Haizhao Dai
CryoFastAR: Fast Cryo-EM Ab Initio Reconstruction Made Easy
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Pose estimation from unordered images is fundamental for 3D reconstruction, robotics, and scientific imaging. Recent geometric foundation models, such as DUSt3R, enable end-to-end dense 3D reconstruction but remain underexplored in scientific imaging fields like cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) for near-atomic protein reconstruction. In cryo-EM, pose estimation and 3D reconstruction from unordered particle images still depend on time-consuming iterative optimization, primarily due to challenges such as low signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) and distortions from the contrast transfer function (CTF). We introduce CryoFastAR, the first geometric foundation model that can directly predict poses from Cryo-EM noisy images for Fast ab initio Reconstruction. By integrating multi-view features and training on large-scale simulated cryo-EM data with realistic noise and CTF modulations, CryoFastAR enhances pose estimation accuracy and generalization. To enhance training stability, we propose a progressive training strategy that first allows the model to extract essential features under simpler conditions before gradually increasing difficulty to improve robustness. Experiments show that CryoFastAR achieves comparable quality while significantly accelerating inference over traditional iterative approaches on both synthetic and real datasets.
BG-Triangle: Bézier Gaussian Triangle for 3D Vectorization and Rendering
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Differentiable rendering enables efficient optimization by allowing gradients to be computed through the rendering process, facilitating 3D reconstruction, inverse rendering and neural scene representation learning. To ensure differentiability, existing solutions approximate or re-formulate traditional rendering operations using smooth, probabilistic proxies such as volumes or Gaussian primitives. Consequently, they struggle to preserve sharp edges due to the lack of explicit boundary definitions. We present a novel hybrid representation, B\'ezier Gaussian Triangle (BG-Triangle), that combines B\'ezier triangle-based vector graphics primitives with Gaussian-based probabilistic models, to maintain accurate shape modeling while conducting resolution-independent differentiable rendering. We present a robust and effective discontinuity-aware rendering technique to reduce uncertainties at object boundaries. We also employ an adaptive densification and pruning scheme for efficient training while reliably handling level-of-detail (LoD) variations. Experiments show that BG-Triangle achieves comparable rendering quality as 3DGS but with superior boundary preservation. More importantly, BG-Triangle uses a much smaller number of primitives than its alternatives, showcasing the benefits of vectorized graphics primitives and the potential to bridge the gap between classic and emerging representations.
DRACO: A Denoising-Reconstruction Autoencoder for Cryo-EM
Oct 15, 2024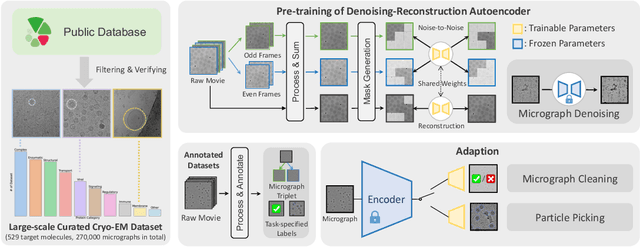
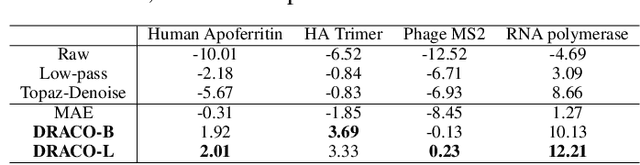
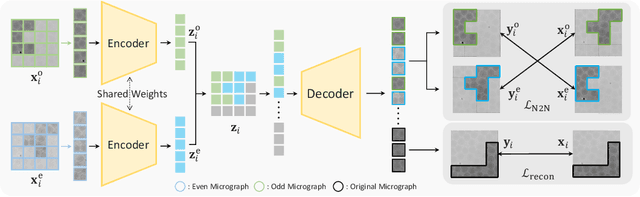
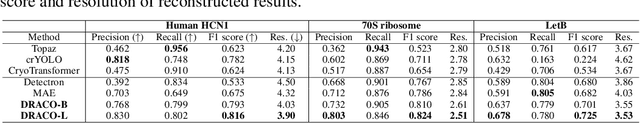
Abstract:Foundation models in computer vision have demonstrated exceptional performance in zero-shot and few-shot tasks by extracting multi-purpose features from large-scale datasets through self-supervised pre-training methods. However, these models often overlook the severe corruption in cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) images by high-level noises. We introduce DRACO, a Denoising-Reconstruction Autoencoder for CryO-EM, inspired by the Noise2Noise (N2N) approach. By processing cryo-EM movies into odd and even images and treating them as independent noisy observations, we apply a denoising-reconstruction hybrid training scheme. We mask both images to create denoising and reconstruction tasks. For DRACO's pre-training, the quality of the dataset is essential, we hence build a high-quality, diverse dataset from an uncurated public database, including over 270,000 movies or micrographs. After pre-training, DRACO naturally serves as a generalizable cryo-EM image denoiser and a foundation model for various cryo-EM downstream tasks. DRACO demonstrates the best performance in denoising, micrograph curation, and particle picking tasks compared to state-of-the-art baselines. We will release the code, pre-trained models, and the curated dataset to stimulate further research.
Sparse-view Signal-domain Photoacoustic Tomography Reconstruction Method Based on Neural Representation
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Photoacoustic tomography is a hybrid biomedical technology, which combines the advantages of acoustic and optical imaging. However, for the conventional image reconstruction method, the image quality is affected obviously by artifacts under the condition of sparse sampling. in this paper, a novel model-based sparse reconstruction method via implicit neural representation was proposed for improving the image quality reconstructed from sparse data. Specially, the initial acoustic pressure distribution was modeled as a continuous function of spatial coordinates, and parameterized by a multi-layer perceptron. The weights of multi-layer perceptron were determined by training the network in self-supervised manner. And the total variation regularization term was used to offer the prior knowledge. We compared our result with some ablation studies, and the results show that out method outperforms existing methods on simulation and experimental data. Under the sparse sampling condition, our method can suppress the artifacts and avoid the ill-posed problem effectively, which reconstruct images with higher signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio than traditional methods. The high-quality results for sparse data make the proposed method hold the potential for further decreasing the hardware cost of photoacoustic tomography system.
Human Performance Modeling and Rendering via Neural Animated Mesh
Sep 18, 2022
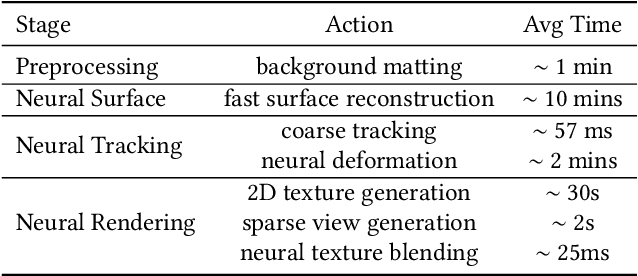
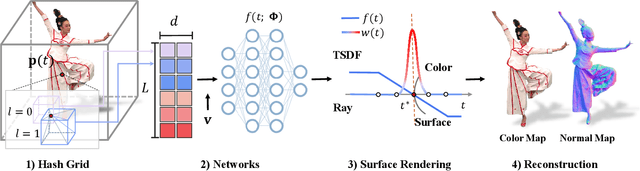

Abstract:We have recently seen tremendous progress in the neural advances for photo-real human modeling and rendering. However, it's still challenging to integrate them into an existing mesh-based pipeline for downstream applications. In this paper, we present a comprehensive neural approach for high-quality reconstruction, compression, and rendering of human performances from dense multi-view videos. Our core intuition is to bridge the traditional animated mesh workflow with a new class of highly efficient neural techniques. We first introduce a neural surface reconstructor for high-quality surface generation in minutes. It marries the implicit volumetric rendering of the truncated signed distance field (TSDF) with multi-resolution hash encoding. We further propose a hybrid neural tracker to generate animated meshes, which combines explicit non-rigid tracking with implicit dynamic deformation in a self-supervised framework. The former provides the coarse warping back into the canonical space, while the latter implicit one further predicts the displacements using the 4D hash encoding as in our reconstructor. Then, we discuss the rendering schemes using the obtained animated meshes, ranging from dynamic texturing to lumigraph rendering under various bandwidth settings. To strike an intricate balance between quality and bandwidth, we propose a hierarchical solution by first rendering 6 virtual views covering the performer and then conducting occlusion-aware neural texture blending. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in a variety of mesh-based applications and photo-realistic free-view experiences on various platforms, i.e., inserting virtual human performances into real environments through mobile AR or immersively watching talent shows with VR headsets.
NeuVV: Neural Volumetric Videos with Immersive Rendering and Editing
Feb 12, 2022



Abstract:Some of the most exciting experiences that Metaverse promises to offer, for instance, live interactions with virtual characters in virtual environments, require real-time photo-realistic rendering. 3D reconstruction approaches to rendering, active or passive, still require extensive cleanup work to fix the meshes or point clouds. In this paper, we present a neural volumography technique called neural volumetric video or NeuVV to support immersive, interactive, and spatial-temporal rendering of volumetric video contents with photo-realism and in real-time. The core of NeuVV is to efficiently encode a dynamic neural radiance field (NeRF) into renderable and editable primitives. We introduce two types of factorization schemes: a hyper-spherical harmonics (HH) decomposition for modeling smooth color variations over space and time and a learnable basis representation for modeling abrupt density and color changes caused by motion. NeuVV factorization can be integrated into a Video Octree (VOctree) analogous to PlenOctree to significantly accelerate training while reducing memory overhead. Real-time NeuVV rendering further enables a class of immersive content editing tools. Specifically, NeuVV treats each VOctree as a primitive and implements volume-based depth ordering and alpha blending to realize spatial-temporal compositions for content re-purposing. For example, we demonstrate positioning varied manifestations of the same performance at different 3D locations with different timing, adjusting color/texture of the performer's clothing, casting spotlight shadows and synthesizing distance falloff lighting, etc, all at an interactive speed. We further develop a hybrid neural-rasterization rendering framework to support consumer-level VR headsets so that the aforementioned volumetric video viewing and editing, for the first time, can be conducted immersively in virtual 3D space.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge