Rohan Badlani
Improving Robustness of LLM-based Speech Synthesis by Learning Monotonic Alignment
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) based text-to-speech (TTS) systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in handling large speech datasets and generating natural speech for new speakers. However, LLM-based TTS models are not robust as the generated output can contain repeating words, missing words and mis-aligned speech (referred to as hallucinations or attention errors), especially when the text contains multiple occurrences of the same token. We examine these challenges in an encoder-decoder transformer model and find that certain cross-attention heads in such models implicitly learn the text and speech alignment when trained for predicting speech tokens for a given text. To make the alignment more robust, we propose techniques utilizing CTC loss and attention priors that encourage monotonic cross-attention over the text tokens. Our guided attention training technique does not introduce any new learnable parameters and significantly improves robustness of LLM-based TTS models.
Audio Flamingo: A Novel Audio Language Model with Few-Shot Learning and Dialogue Abilities
Feb 02, 2024



Abstract:Augmenting large language models (LLMs) to understand audio -- including non-speech sounds and non-verbal speech -- is critically important for diverse real-world applications of LLMs. In this paper, we propose Audio Flamingo, a novel audio language model with 1) strong audio understanding abilities, 2) the ability to quickly adapt to unseen tasks via in-context learning and retrieval, and 3) strong multi-turn dialogue abilities. We introduce a series of training techniques, architecture design, and data strategies to enhance our model with these abilities. Extensive evaluations across various audio understanding tasks confirm the efficacy of our method, setting new state-of-the-art benchmarks.
Scaling NVIDIA's Multi-speaker Multi-lingual TTS Systems with Zero-Shot TTS to Indic Languages
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we describe the TTS models developed by NVIDIA for the MMITS-VC (Multi-speaker, Multi-lingual Indic TTS with Voice Cloning) 2024 Challenge. In Tracks 1 and 2, we utilize RAD-MMM to perform few-shot TTS by training additionally on 5 minutes of target speaker data. In Track 3, we utilize P-Flow to perform zero-shot TTS by training on the challenge dataset as well as external datasets. We use HiFi-GAN vocoders for all submissions. RAD-MMM performs competitively on Tracks 1 and 2, while P-Flow ranks first on Track 3, with mean opinion score (MOS) 4.4 and speaker similarity score (SMOS) of 3.62.
VANI: Very-lightweight Accent-controllable TTS for Native and Non-native speakers with Identity Preservation
Mar 14, 2023
Abstract:We introduce VANI, a very lightweight multi-lingual accent controllable speech synthesis system. Our model builds upon disentanglement strategies proposed in RADMMM and supports explicit control of accent, language, speaker and fine-grained $F_0$ and energy features for speech synthesis. We utilize the Indic languages dataset, released for LIMMITS 2023 as part of ICASSP Signal Processing Grand Challenge, to synthesize speech in 3 different languages. Our model supports transferring the language of a speaker while retaining their voice and the native accent of the target language. We utilize the large-parameter RADMMM model for Track $1$ and lightweight VANI model for Track $2$ and $3$ of the competition.
Multilingual Multiaccented Multispeaker TTS with RADTTS
Jan 24, 2023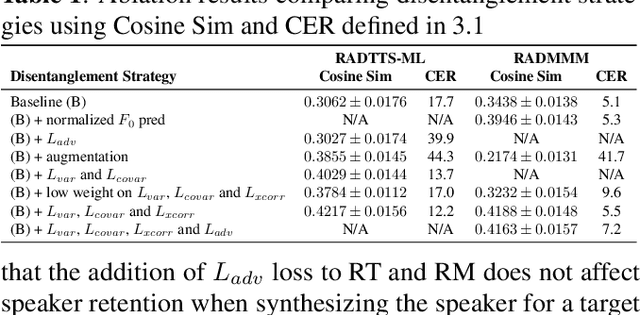
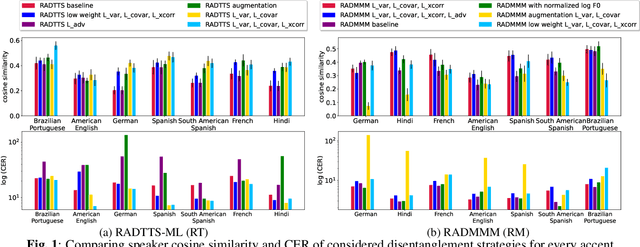
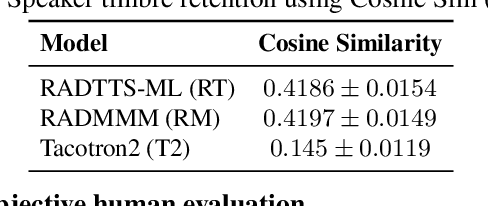
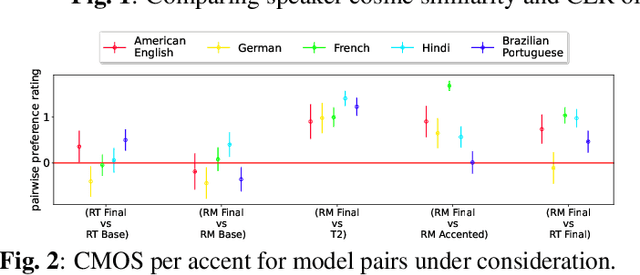
Abstract:We work to create a multilingual speech synthesis system which can generate speech with the proper accent while retaining the characteristics of an individual voice. This is challenging to do because it is expensive to obtain bilingual training data in multiple languages, and the lack of such data results in strong correlations that entangle speaker, language, and accent, resulting in poor transfer capabilities. To overcome this, we present a multilingual, multiaccented, multispeaker speech synthesis model based on RADTTS with explicit control over accent, language, speaker and fine-grained $F_0$ and energy features. Our proposed model does not rely on bilingual training data. We demonstrate an ability to control synthesized accent for any speaker in an open-source dataset comprising of 7 accents. Human subjective evaluation demonstrates that our model can better retain a speaker's voice and accent quality than controlled baselines while synthesizing fluent speech in all target languages and accents in our dataset.
Generative Modeling for Low Dimensional Speech Attributes with Neural Spline Flows
Mar 07, 2022
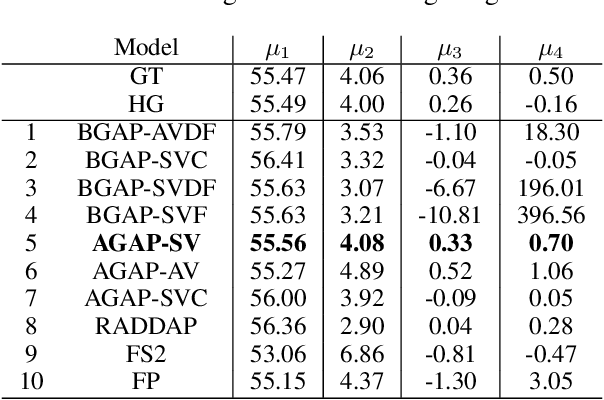

Abstract:Despite recent advances in generative modeling for text-to-speech synthesis, these models do not yet have the same fine-grained adjustability of pitch-conditioned deterministic models such as FastPitch and FastSpeech2. Pitch information is not only low-dimensional, but also discontinuous, making it particularly difficult to model in a generative setting. Our work explores several techniques for handling the aforementioned issues in the context of Normalizing Flow models. We also find this problem to be very well suited for Neural Spline flows, which is a highly expressive alternative to the more common affine-coupling mechanism in Normalizing Flows.
One TTS Alignment To Rule Them All
Aug 23, 2021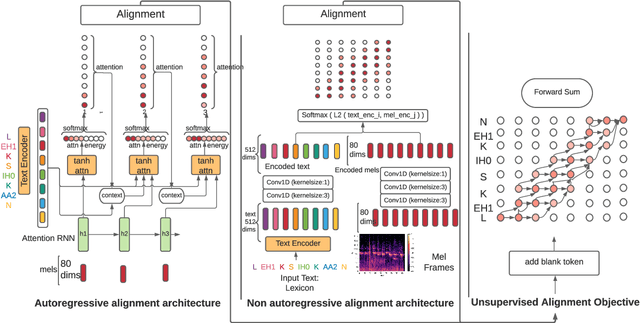
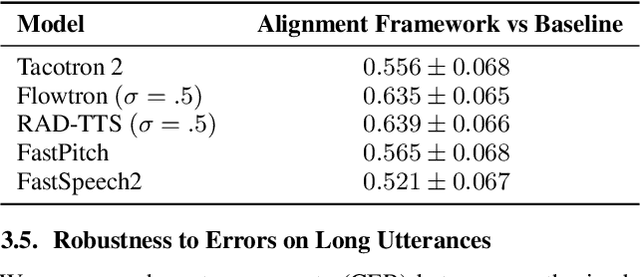


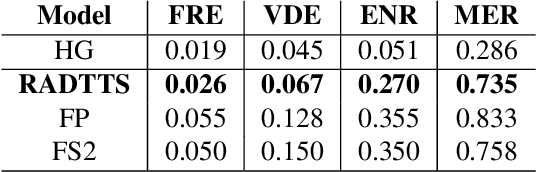
Abstract:Speech-to-text alignment is a critical component of neural textto-speech (TTS) models. Autoregressive TTS models typically use an attention mechanism to learn these alignments on-line. However, these alignments tend to be brittle and often fail to generalize to long utterances and out-of-domain text, leading to missing or repeating words. Most non-autoregressive endto-end TTS models rely on durations extracted from external sources. In this paper we leverage the alignment mechanism proposed in RAD-TTS as a generic alignment learning framework, easily applicable to a variety of neural TTS models. The framework combines forward-sum algorithm, the Viterbi algorithm, and a simple and efficient static prior. In our experiments, the alignment learning framework improves all tested TTS architectures, both autoregressive (Flowtron, Tacotron 2) and non-autoregressive (FastPitch, FastSpeech 2, RAD-TTS). Specifically, it improves alignment convergence speed of existing attention-based mechanisms, simplifies the training pipeline, and makes the models more robust to errors on long utterances. Most importantly, the framework improves the perceived speech synthesis quality, as judged by human evaluators.
Relation Extraction with Contextualized Relation Embedding (CRE)
Nov 19, 2020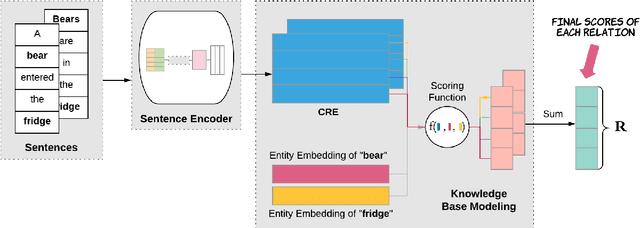

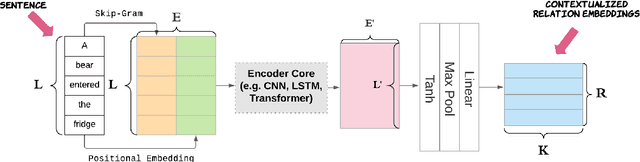
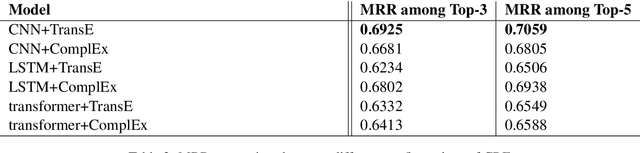
Abstract:Relation extraction is the task of identifying relation instance between two entities given a corpus whereas Knowledge base modeling is the task of representing a knowledge base, in terms of relations between entities. This paper proposes an architecture for the relation extraction task that integrates semantic information with knowledge base modeling in a novel manner. Existing approaches for relation extraction either do not utilize knowledge base modelling or use separately trained KB models for the RE task. We present a model architecture that internalizes KB modeling in relation extraction. This model applies a novel approach to encode sentences into contextualized relation embeddings, which can then be used together with parameterized entity embeddings to score relation instances. The proposed CRE model achieves state of the art performance on datasets derived from The New York Times Annotated Corpus and FreeBase. The source code has been made available.
Framework for evaluation of sound event detection in web videos
Apr 04, 2018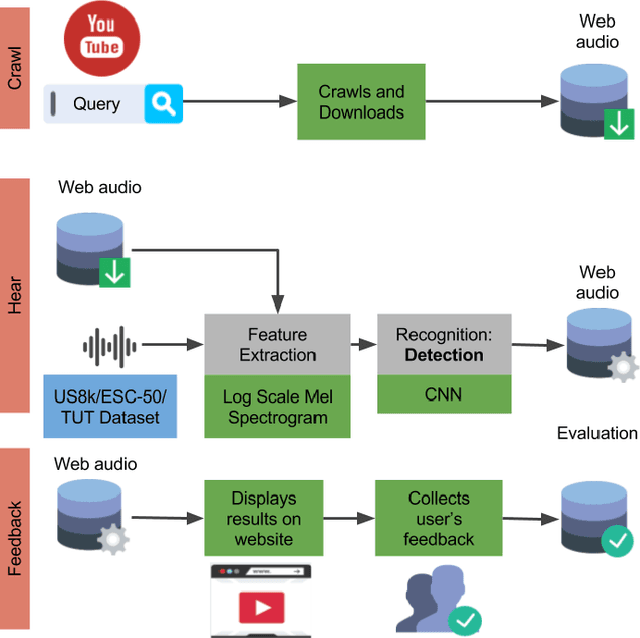
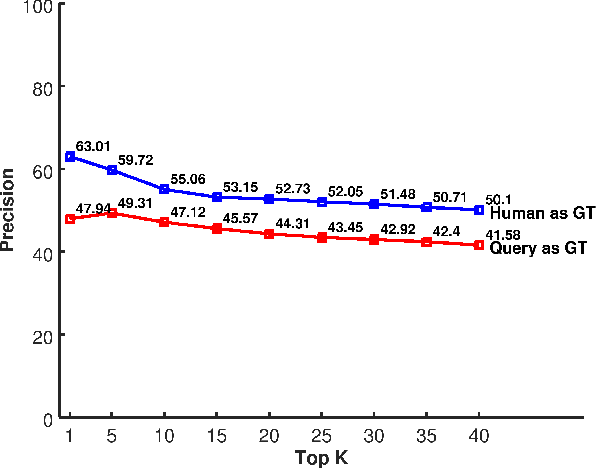
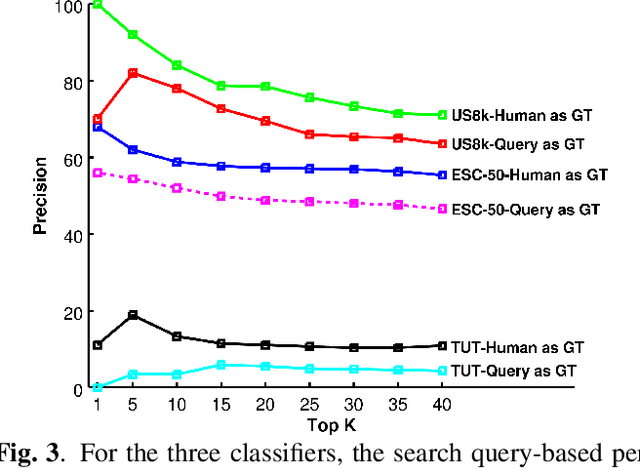

Abstract:The largest source of sound events is web videos. Most videos lack sound event labels at segment level, however, a significant number of them do respond to text queries, from a match found using metadata by search engines. In this paper we explore the extent to which a search query can be used as the true label for detection of sound events in videos. We present a framework for large-scale sound event recognition on web videos. The framework crawls videos using search queries corresponding to 78 sound event labels drawn from three datasets. The datasets are used to train three classifiers, and we obtain a prediction on 3.7 million web video segments. We evaluated performance using the search query as true label and compare it with human labeling. Both types of ground truth exhibited close performance, to within 10%, and similar performance trend with increasing number of evaluated segments. Hence, our experiments show potential for using search query as a preliminary true label for sound event recognition in web videos.
An Approach for Self-Training Audio Event Detectors Using Web Data
Jun 27, 2017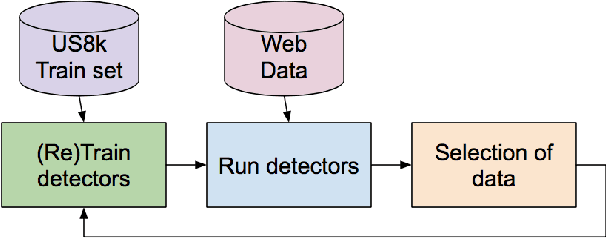
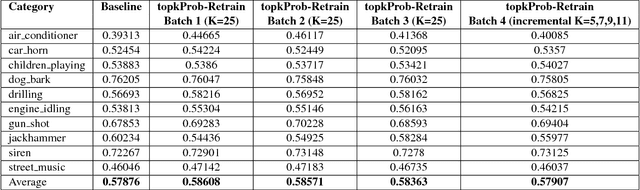
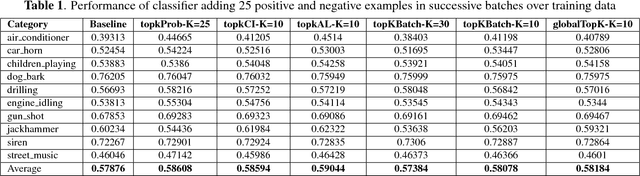
Abstract:Audio Event Detection (AED) aims to recognize sounds within audio and video recordings. AED employs machine learning algorithms commonly trained and tested on annotated datasets. However, available datasets are limited in number of samples and hence it is difficult to model acoustic diversity. Therefore, we propose combining labeled audio from a dataset and unlabeled audio from the web to improve the sound models. The audio event detectors are trained on the labeled audio and ran on the unlabeled audio downloaded from YouTube. Whenever the detectors recognized any of the known sounds with high confidence, the unlabeled audio was use to re-train the detectors. The performance of the re-trained detectors is compared to the one from the original detectors using the annotated test set. Results showed an improvement of the AED, and uncovered challenges of using web audio from videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge