Hanan Aldarmaki
Code-Switching in End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition: A Systematic Literature Review
Jul 10, 2025
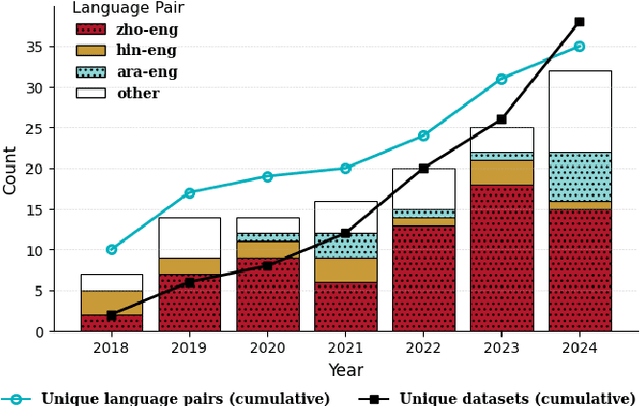
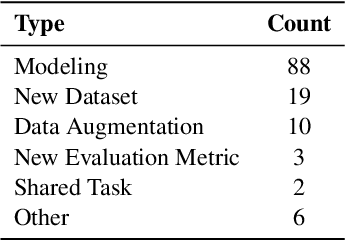
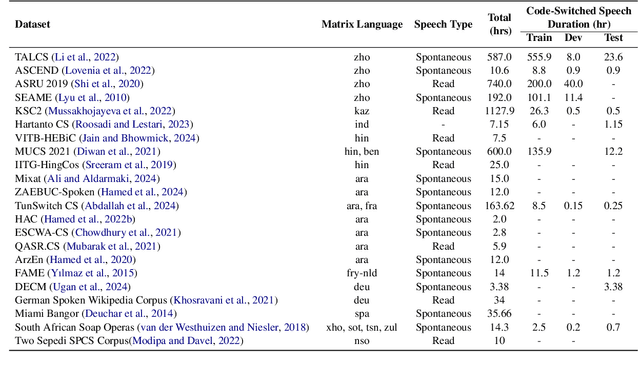
Abstract:Motivated by a growing research interest into automatic speech recognition (ASR), and the growing body of work for languages in which code-switching (CS) often occurs, we present a systematic literature review of code-switching in end-to-end ASR models. We collect and manually annotate papers published in peer reviewed venues. We document the languages considered, datasets, metrics, model choices, and performance, and present a discussion of challenges in end-to-end ASR for code-switching. Our analysis thus provides insights on current research efforts and available resources as well as opportunities and gaps to guide future research.
Are LLMs Good Text Diacritizers? An Arabic and Yorùbá Case Study
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:We investigate the effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) for text diacritization in two typologically distinct languages: Arabic and Yoruba. To enable a rigorous evaluation, we introduce a novel multilingual dataset MultiDiac, with diverse samples that capture a range of diacritic ambiguities. We evaluate 14 LLMs varying in size, accessibility, and language coverage, and benchmark them against 6 specialized diacritization models. Additionally, we fine-tune four small open-source models using LoRA for Yoruba. Our results show that many off-the-shelf LLMs outperform specialized diacritization models for both Arabic and Yoruba, but smaller models suffer from hallucinations. Fine-tuning on a small dataset can help improve diacritization performance and reduce hallucination rates.
ArVoice: A Multi-Speaker Dataset for Arabic Speech Synthesis
May 26, 2025Abstract:We introduce ArVoice, a multi-speaker Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) speech corpus with diacritized transcriptions, intended for multi-speaker speech synthesis, and can be useful for other tasks such as speech-based diacritic restoration, voice conversion, and deepfake detection. ArVoice comprises: (1) a new professionally recorded set from six voice talents with diverse demographics, (2) a modified subset of the Arabic Speech Corpus; and (3) high-quality synthetic speech from two commercial systems. The complete corpus consists of a total of 83.52 hours of speech across 11 voices; around 10 hours consist of human voices from 7 speakers. We train three open-source TTS and two voice conversion systems to illustrate the use cases of the dataset. The corpus is available for research use.
Voice of a Continent: Mapping Africa's Speech Technology Frontier
May 24, 2025Abstract:Africa's rich linguistic diversity remains significantly underrepresented in speech technologies, creating barriers to digital inclusion. To alleviate this challenge, we systematically map the continent's speech space of datasets and technologies, leading to a new comprehensive benchmark SimbaBench for downstream African speech tasks. Using SimbaBench, we introduce the Simba family of models, achieving state-of-the-art performance across multiple African languages and speech tasks. Our benchmark analysis reveals critical patterns in resource availability, while our model evaluation demonstrates how dataset quality, domain diversity, and language family relationships influence performance across languages. Our work highlights the need for expanded speech technology resources that better reflect Africa's linguistic diversity and provides a solid foundation for future research and development efforts toward more inclusive speech technologies.
JEEM: Vision-Language Understanding in Four Arabic Dialects
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:We introduce JEEM, a benchmark designed to evaluate Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on visual understanding across four Arabic-speaking countries: Jordan, The Emirates, Egypt, and Morocco. JEEM includes the tasks of image captioning and visual question answering, and features culturally rich and regionally diverse content. This dataset aims to assess the ability of VLMs to generalize across dialects and accurately interpret cultural elements in visual contexts. In an evaluation of five prominent open-source Arabic VLMs and GPT-4V, we find that the Arabic VLMs consistently underperform, struggling with both visual understanding and dialect-specific generation. While GPT-4V ranks best in this comparison, the model's linguistic competence varies across dialects, and its visual understanding capabilities lag behind. This underscores the need for more inclusive models and the value of culturally-diverse evaluation paradigms.
Infant Cry Detection Using Causal Temporal Representation
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses a major challenge in acoustic event detection, in particular infant cry detection in the presence of other sounds and background noises: the lack of precise annotated data. We present two contributions for supervised and unsupervised infant cry detection. The first is an annotated dataset for cry segmentation, which enables supervised models to achieve state-of-the-art performance. Additionally, we propose a novel unsupervised method, Causal Representation Spare Transition Clustering (CRSTC), based on causal temporal representation, which helps address the issue of data scarcity more generally. By integrating the detected cry segments, we significantly improve the performance of downstream infant cry classification, highlighting the potential of this approach for infant care applications.
SparQLe: Speech Queries to Text Translation Through LLMs
Feb 13, 2025



Abstract:With the growing influence of Large Language Models (LLMs), there is increasing interest in integrating speech representations with them to enable more seamless multi-modal processing and speech understanding. This study introduces a novel approach that leverages self-supervised speech representations in combination with instruction-tuned LLMs for speech-to-text translation. The proposed approach leverages a modality adapter to align extracted speech features with instruction-tuned LLMs using English-language data. Our experiments demonstrate that this method effectively preserves the semantic content of the input speech and serves as an effective bridge between self-supervised speech models and instruction-tuned LLMs, offering a promising solution for various speech understanding applications.
Dialectal Coverage And Generalization in Arabic Speech Recognition
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Developing robust automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems for Arabic, a language characterized by its rich dialectal diversity and often considered a low-resource language in speech technology, demands effective strategies to manage its complexity. This study explores three critical factors influencing ASR performance: the role of dialectal coverage in pre-training, the effectiveness of dialect-specific fine-tuning compared to a multi-dialectal approach, and the ability to generalize to unseen dialects. Through extensive experiments across different dialect combinations, our findings offer key insights towards advancing the development of ASR systems for pluricentric languages like Arabic.
STTATTS: Unified Speech-To-Text And Text-To-Speech Model
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Speech recognition and speech synthesis models are typically trained separately, each with its own set of learning objectives, training data, and model parameters, resulting in two distinct large networks. We propose a parameter-efficient approach to learning ASR and TTS jointly via a multi-task learning objective and shared parameters. Our evaluation demonstrates that the performance of our multi-task model is comparable to that of individually trained models while significantly saving computational and memory costs ($\sim$50\% reduction in the total number of parameters required for the two tasks combined). We experiment with English as a resource-rich language, and Arabic as a relatively low-resource language due to shortage of TTS data. Our models are trained with publicly available data, and both the training code and model checkpoints are openly available for further research.
RelUNet: Relative Channel Fusion U-Net for Multichannel Speech Enhancement
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Neural multi-channel speech enhancement models, in particular those based on the U-Net architecture, demonstrate promising performance and generalization potential. These models typically encode input channels independently, and integrate the channels during later stages of the network. In this paper, we propose a novel modification of these models by incorporating relative information from the outset, where each channel is processed in conjunction with a reference channel through stacking. This input strategy exploits comparative differences to adaptively fuse information between channels, thereby capturing crucial spatial information and enhancing the overall performance. The experiments conducted on the CHiME-3 dataset demonstrate improvements in speech enhancement metrics across various architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge