Maha Tufail Agro
A Parallel Cross-Lingual Benchmark for Multimodal Idiomaticity Understanding
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Potentially idiomatic expressions (PIEs) construe meanings inherently tied to the everyday experience of a given language community. As such, they constitute an interesting challenge for assessing the linguistic (and to some extent cultural) capabilities of NLP systems. In this paper, we present XMPIE, a parallel multilingual and multimodal dataset of potentially idiomatic expressions. The dataset, containing 34 languages and over ten thousand items, allows comparative analyses of idiomatic patterns among language-specific realisations and preferences in order to gather insights about shared cultural aspects. This parallel dataset allows to evaluate model performance for a given PIE in different languages and whether idiomatic understanding in one language can be transferred to another. Moreover, the dataset supports the study of PIEs across textual and visual modalities, to measure to what extent PIE understanding in one modality transfers or implies in understanding in another modality (text vs. image). The data was created by language experts, with both textual and visual components crafted under multilingual guidelines, and each PIE is accompanied by five images representing a spectrum from idiomatic to literal meanings, including semantically related and random distractors. The result is a high-quality benchmark for evaluating multilingual and multimodal idiomatic language understanding.
Code-Switching in End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition: A Systematic Literature Review
Jul 10, 2025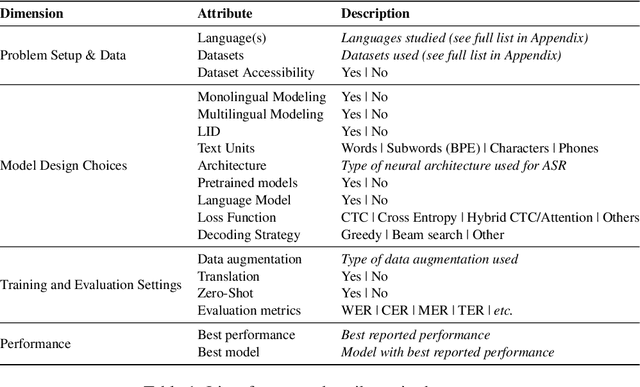
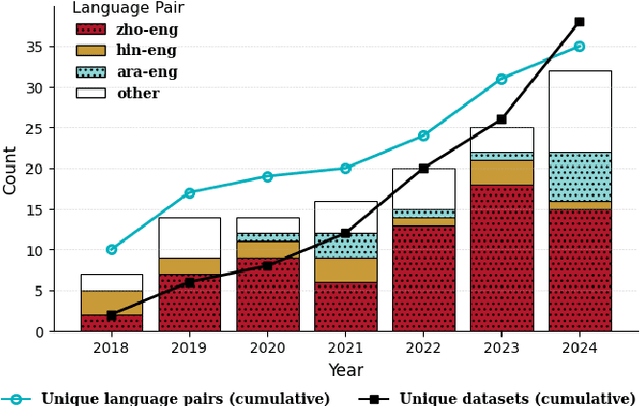
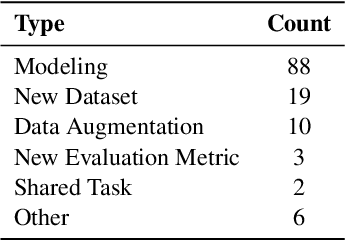
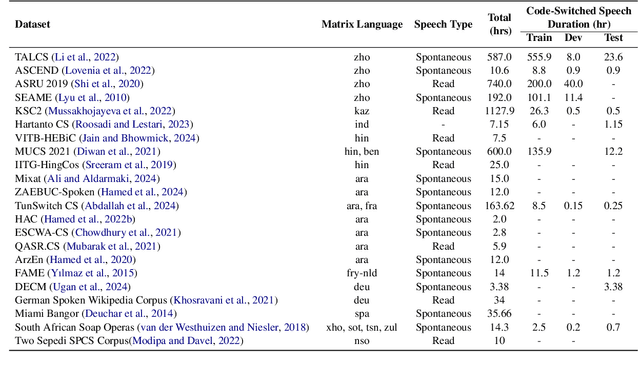
Abstract:Motivated by a growing research interest into automatic speech recognition (ASR), and the growing body of work for languages in which code-switching (CS) often occurs, we present a systematic literature review of code-switching in end-to-end ASR models. We collect and manually annotate papers published in peer reviewed venues. We document the languages considered, datasets, metrics, model choices, and performance, and present a discussion of challenges in end-to-end ASR for code-switching. Our analysis thus provides insights on current research efforts and available resources as well as opportunities and gaps to guide future research.
Profiling News Media for Factuality and Bias Using LLMs and the Fact-Checking Methodology of Human Experts
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:In an age characterized by the proliferation of mis- and disinformation online, it is critical to empower readers to understand the content they are reading. Important efforts in this direction rely on manual or automatic fact-checking, which can be challenging for emerging claims with limited information. Such scenarios can be handled by assessing the reliability and the political bias of the source of the claim, i.e., characterizing entire news outlets rather than individual claims or articles. This is an important but understudied research direction. While prior work has looked into linguistic and social contexts, we do not analyze individual articles or information in social media. Instead, we propose a novel methodology that emulates the criteria that professional fact-checkers use to assess the factuality and political bias of an entire outlet. Specifically, we design a variety of prompts based on these criteria and elicit responses from large language models (LLMs), which we aggregate to make predictions. In addition to demonstrating sizable improvements over strong baselines via extensive experiments with multiple LLMs, we provide an in-depth error analysis of the effect of media popularity and region on model performance. Further, we conduct an ablation study to highlight the key components of our dataset that contribute to these improvements. To facilitate future research, we released our dataset and code at https://github.com/mbzuai-nlp/llm-media-profiling.
PALM: Few-Shot Prompt Learning for Audio Language Models
Sep 29, 2024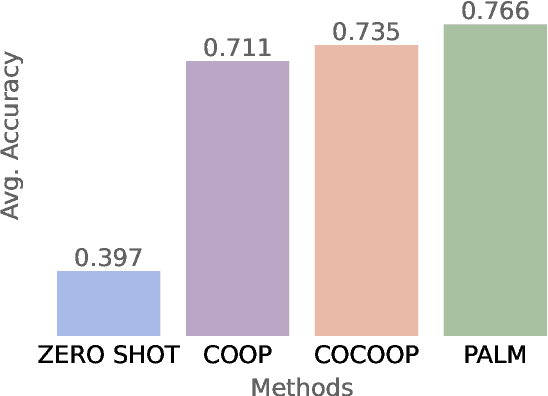
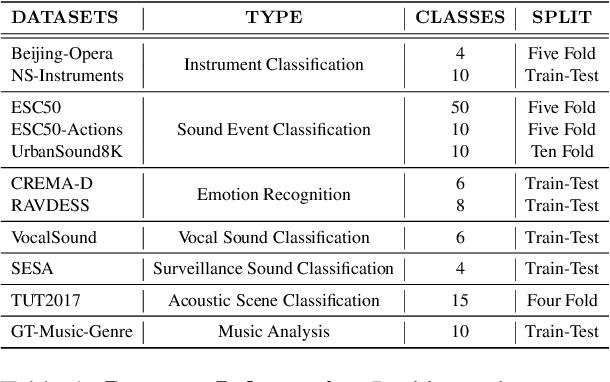
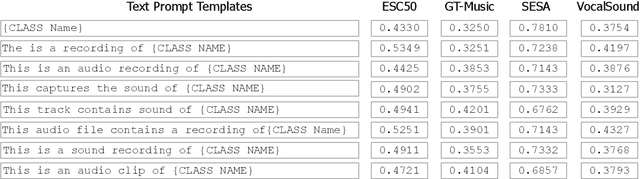
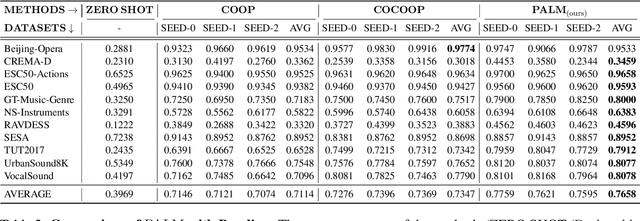
Abstract:Audio-Language Models (ALMs) have recently achieved remarkable success in zero-shot audio recognition tasks, which match features of audio waveforms with class-specific text prompt features, inspired by advancements in Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Given the sensitivity of zero-shot performance to the choice of hand-crafted text prompts, many prompt learning techniques have been developed for VLMs. We explore the efficacy of these approaches in ALMs and propose a novel method, Prompt Learning in Audio Language Models (PALM), which optimizes the feature space of the text encoder branch. Unlike existing methods that work in the input space, our approach results in greater training efficiency. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on 11 audio recognition datasets, encompassing a variety of speech-processing tasks, and compare the results with three baselines in a few-shot learning setup. Our method is either on par with or outperforms other approaches while being computationally less demanding. Code is available at https://asif-hanif.github.io/palm/
Handling Realistic Label Noise in BERT Text Classification
May 23, 2023Abstract:Labels noise refers to errors in training labels caused by cheap data annotation methods, such as web scraping or crowd-sourcing, which can be detrimental to the performance of supervised classifiers. Several methods have been proposed to counteract the effect of random label noise in supervised classification, and some studies have shown that BERT is already robust against high rates of randomly injected label noise. However, real label noise is not random; rather, it is often correlated with input features or other annotator-specific factors. In this paper, we evaluate BERT in the presence of two types of realistic label noise: feature-dependent label noise, and synthetic label noise from annotator disagreements. We show that the presence of these types of noise significantly degrades BERT classification performance. To improve robustness, we evaluate different types of ensembles and noise-cleaning methods and compare their effectiveness against label noise across different datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge