Fitsum Reda
InfoTok: Adaptive Discrete Video Tokenizer via Information-Theoretic Compression
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Accurate and efficient discrete video tokenization is essential for long video sequences processing. Yet, the inherent complexity and variable information density of videos present a significant bottleneck for current tokenizers, which rigidly compress all content at a fixed rate, leading to redundancy or information loss. Drawing inspiration from Shannon's information theory, this paper introduces InfoTok, a principled framework for adaptive video tokenization. We rigorously prove that existing data-agnostic training methods are suboptimal in representation length, and present a novel evidence lower bound (ELBO)-based algorithm that approaches theoretical optimality. Leveraging this framework, we develop a transformer-based adaptive compressor that enables adaptive tokenization. Empirical results demonstrate state-of-the-art compression performance, saving 20% tokens without influence on performance, and achieving 2.3x compression rates while still outperforming prior heuristic adaptive approaches. By allocating tokens according to informational richness, InfoTok enables a more compressed yet accurate tokenization for video representation, offering valuable insights for future research.
Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform for Physical AI
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Physical AI needs to be trained digitally first. It needs a digital twin of itself, the policy model, and a digital twin of the world, the world model. In this paper, we present the Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform to help developers build customized world models for their Physical AI setups. We position a world foundation model as a general-purpose world model that can be fine-tuned into customized world models for downstream applications. Our platform covers a video curation pipeline, pre-trained world foundation models, examples of post-training of pre-trained world foundation models, and video tokenizers. To help Physical AI builders solve the most critical problems of our society, we make our platform open-source and our models open-weight with permissive licenses available via https://github.com/NVIDIA/Cosmos.
Edify Image: High-Quality Image Generation with Pixel Space Laplacian Diffusion Models
Nov 11, 2024Abstract:We introduce Edify Image, a family of diffusion models capable of generating photorealistic image content with pixel-perfect accuracy. Edify Image utilizes cascaded pixel-space diffusion models trained using a novel Laplacian diffusion process, in which image signals at different frequency bands are attenuated at varying rates. Edify Image supports a wide range of applications, including text-to-image synthesis, 4K upsampling, ControlNets, 360 HDR panorama generation, and finetuning for image customization.
TryOnDiffusion: A Tale of Two UNets
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:Given two images depicting a person and a garment worn by another person, our goal is to generate a visualization of how the garment might look on the input person. A key challenge is to synthesize a photorealistic detail-preserving visualization of the garment, while warping the garment to accommodate a significant body pose and shape change across the subjects. Previous methods either focus on garment detail preservation without effective pose and shape variation, or allow try-on with the desired shape and pose but lack garment details. In this paper, we propose a diffusion-based architecture that unifies two UNets (referred to as Parallel-UNet), which allows us to preserve garment details and warp the garment for significant pose and body change in a single network. The key ideas behind Parallel-UNet include: 1) garment is warped implicitly via a cross attention mechanism, 2) garment warp and person blend happen as part of a unified process as opposed to a sequence of two separate tasks. Experimental results indicate that TryOnDiffusion achieves state-of-the-art performance both qualitatively and quantitatively.
What Makes RAFT Better Than PWC-Net?
Mar 21, 2022
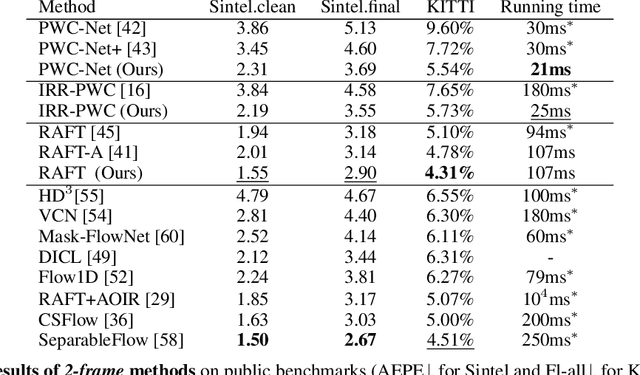

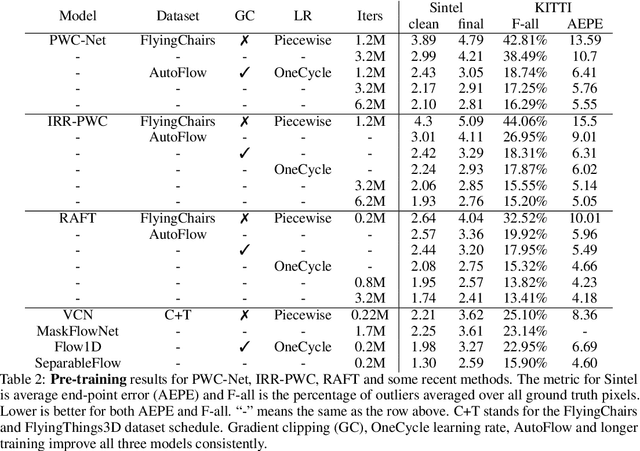
Abstract:How important are training details and datasets to recent optical flow models like RAFT? And do they generalize? To explore these questions, rather than develop a new model, we revisit three prominent models, PWC-Net, IRR-PWC and RAFT, with a common set of modern training techniques and datasets, and observe significant performance gains, demonstrating the importance and generality of these training details. Our newly trained PWC-Net and IRR-PWC models show surprisingly large improvements, up to 30% versus original published results on Sintel and KITTI 2015 benchmarks. They outperform the more recent Flow1D on KITTI 2015 while being 3x faster during inference. Our newly trained RAFT achieves an Fl-all score of 4.31% on KITTI 2015, more accurate than all published optical flow methods at the time of writing. Our results demonstrate the benefits of separating the contributions of models, training techniques and datasets when analyzing performance gains of optical flow methods. Our source code will be publicly available.
FILM: Frame Interpolation for Large Motion
Feb 12, 2022



Abstract:We present a frame interpolation algorithm that synthesizes multiple intermediate frames from two input images with large in-between motion. Recent methods use multiple networks to estimate optical flow or depth and a separate network dedicated to frame synthesis. This is often complex and requires scarce optical flow or depth ground-truth. In this work, we present a single unified network, distinguished by a multi-scale feature extractor that shares weights at all scales, and is trainable from frames alone. To synthesize crisp and pleasing frames, we propose to optimize our network with the Gram matrix loss that measures the correlation difference between feature maps. Our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the Xiph large motion benchmark. We also achieve higher scores on Vimeo-90K, Middlebury and UCF101, when comparing to methods that use perceptual losses. We study the effect of weight sharing and of training with datasets of increasing motion range. Finally, we demonstrate our model's effectiveness in synthesizing high quality and temporally coherent videos on a challenging near-duplicate photos dataset. Codes and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/google-research/frame-interpolation.
EVRNet: Efficient Video Restoration on Edge Devices
Dec 03, 2020


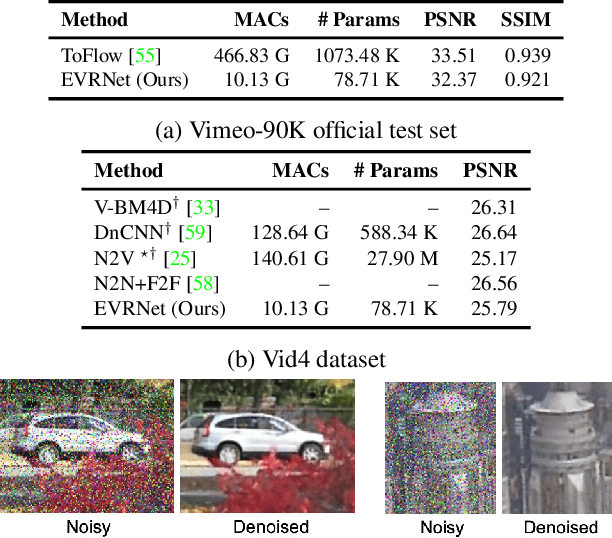
Abstract:Video transmission applications (e.g., conferencing) are gaining momentum, especially in times of global health pandemic. Video signals are transmitted over lossy channels, resulting in low-quality received signals. To restore videos on recipient edge devices in real-time, we introduce an efficient video restoration network, EVRNet. EVRNet efficiently allocates parameters inside the network using alignment, differential, and fusion modules. With extensive experiments on video restoration tasks (deblocking, denoising, and super-resolution), we demonstrate that EVRNet delivers competitive performance to existing methods with significantly fewer parameters and MACs. For example, EVRNet has 260 times fewer parameters and 958 times fewer MACs than enhanced deformable convolution-based video restoration network (EDVR) for 4 times video super-resolution while its SSIM score is 0.018 less than EDVR. We also evaluated the performance of EVRNet under multiple distortions on unseen dataset to demonstrate its ability in modeling variable-length sequences under both camera and object motion.
Neural ODEs for Image Segmentation with Level Sets
Dec 25, 2019


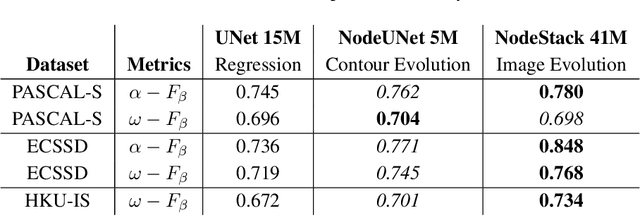
Abstract:We propose a novel approach for image segmentation that combines Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (NODEs) and the Level Set method. Our approach parametrizes the evolution of an initial contour with a NODE that implicitly learns from data a speed function describing the evolution. In addition, for cases where an initial contour is not available and to alleviate the need for careful choice or design of contour embedding functions, we propose a NODE-based method that evolves an image embedding into a dense per-pixel semantic label space. We evaluate our methods on kidney segmentation (KiTS19) and on salient object detection (PASCAL-S, ECSSD and HKU-IS). In addition to improving initial contours provided by deep learning models while using a fraction of their number of parameters, our approach achieves F scores that are higher than several state-of-the-art deep learning algorithms.
Hierarchical Latent Word Clustering
Jan 20, 2016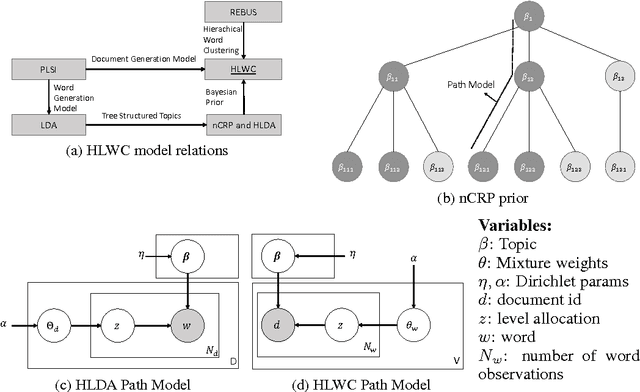
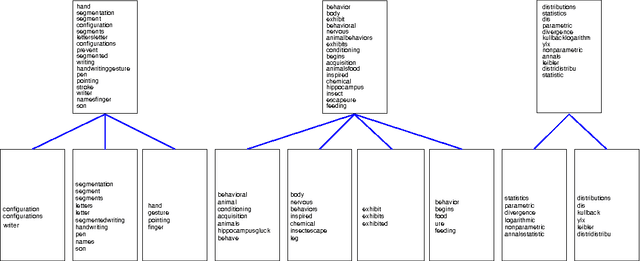
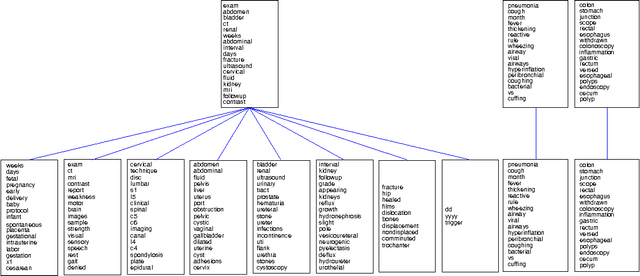
Abstract:This paper presents a new Bayesian non-parametric model by extending the usage of Hierarchical Dirichlet Allocation to extract tree structured word clusters from text data. The inference algorithm of the model collects words in a cluster if they share similar distribution over documents. In our experiments, we observed meaningful hierarchical structures on NIPS corpus and radiology reports collected from public repositories.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge