Haoyang Wang
Oklahoma State University
Count Every Rotation and Every Rotation Counts: Exploring Drone Dynamics via Propeller Sensing
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:As drone-based applications proliferate, paramount contactless sensing of airborne drones from the ground becomes indispensable. This work demonstrates concentrating on propeller rotational speed will substantially improve drone sensing performance and proposes an event-camera-based solution, \sysname. \sysname features two components: \textit{Count Every Rotation} achieves accurate, real-time propeller speed estimation by mitigating ultra-high sensitivity of event cameras to environmental noise. \textit{Every Rotation Counts} leverages these speeds to infer both internal and external drone dynamics. Extensive evaluations in real-world drone delivery scenarios show that \sysname achieves a sensing latency of 3$ms$ and a rotational speed estimation error of merely 0.23\%. Additionally, \sysname infers drone flight commands with 96.5\% precision and improves drone tracking accuracy by over 22\% when combined with other sensing modalities. \textit{ Demo: {\color{blue}https://eventpro25.github.io/EventPro/.} }
Enabling High-Frequency Cross-Modality Visual Positioning Service for Accurate Drone Landing
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:After years of growth, drone-based delivery is transforming logistics. At its core, real-time 6-DoF drone pose tracking enables precise flight control and accurate drone landing. With the widespread availability of urban 3D maps, the Visual Positioning Service (VPS), a mobile pose estimation system, has been adapted to enhance drone pose tracking during the landing phase, as conventional systems like GPS are unreliable in urban environments due to signal attenuation and multi-path propagation. However, deploying the current VPS on drones faces limitations in both estimation accuracy and efficiency. In this work, we redesign drone-oriented VPS with the event camera and introduce EV-Pose to enable accurate, high-frequency 6-DoF pose tracking for accurate drone landing. EV-Pose introduces a spatio-temporal feature-instructed pose estimation module that extracts a temporal distance field to enable 3D point map matching for pose estimation; and a motion-aware hierarchical fusion and optimization scheme to enhance the above estimation in accuracy and efficiency, by utilizing drone motion in the \textit{early stage} of event filtering and the \textit{later stage} of pose optimization. Evaluation shows that EV-Pose achieves a rotation accuracy of 1.34$\degree$ and a translation accuracy of 6.9$mm$ with a tracking latency of 10.08$ms$, outperforming baselines by $>$50\%, \tmcrevise{thus enabling accurate drone landings.} Demo: https://ev-pose.github.io/
R-Meshfusion: Reinforcement Learning Powered Sparse-View Mesh Reconstruction with Diffusion Priors
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Mesh reconstruction from multi-view images is a fundamental problem in computer vision, but its performance degrades significantly under sparse-view conditions, especially in unseen regions where no ground-truth observations are available. While recent advances in diffusion models have demonstrated strong capabilities in synthesizing novel views from limited inputs, their outputs often suffer from visual artifacts and lack 3D consistency, posing challenges for reliable mesh optimization. In this paper, we propose a novel framework that leverages diffusion models to enhance sparse-view mesh reconstruction in a principled and reliable manner. To address the instability of diffusion outputs, we propose a Consensus Diffusion Module that filters unreliable generations via interquartile range (IQR) analysis and performs variance-aware image fusion to produce robust pseudo-supervision. Building on this, we design an online reinforcement learning strategy based on the Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) to adaptively select the most informative viewpoints for enhancement, guided by diffusion loss. Finally, the fused images are used to jointly supervise a NeRF-based model alongside sparse-view ground truth, ensuring consistency across both geometry and appearance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves significant improvements in both geometric quality and rendering quality.
GaussVideoDreamer: 3D Scene Generation with Video Diffusion and Inconsistency-Aware Gaussian Splatting
Apr 16, 2025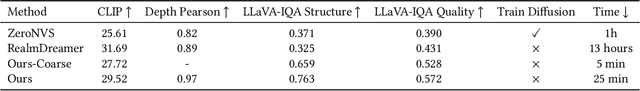
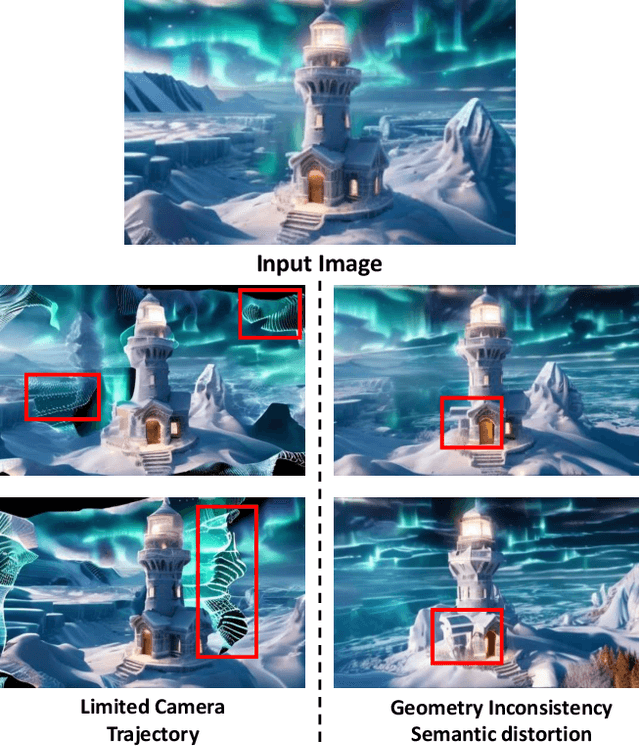
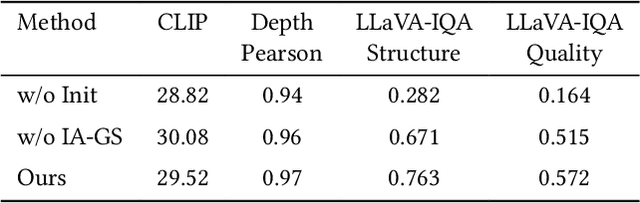
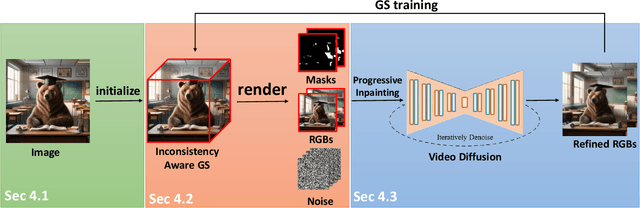
Abstract:Single-image 3D scene reconstruction presents significant challenges due to its inherently ill-posed nature and limited input constraints. Recent advances have explored two promising directions: multiview generative models that train on 3D consistent datasets but struggle with out-of-distribution generalization, and 3D scene inpainting and completion frameworks that suffer from cross-view inconsistency and suboptimal error handling, as they depend exclusively on depth data or 3D smoothness, which ultimately degrades output quality and computational performance. Building upon these approaches, we present GaussVideoDreamer, which advances generative multimedia approaches by bridging the gap between image, video, and 3D generation, integrating their strengths through two key innovations: (1) A progressive video inpainting strategy that harnesses temporal coherence for improved multiview consistency and faster convergence. (2) A 3D Gaussian Splatting consistency mask to guide the video diffusion with 3D consistent multiview evidence. Our pipeline combines three core components: a geometry-aware initialization protocol, Inconsistency-Aware Gaussian Splatting, and a progressive video inpainting strategy. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves 32% higher LLaVA-IQA scores and at least 2x speedup compared to existing methods while maintaining robust performance across diverse scenes.
Towards Mobile Sensing with Event Cameras on High-mobility Resource-constrained Devices: A Survey
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:With the increasing complexity of mobile device applications, these devices are evolving toward high mobility. This shift imposes new demands on mobile sensing, particularly in terms of achieving high accuracy and low latency. Event-based vision has emerged as a disruptive paradigm, offering high temporal resolution, low latency, and energy efficiency, making it well-suited for high-accuracy and low-latency sensing tasks on high-mobility platforms. However, the presence of substantial noisy events, the lack of inherent semantic information, and the large data volume pose significant challenges for event-based data processing on resource-constrained mobile devices. This paper surveys the literature over the period 2014-2024, provides a comprehensive overview of event-based mobile sensing systems, covering fundamental principles, event abstraction methods, algorithmic advancements, hardware and software acceleration strategies. We also discuss key applications of event cameras in mobile sensing, including visual odometry, object tracking, optical flow estimation, and 3D reconstruction, while highlighting the challenges associated with event data processing, sensor fusion, and real-time deployment. Furthermore, we outline future research directions, such as improving event camera hardware with advanced optics, leveraging neuromorphic computing for efficient processing, and integrating bio-inspired algorithms to enhance perception. To support ongoing research, we provide an open-source \textit{Online Sheet} with curated resources and recent developments. We hope this survey serves as a valuable reference, facilitating the adoption of event-based vision across diverse applications.
PromptMobile: Efficient Promptus for Low Bandwidth Mobile Video Streaming
Mar 20, 2025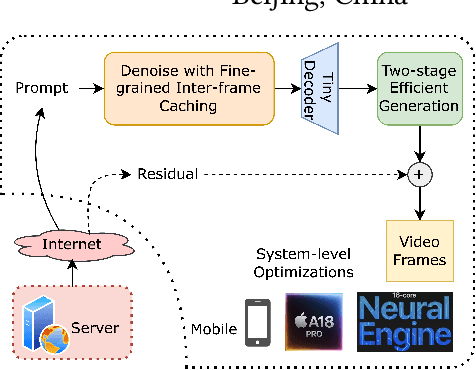
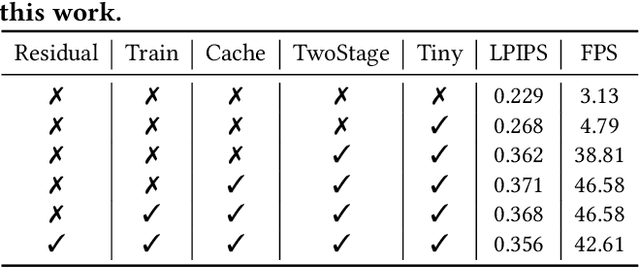
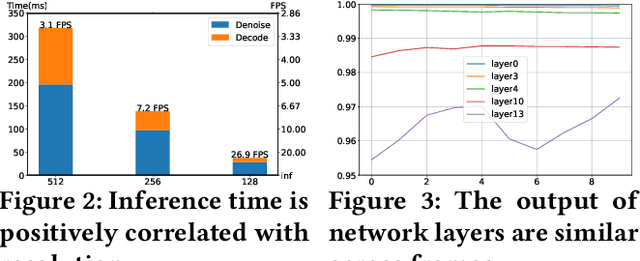

Abstract:Traditional video compression algorithms exhibit significant quality degradation at extremely low bitrates. Promptus emerges as a new paradigm for video streaming, substantially cutting down the bandwidth essential for video streaming. However, Promptus is computationally intensive and can not run in real-time on mobile devices. This paper presents PromptMobile, an efficient acceleration framework tailored for on-device Promptus. Specifically, we propose (1) a two-stage efficient generation framework to reduce computational cost by 8.1x, (2) a fine-grained inter-frame caching to reduce redundant computations by 16.6\%, (3) system-level optimizations to further enhance efficiency. The evaluations demonstrate that compared with the original Promptus, PromptMobile achieves a 13.6x increase in image generation speed. Compared with other streaming methods, PromptMobile achives an average LPIPS improvement of 0.016 (compared with H.265), reducing 60\% of severely distorted frames (compared to VQGAN).
Bio-Skin: A Cost-Effective Thermostatic Tactile Sensor with Multi-Modal Force and Temperature Detection
Mar 11, 2025
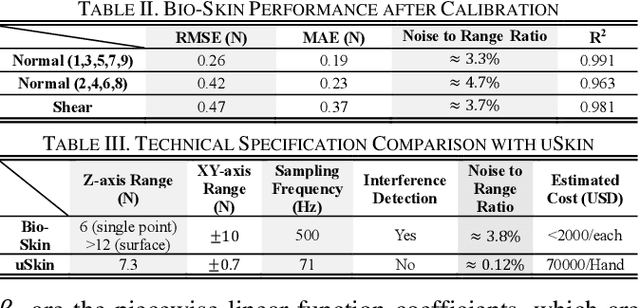

Abstract:Tactile sensors can significantly enhance the perception of humanoid robotics systems by providing contact information that facilitates human-like interactions. However, existing commercial tactile sensors focus on improving the resolution and sensitivity of single-modal detection with high-cost components and densely integrated design, incurring complex manufacturing processes and unaffordable prices. In this work, we present Bio-Skin, a cost-effective multi-modal tactile sensor that utilizes single-axis Hall-effect sensors for planar normal force measurement and bar-shape piezo resistors for 2D shear force measurement. A thermistor coupling with a heating wire is integrated into a silicone body to achieve temperature sensation and thermostatic function analogous to human skin. We also present a cross-reference framework to validate the two modalities of the force sensing signal, improving the sensing fidelity in a complex electromagnetic environment. Bio-Skin has a multi-layer design, and each layer is manufactured sequentially and subsequently integrated, thereby offering a fast production pathway. After calibration, Bio-Skin demonstrates performance metrics-including signal-to-range ratio, sampling rate, and measurement range-comparable to current commercial products, with one-tenth of the cost. The sensor's real-world performance is evaluated using an Allegro hand in object grasping tasks, while its temperature regulation functionality was assessed in a material detection task.
Adaptive Anomaly Recovery for Telemanipulation: A Diffusion Model Approach to Vision-Based Tracking
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Dexterous telemanipulation critically relies on the continuous and stable tracking of the human operator's commands to ensure robust operation. Vison-based tracking methods are widely used but have low stability due to anomalies such as occlusions, inadequate lighting, and loss of sight. Traditional filtering, regression, and interpolation methods are commonly used to compensate for explicit information such as angles and positions. These approaches are restricted to low-dimensional data and often result in information loss compared to the original high-dimensional image and video data. Recent advances in diffusion-based approaches, which can operate on high-dimensional data, have achieved remarkable success in video reconstruction and generation. However, these methods have not been fully explored in continuous control tasks in robotics. This work introduces the Diffusion-Enhanced Telemanipulation (DET) framework, which incorporates the Frame-Difference Detection (FDD) technique to identify and segment anomalies in video streams. These anomalous clips are replaced after reconstruction using diffusion models, ensuring robust telemanipulation performance under challenging visual conditions. We validated this approach in various anomaly scenarios and compared it with the baseline methods. Experiments show that DET achieves an average RMSE reduction of 17.2% compared to the cubic spline and 51.1% compared to FFT-based interpolation for different occlusion durations.
Ultra-High-Frequency Harmony: mmWave Radar and Event Camera Orchestrate Accurate Drone Landing
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:For precise, efficient, and safe drone landings, ground platforms should real-time, accurately locate descending drones and guide them to designated spots. While mmWave sensing combined with cameras improves localization accuracy, the lower sampling frequency of traditional frame cameras compared to mmWave radar creates bottlenecks in system throughput. In this work, we replace the traditional frame camera with event camera, a novel sensor that harmonizes in sampling frequency with mmWave radar within the ground platform setup, and introduce mmE-Loc, a high-precision, low-latency ground localization system designed for drone landings. To fully leverage the \textit{temporal consistency} and \textit{spatial complementarity} between these modalities, we propose two innovative modules, \textit{consistency-instructed collaborative tracking} and \textit{graph-informed adaptive joint optimization}, for accurate drone measurement extraction and efficient sensor fusion. Extensive real-world experiments in landing scenarios from a leading drone delivery company demonstrate that mmE-Loc outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both localization accuracy and latency.
Real-time volumetric free-hand ultrasound imaging for large-sized organs: A study of imaging the whole spine
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound imaging can overcome the limitations of conventional two dimensional (2D) ultrasound imaging in structural observation and measurement. However, conducting volumetric ultrasound imaging for large-sized organs still faces difficulties including long acquisition time, inevitable patient movement, and 3D feature recognition. In this study, we proposed a real-time volumetric free-hand ultrasound imaging system optimized for the above issues and applied it to the clinical diagnosis of scoliosis. This study employed an incremental imaging method coupled with algorithmic acceleration to enable real-time processing and visualization of the large amounts of data generated when scanning large-sized organs. Furthermore, to deal with the difficulty of image feature recognition, we proposed two tissue segmentation algorithms to reconstruct and visualize the spinal anatomy in 3D space by approximating the depth at which the bone structures are located and segmenting the ultrasound images at different depths. We validated the adaptability of our system by deploying it to multiple models of ultra-sound equipment and conducting experiments using different types of ultrasound probes. We also conducted experiments on 6 scoliosis patients and 10 normal volunteers to evaluate the performance of our proposed method. Ultrasound imaging of a volunteer spine from shoulder to crotch (more than 500 mm) was performed in 2 minutes, and the 3D imaging results displayed in real-time were compared with the corresponding X-ray images with a correlation coefficient of 0.96 in spinal curvature. Our proposed volumetric ultrasound imaging system might hold the potential to be clinically applied to other large-sized organs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge