Rafael Valle
Speech-Hands: A Self-Reflection Voice Agentic Approach to Speech Recognition and Audio Reasoning with Omni Perception
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We introduce a voice-agentic framework that learns one critical omni-understanding skill: knowing when to trust itself versus when to consult external audio perception. Our work is motivated by a crucial yet counterintuitive finding: naively fine-tuning an omni-model on both speech recognition and external sound understanding tasks often degrades performance, as the model can be easily misled by noisy hypotheses. To address this, our framework, Speech-Hands, recasts the problem as an explicit self-reflection decision. This learnable reflection primitive proves effective in preventing the model from being derailed by flawed external candidates. We show that this agentic action mechanism generalizes naturally from speech recognition to complex, multiple-choice audio reasoning. Across the OpenASR leaderboard, Speech-Hands consistently outperforms strong baselines by 12.1% WER on seven benchmarks. The model also achieves 77.37% accuracy and high F1 on audio QA decisions, showing robust generalization and reliability across diverse audio question answering datasets. By unifying perception and decision-making, our work offers a practical path toward more reliable and resilient audio intelligence.
Multi-Domain Audio Question Answering Toward Acoustic Content Reasoning in The DCASE 2025 Challenge
May 12, 2025Abstract:We present Task 5 of the DCASE 2025 Challenge: an Audio Question Answering (AQA) benchmark spanning multiple domains of sound understanding. This task defines three QA subsets (Bioacoustics, Temporal Soundscapes, and Complex QA) to test audio-language models on interactive question-answering over diverse acoustic scenes. We describe the dataset composition (from marine mammal calls to soundscapes and complex real-world clips), the evaluation protocol (top-1 accuracy with answer-shuffling robustness), and baseline systems (Qwen2-Audio-7B, AudioFlamingo 2, Gemini-2-Flash). Preliminary results on the development set are compared, showing strong variation across models and subsets. This challenge aims to advance the audio understanding and reasoning capabilities of audio-language models toward human-level acuity, which are crucial for enabling AI agents to perceive and interact about the world effectively.
Audio Flamingo 2: An Audio-Language Model with Long-Audio Understanding and Expert Reasoning Abilities
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Understanding and reasoning over non-speech sounds and music are crucial for both humans and AI agents to interact effectively with their environments. In this paper, we introduce Audio Flamingo 2 (AF2), an Audio-Language Model (ALM) with advanced audio understanding and reasoning capabilities. AF2 leverages (i) a custom CLAP model, (ii) synthetic Audio QA data for fine-grained audio reasoning, and (iii) a multi-stage curriculum learning strategy. AF2 achieves state-of-the-art performance with only a 3B parameter small language model, surpassing large open-source and proprietary models across over 20 benchmarks. Next, for the first time, we extend audio understanding to long audio segments (30 secs to 5 mins) and propose LongAudio, a large and novel dataset for training ALMs on long audio captioning and question-answering tasks. Fine-tuning AF2 on LongAudio leads to exceptional performance on our proposed LongAudioBench, an expert annotated benchmark for evaluating ALMs on long audio understanding capabilities. We conduct extensive ablation studies to confirm the efficacy of our approach. Project Website: https://research.nvidia.com/labs/adlr/AF2/.
Koel-TTS: Enhancing LLM based Speech Generation with Preference Alignment and Classifier Free Guidance
Feb 07, 2025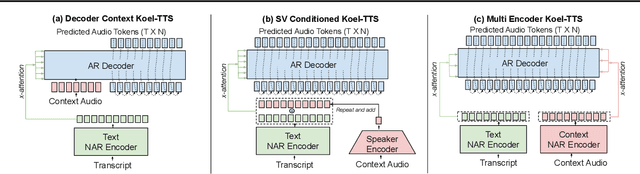
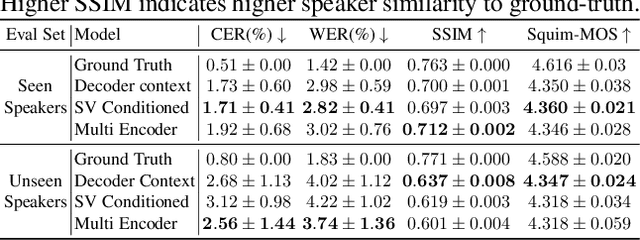
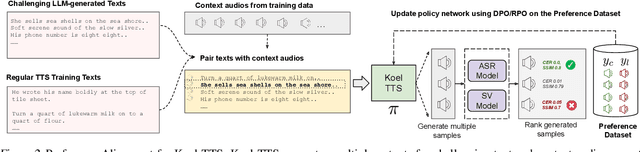
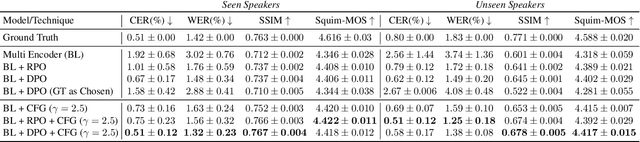
Abstract:While autoregressive speech token generation models produce speech with remarkable variety and naturalness, their inherent lack of controllability often results in issues such as hallucinations and undesired vocalizations that do not conform to conditioning inputs. We introduce Koel-TTS, a suite of enhanced encoder-decoder Transformer TTS models that address these challenges by incorporating preference alignment techniques guided by automatic speech recognition and speaker verification models. Additionally, we incorporate classifier-free guidance to further improve synthesis adherence to the transcript and reference speaker audio. Our experiments demonstrate that these optimizations significantly enhance target speaker similarity, intelligibility, and naturalness of synthesized speech. Notably, Koel-TTS directly maps text and context audio to acoustic tokens, and on the aforementioned metrics, outperforms state-of-the-art TTS models, despite being trained on a significantly smaller dataset. Audio samples and demos are available on our website.
A2SB: Audio-to-Audio Schrodinger Bridges
Jan 20, 2025Abstract:Audio in the real world may be perturbed due to numerous factors, causing the audio quality to be degraded. The following work presents an audio restoration model tailored for high-res music at 44.1kHz. Our model, Audio-to-Audio Schrodinger Bridges (A2SB), is capable of both bandwidth extension (predicting high-frequency components) and inpainting (re-generating missing segments). Critically, A2SB is end-to-end without need of a vocoder to predict waveform outputs, able to restore hour-long audio inputs, and trained on permissively licensed music data. A2SB is capable of achieving state-of-the-art bandwidth extension and inpainting quality on several out-of-distribution music test sets. Our demo website is https: //research.nvidia.com/labs/adlr/A2SB/.
TangoFlux: Super Fast and Faithful Text to Audio Generation with Flow Matching and Clap-Ranked Preference Optimization
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:We introduce TangoFlux, an efficient Text-to-Audio (TTA) generative model with 515M parameters, capable of generating up to 30 seconds of 44.1kHz audio in just 3.7 seconds on a single A40 GPU. A key challenge in aligning TTA models lies in the difficulty of creating preference pairs, as TTA lacks structured mechanisms like verifiable rewards or gold-standard answers available for Large Language Models (LLMs). To address this, we propose CLAP-Ranked Preference Optimization (CRPO), a novel framework that iteratively generates and optimizes preference data to enhance TTA alignment. We demonstrate that the audio preference dataset generated using CRPO outperforms existing alternatives. With this framework, TangoFlux achieves state-of-the-art performance across both objective and subjective benchmarks. We open source all code and models to support further research in TTA generation.
ETTA: Elucidating the Design Space of Text-to-Audio Models
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:Recent years have seen significant progress in Text-To-Audio (TTA) synthesis, enabling users to enrich their creative workflows with synthetic audio generated from natural language prompts. Despite this progress, the effects of data, model architecture, training objective functions, and sampling strategies on target benchmarks are not well understood. With the purpose of providing a holistic understanding of the design space of TTA models, we set up a large-scale empirical experiment focused on diffusion and flow matching models. Our contributions include: 1) AF-Synthetic, a large dataset of high quality synthetic captions obtained from an audio understanding model; 2) a systematic comparison of different architectural, training, and inference design choices for TTA models; 3) an analysis of sampling methods and their Pareto curves with respect to generation quality and inference speed. We leverage the knowledge obtained from this extensive analysis to propose our best model dubbed Elucidated Text-To-Audio (ETTA). When evaluated on AudioCaps and MusicCaps, ETTA provides improvements over the baselines trained on publicly available data, while being competitive with models trained on proprietary data. Finally, we show ETTA's improved ability to generate creative audio following complex and imaginative captions -- a task that is more challenging than current benchmarks.
OMCAT: Omni Context Aware Transformer
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have made significant strides in text generation and comprehension, with recent advancements extending into multimodal LLMs that integrate visual and audio inputs. However, these models continue to struggle with fine-grained, cross-modal temporal understanding, particularly when correlating events across audio and video streams. We address these challenges with two key contributions: a new dataset and model, called OCTAV and OMCAT respectively. OCTAV (Omni Context and Temporal Audio Video) is a novel dataset designed to capture event transitions across audio and video. Second, OMCAT (Omni Context Aware Transformer) is a powerful model that leverages RoTE (Rotary Time Embeddings), an innovative extension of RoPE, to enhance temporal grounding and computational efficiency in time-anchored tasks. Through a robust three-stage training pipeline-feature alignment, instruction tuning, and OCTAV-specific training-OMCAT excels in cross-modal temporal understanding. Our model demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on Audio-Visual Question Answering (AVQA) tasks and the OCTAV benchmark, showcasing significant gains in temporal reasoning and cross-modal alignment, as validated through comprehensive experiments and ablation studies. Our dataset and code will be made publicly available. The link to our demo page is https://om-cat.github.io.
Synthio: Augmenting Small-Scale Audio Classification Datasets with Synthetic Data
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:We present Synthio, a novel approach for augmenting small-scale audio classification datasets with synthetic data. Our goal is to improve audio classification accuracy with limited labeled data. Traditional data augmentation techniques, which apply artificial transformations (e.g., adding random noise or masking segments), struggle to create data that captures the true diversity present in real-world audios. To address this shortcoming, we propose to augment the dataset with synthetic audio generated from text-to-audio (T2A) diffusion models. However, synthesizing effective augmentations is challenging because not only should the generated data be acoustically consistent with the underlying small-scale dataset, but they should also have sufficient compositional diversity. To overcome the first challenge, we align the generations of the T2A model with the small-scale dataset using preference optimization. This ensures that the acoustic characteristics of the generated data remain consistent with the small-scale dataset. To address the second challenge, we propose a novel caption generation technique that leverages the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models to (1) generate diverse and meaningful audio captions and (2) iteratively refine their quality. The generated captions are then used to prompt the aligned T2A model. We extensively evaluate Synthio on ten datasets and four simulated limited-data settings. Results indicate our method consistently outperforms all baselines by 0.1%-39% using a T2A model trained only on weakly-captioned AudioSet.
Improving Robustness of LLM-based Speech Synthesis by Learning Monotonic Alignment
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) based text-to-speech (TTS) systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling large speech datasets and generating natural speech for new speakers. However, LLM-based TTS models are not robust as the generated output can contain repeating words, missing words and mis-aligned speech (referred to as hallucinations or attention errors), especially when the text contains multiple occurrences of the same token. We examine these challenges in an encoder-decoder transformer model and find that certain cross-attention heads in such models implicitly learn the text and speech alignment when trained for predicting speech tokens for a given text. To make the alignment more robust, we propose techniques utilizing CTC loss and attention priors that encourage monotonic cross-attention over the text tokens. Our guided attention training technique does not introduce any new learnable parameters and significantly improves robustness of LLM-based TTS models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge