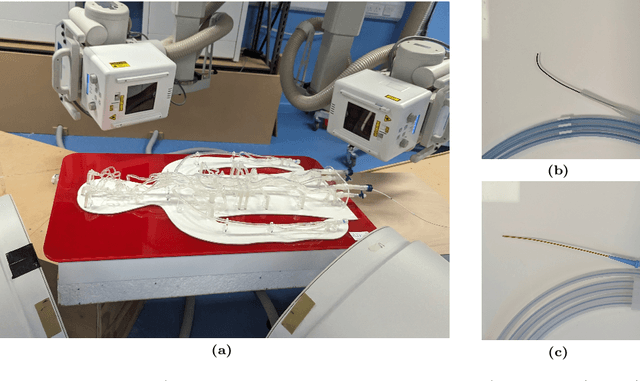
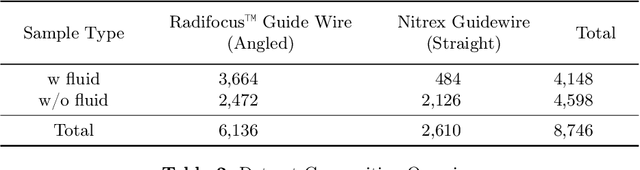
Abstract:Endovascular surgical tool reconstruction represents an important factor in advancing endovascular tool navigation, which is an important step in endovascular surgery. However, the lack of publicly available datasets significantly restricts the development and validation of novel machine learning approaches. Moreover, due to the need for specialized equipment such as biplanar scanners, most of the previous research employs monoplanar fluoroscopic technologies, hence only capturing the data from a single view and significantly limiting the reconstruction accuracy. To bridge this gap, we introduce Guide3D, a bi-planar X-ray dataset for 3D reconstruction. The dataset represents a collection of high resolution bi-planar, manually annotated fluoroscopic videos, captured in real-world settings. Validating our dataset within a simulated environment reflective of clinical settings confirms its applicability for real-world applications. Furthermore, we propose a new benchmark for guidewrite shape prediction, serving as a strong baseline for future work. Guide3D not only addresses an essential need by offering a platform for advancing segmentation and 3D reconstruction techniques but also aids the development of more accurate and efficient endovascular surgery interventions. Our project is available at https://airvlab.github.io/guide3d/.
CathAction: A Benchmark for Endovascular Intervention Understanding
Aug 23, 2024Abstract:Real-time visual feedback from catheterization analysis is crucial for enhancing surgical safety and efficiency during endovascular interventions. However, existing datasets are often limited to specific tasks, small scale, and lack the comprehensive annotations necessary for broader endovascular intervention understanding. To tackle these limitations, we introduce CathAction, a large-scale dataset for catheterization understanding. Our CathAction dataset encompasses approximately 500,000 annotated frames for catheterization action understanding and collision detection, and 25,000 ground truth masks for catheter and guidewire segmentation. For each task, we benchmark recent related works in the field. We further discuss the challenges of endovascular intentions compared to traditional computer vision tasks and point out open research questions. We hope that CathAction will facilitate the development of endovascular intervention understanding methods that can be applied to real-world applications. The dataset is available at https://airvlab.github.io/cathdata/.
Autonomous Catheterization with Open-source Simulator and Expert Trajectory
Jan 20, 2024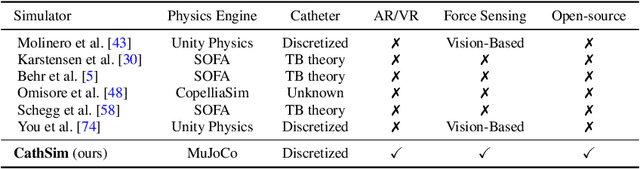
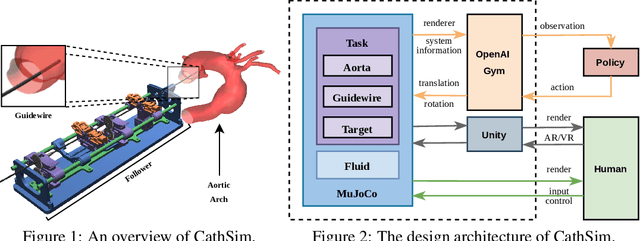
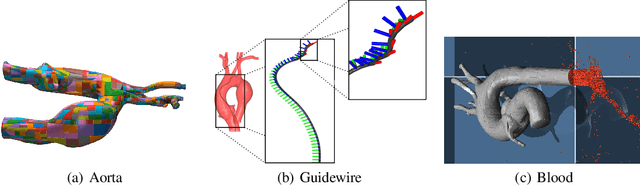
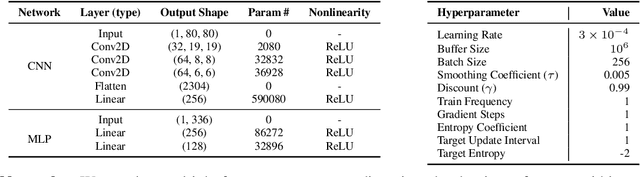
Abstract:Endovascular robots have been actively developed in both academia and industry. However, progress toward autonomous catheterization is often hampered by the widespread use of closed-source simulators and physical phantoms. Additionally, the acquisition of large-scale datasets for training machine learning algorithms with endovascular robots is usually infeasible due to expensive medical procedures. In this chapter, we introduce CathSim, the first open-source simulator for endovascular intervention to address these limitations. CathSim emphasizes real-time performance to enable rapid development and testing of learning algorithms. We validate CathSim against the real robot and show that our simulator can successfully mimic the behavior of the real robot. Based on CathSim, we develop a multimodal expert navigation network and demonstrate its effectiveness in downstream endovascular navigation tasks. The intensive experimental results suggest that CathSim has the potential to significantly accelerate research in the autonomous catheterization field. Our project is publicly available at https://github.com/airvlab/cathsim.
Shape-Sensitive Loss for Catheter and Guidewire Segmentation
Nov 19, 2023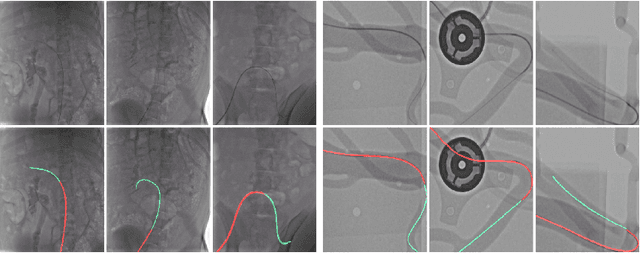
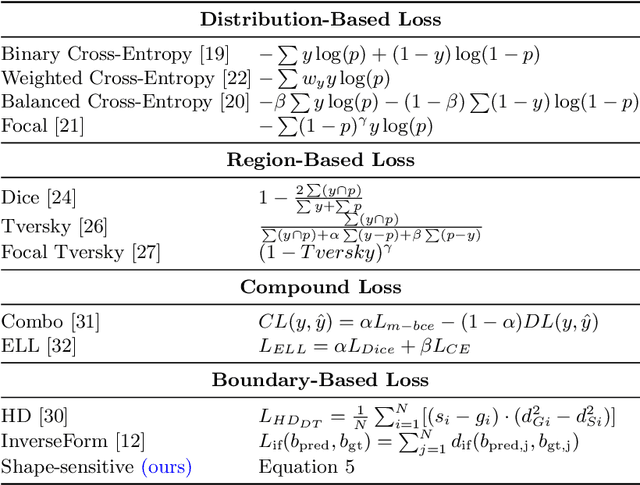
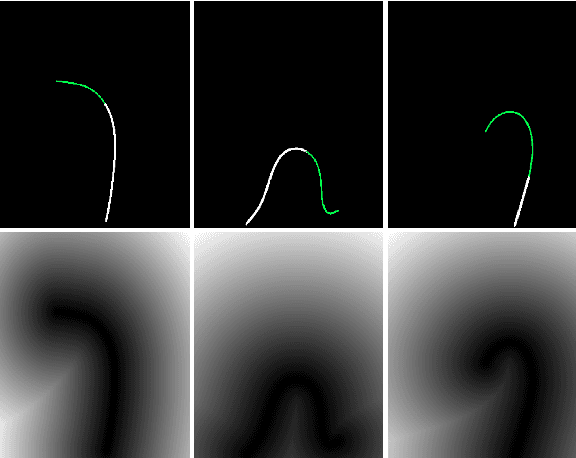
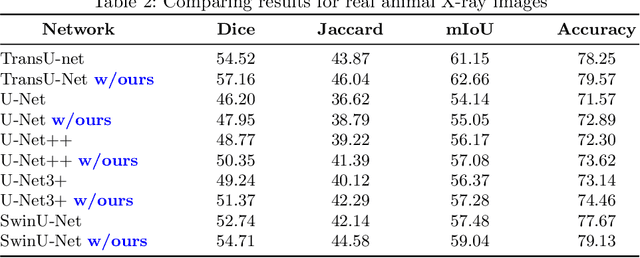
Abstract:We introduce a shape-sensitive loss function for catheter and guidewire segmentation and utilize it in a vision transformer network to establish a new state-of-the-art result on a large-scale X-ray images dataset. We transform network-derived predictions and their corresponding ground truths into signed distance maps, thereby enabling any networks to concentrate on the essential boundaries rather than merely the overall contours. These SDMs are subjected to the vision transformer, efficiently producing high-dimensional feature vectors encapsulating critical image attributes. By computing the cosine similarity between these feature vectors, we gain a nuanced understanding of image similarity that goes beyond the limitations of traditional overlap-based measures. The advantages of our approach are manifold, ranging from scale and translation invariance to superior detection of subtle differences, thus ensuring precise localization and delineation of the medical instruments within the images. Comprehensive quantitative and qualitative analyses substantiate the significant enhancement in performance over existing baselines, demonstrating the promise held by our new shape-sensitive loss function for improving catheter and guidewire segmentation.
Universal Representation for Code
Mar 04, 2021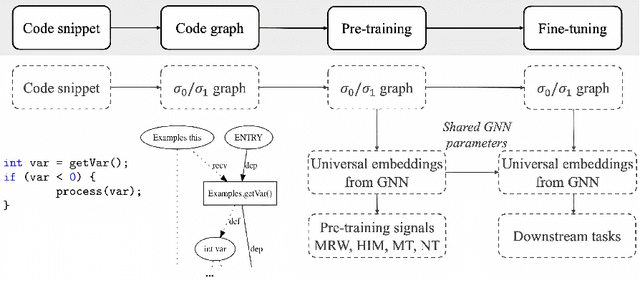
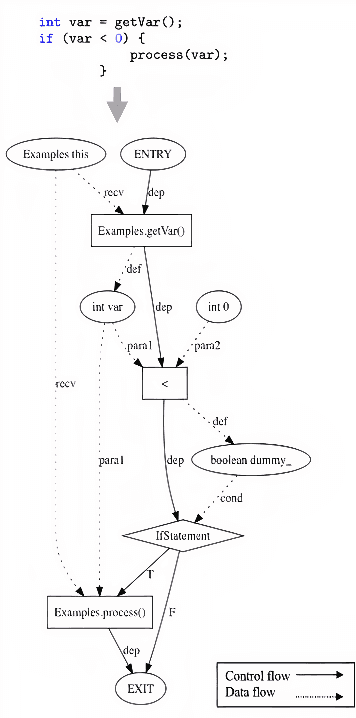

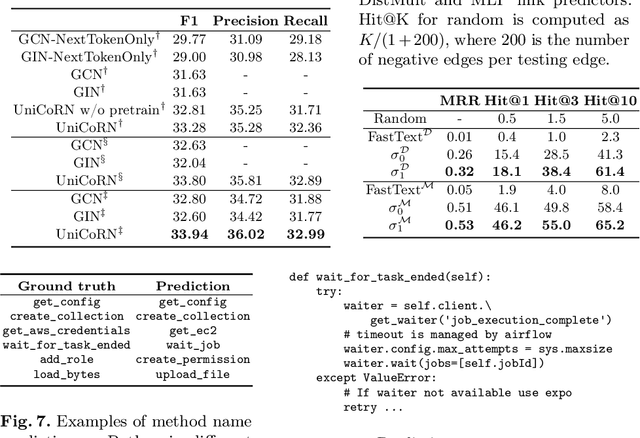
Abstract:Learning from source code usually requires a large amount of labeled data. Despite the possible scarcity of labeled data, the trained model is highly task-specific and lacks transferability to different tasks. In this work, we present effective pre-training strategies on top of a novel graph-based code representation, to produce universal representations for code. Specifically, our graph-based representation captures important semantics between code elements (e.g., control flow and data flow). We pre-train graph neural networks on the representation to extract universal code properties. The pre-trained model then enables the possibility of fine-tuning to support various downstream applications. We evaluate our model on two real-world datasets -- spanning over 30M Java methods and 770K Python methods. Through visualization, we reveal discriminative properties in our universal code representation. By comparing multiple benchmarks, we demonstrate that the proposed framework achieves state-of-the-art results on method name prediction and code graph link prediction.
Does BLEU Score Work for Code Migration?
Jun 12, 2019

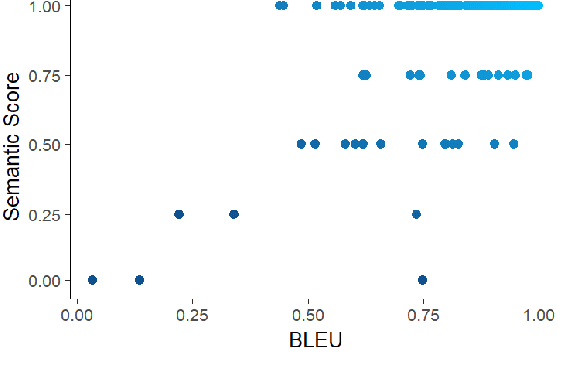

Abstract:Statistical machine translation (SMT) is a fast-growing sub-field of computational linguistics. Until now, the most popular automatic metric to measure the quality of SMT is BiLingual Evaluation Understudy (BLEU) score. Lately, SMT along with the BLEU metric has been applied to a Software Engineering task named code migration. (In)Validating the use of BLEU score could advance the research and development of SMT-based code migration tools. Unfortunately, there is no study to approve or disapprove the use of BLEU score for source code. In this paper, we conducted an empirical study on BLEU score to (in)validate its suitability for the code migration task due to its inability to reflect the semantics of source code. In our work, we use human judgment as the ground truth to measure the semantic correctness of the migrated code. Our empirical study demonstrates that BLEU does not reflect translation quality due to its weak correlation with the semantic correctness of translated code. We provided counter-examples to show that BLEU is ineffective in comparing the translation quality between SMT-based models. Due to BLEU's ineffectiveness for code migration task, we propose an alternative metric RUBY, which considers lexical, syntactical, and semantic representations of source code. We verified that RUBY achieves a higher correlation coefficient with the semantic correctness of migrated code, 0.775 in comparison with 0.583 of BLEU score. We also confirmed the effectiveness of RUBY in reflecting the changes in translation quality of SMT-based translation models. With its advantages, RUBY can be used to evaluate SMT-based code migration models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge