Erxue Min
Staying in the Sweet Spot: Responsive Reasoning Evolution via Capability-Adaptive Hint Scaffolding
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has achieved remarkable success in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, existing RLVR methods often suffer from exploration inefficiency due to mismatches between the training data's difficulty and the model's capability. LLMs fail to discover viable reasoning paths when problems are overly difficult, while learning little new capability when problems are too simple. In this work, we formalize the impact of problem difficulty by quantifying the relationship between loss descent speed and rollout accuracy. Building on this analysis, we propose SEELE, a novel supervision-aided RLVR framework that dynamically adjusts problem difficulty to stay within the high-efficiency region. SEELE augments each training sample by appending a hint (part of a full solution) after the original problem. Unlike previous hint-based approaches, SEELE deliberately and adaptively adjusts the hint length for each problem to achieve an optimal difficulty. To determine the optimal hint length, SEELE employs a multi-round rollout sampling strategy. In each round, it fits an item response theory model to the accuracy-hint pairs collected in preceding rounds to predict the required hint length for the next round. This instance-level, real-time difficulty adjustment aligns problem difficulty with the evolving model capability, thereby improving exploration efficiency. Experimental results show that SEELE outperforms Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) and Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) by +11.8 and +10.5 points, respectively, and surpasses the best previous supervision-aided approach by +3.6 points on average across six math reasoning benchmarks.
A Question Answering Dataset for Temporal-Sensitive Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Aug 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce ChronoQA, a large-scale benchmark dataset for Chinese question answering, specifically designed to evaluate temporal reasoning in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. ChronoQA is constructed from over 300,000 news articles published between 2019 and 2024, and contains 5,176 high-quality questions covering absolute, aggregate, and relative temporal types with both explicit and implicit time expressions. The dataset supports both single- and multi-document scenarios, reflecting the real-world requirements for temporal alignment and logical consistency. ChronoQA features comprehensive structural annotations and has undergone multi-stage validation, including rule-based, LLM-based, and human evaluation, to ensure data quality. By providing a dynamic, reliable, and scalable resource, ChronoQA enables structured evaluation across a wide range of temporal tasks, and serves as a robust benchmark for advancing time-sensitive retrieval-augmented question answering systems.
From Prompting to Alignment: A Generative Framework for Query Recommendation
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:In modern search systems, search engines often suggest relevant queries to users through various panels or components, helping refine their information needs. Traditionally, these recommendations heavily rely on historical search logs to build models, which suffer from cold-start or long-tail issues. Furthermore, tasks such as query suggestion, completion or clarification are studied separately by specific design, which lacks generalizability and hinders adaptation to novel applications. Despite recent attempts to explore the use of LLMs for query recommendation, these methods mainly rely on the inherent knowledge of LLMs or external sources like few-shot examples, retrieved documents, or knowledge bases, neglecting the importance of the calibration and alignment with user feedback, thus limiting their practical utility. To address these challenges, we first propose a general Generative Query Recommendation (GQR) framework that aligns LLM-based query generation with user preference. Specifically, we unify diverse query recommendation tasks by a universal prompt framework, leveraging the instruct-following capability of LLMs for effective generation. Secondly, we align LLMs with user feedback via presenting a CTR-alignment framework, which involves training a query-wise CTR predictor as a process reward model and employing list-wise preference alignment to maximize the click probability of the generated query list. Furthermore, recognizing the inconsistency between LLM knowledge and proactive search intents arising from the separation of user-initiated queries from models, we align LLMs with user initiative via retrieving co-occurrence queries as side information when historical logs are available.
LLMs + Persona-Plug = Personalized LLMs
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:Personalization plays a critical role in numerous language tasks and applications, since users with the same requirements may prefer diverse outputs based on their individual interests. This has led to the development of various personalized approaches aimed at adapting large language models (LLMs) to generate customized outputs aligned with user preferences. Some of them involve fine-tuning a unique personalized LLM for each user, which is too expensive for widespread application. Alternative approaches introduce personalization information in a plug-and-play manner by retrieving the user's relevant historical texts as demonstrations. However, this retrieval-based strategy may break the continuity of the user history and fail to capture the user's overall styles and patterns, hence leading to sub-optimal performance. To address these challenges, we propose a novel personalized LLM model, \ours{}. It constructs a user-specific embedding for each individual by modeling all her historical contexts through a lightweight plug-in user embedder module. By attaching this embedding to the task input, LLMs can better understand and capture user habits and preferences, thereby producing more personalized outputs without tuning their own parameters. Extensive experiments on various tasks in the language model personalization (LaMP) benchmark demonstrate that the proposed model significantly outperforms existing personalized LLM approaches.
Selective Preference Optimization via Token-Level Reward Function Estimation
Aug 24, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language model alignment leverage token-level supervisions to perform fine-grained preference optimization. However, existing token-level alignment methods either optimize on all available tokens, which can be noisy and inefficient, or perform selective training with complex and expensive key token selection strategies. In this work, we propose Selective Preference Optimization (SePO), a novel selective alignment strategy that centers on efficient key token selection. SePO proposes the first token selection method based on Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), which trains an oracle model to estimate a token-level reward function on the target data. This method applies to any existing alignment datasets with response-level annotations and enables cost-efficient token selection with small-scale oracle models and training data. The estimated reward function is then utilized to score all tokens within the target dataset, where only the key tokens are selected to supervise the target policy model with a reference model-free contrastive objective function. Extensive experiments on three public evaluation benchmarks show that SePO significantly outperforms competitive baseline methods by only optimizing 30% key tokens on the target dataset. SePO applications on weak-to-strong generalization show that weak oracle models effectively supervise strong policy models with up to 16.8x more parameters. SePO also effectively selects key tokens from out-of-distribution data to enhance strong policy models and alleviate the over-optimization problem.
DaRec: A Disentangled Alignment Framework for Large Language Model and Recommender System
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:Benefiting from the strong reasoning capabilities, Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in recommender systems. Various efforts have been made to distill knowledge from LLMs to enhance collaborative models, employing techniques like contrastive learning for representation alignment. In this work, we prove that directly aligning the representations of LLMs and collaborative models is sub-optimal for enhancing downstream recommendation tasks performance, based on the information theorem. Consequently, the challenge of effectively aligning semantic representations between collaborative models and LLMs remains unresolved. Inspired by this viewpoint, we propose a novel plug-and-play alignment framework for LLMs and collaborative models. Specifically, we first disentangle the latent representations of both LLMs and collaborative models into specific and shared components via projection layers and representation regularization. Subsequently, we perform both global and local structure alignment on the shared representations to facilitate knowledge transfer. Additionally, we theoretically prove that the specific and shared representations contain more pertinent and less irrelevant information, which can enhance the effectiveness of downstream recommendation tasks. Extensive experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method is superior to existing state-of-the-art algorithms.
Hyperbolic Knowledge Transfer in Cross-Domain Recommendation System
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:Cross-Domain Recommendation (CDR) seeks to utilize knowledge from different domains to alleviate the problem of data sparsity in the target recommendation domain, and it has been gaining more attention in recent years. Although there have been notable advancements in this area, most current methods represent users and items in Euclidean space, which is not ideal for handling long-tail distributed data in recommendation systems. Additionally, adding data from other domains can worsen the long-tail characteristics of the entire dataset, making it harder to train CDR models effectively. Recent studies have shown that hyperbolic methods are particularly suitable for modeling long-tail distributions, which has led us to explore hyperbolic representations for users and items in CDR scenarios. However, due to the distinct characteristics of the different domains, applying hyperbolic representation learning to CDR tasks is quite challenging. In this paper, we introduce a new framework called Hyperbolic Contrastive Learning (HCTS), designed to capture the unique features of each domain while enabling efficient knowledge transfer between domains. We achieve this by embedding users and items from each domain separately and mapping them onto distinct hyperbolic manifolds with adjustable curvatures for prediction. To improve the representations of users and items in the target domain, we develop a hyperbolic contrastive learning module for knowledge transfer. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that hyperbolic manifolds are a promising alternative to Euclidean space for CDR tasks.
Transformer for Graphs: An Overview from Architecture Perspective
Feb 17, 2022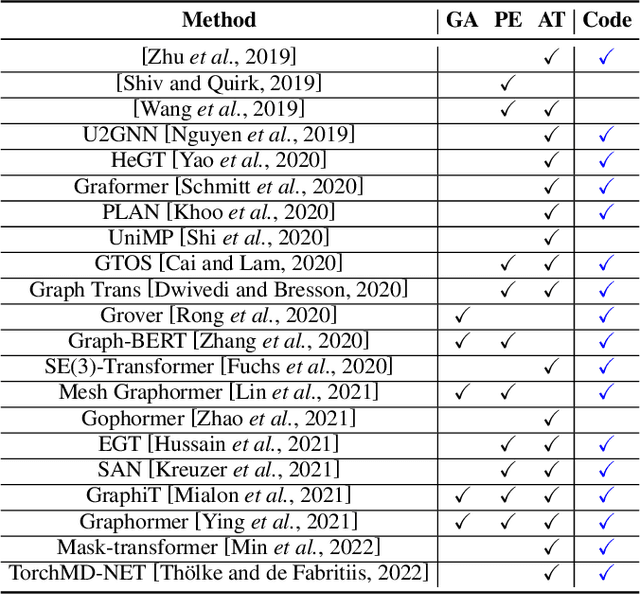
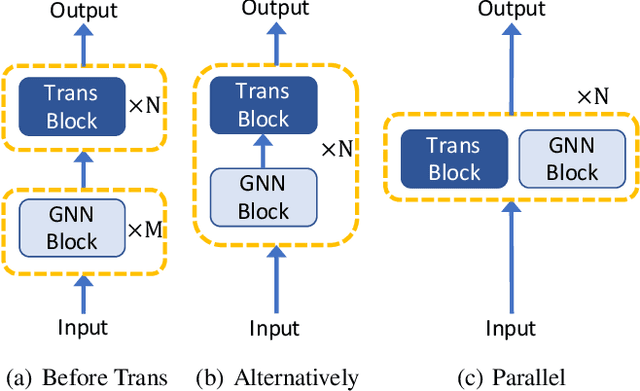
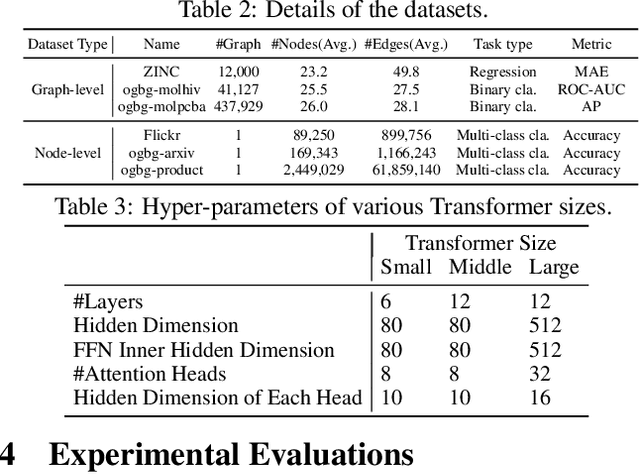
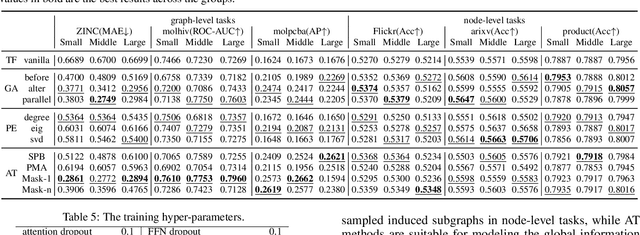
Abstract:Recently, Transformer model, which has achieved great success in many artificial intelligence fields, has demonstrated its great potential in modeling graph-structured data. Till now, a great variety of Transformers has been proposed to adapt to the graph-structured data. However, a comprehensive literature review and systematical evaluation of these Transformer variants for graphs are still unavailable. It's imperative to sort out the existing Transformer models for graphs and systematically investigate their effectiveness on various graph tasks. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of various Graph Transformer models from the architectural design perspective. We first disassemble the existing models and conclude three typical ways to incorporate the graph information into the vanilla Transformer: 1) GNNs as Auxiliary Modules, 2) Improved Positional Embedding from Graphs, and 3) Improved Attention Matrix from Graphs. Furthermore, we implement the representative components in three groups and conduct a comprehensive comparison on various kinds of famous graph data benchmarks to investigate the real performance gain of each component. Our experiments confirm the benefits of current graph-specific modules on Transformer and reveal their advantages on different kinds of graph tasks.
Masked Transformer for Neighhourhood-aware Click-Through Rate Prediction
Jan 25, 2022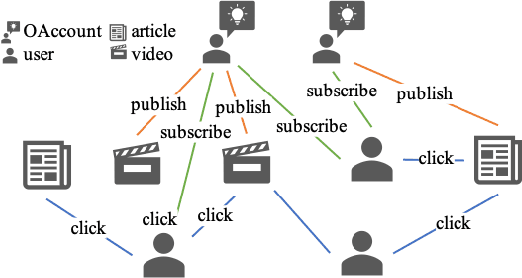
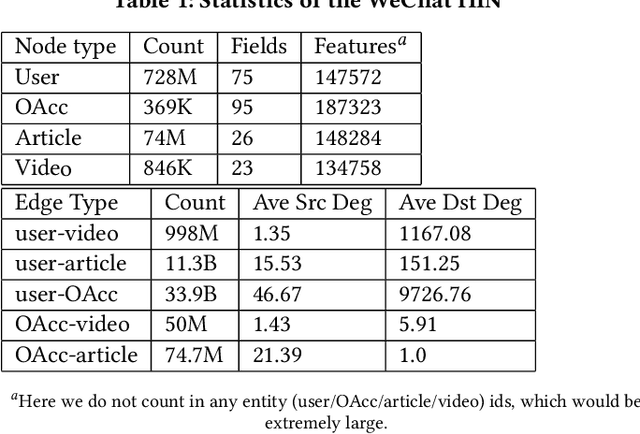
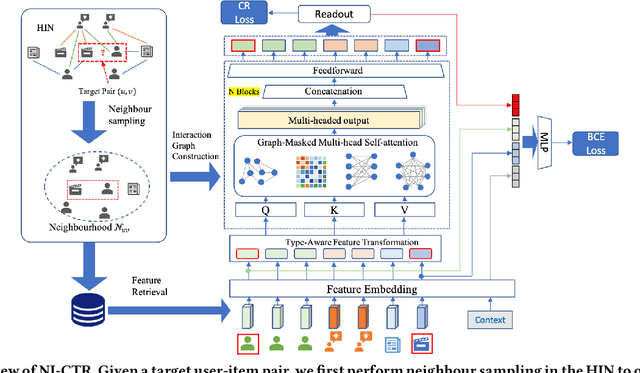
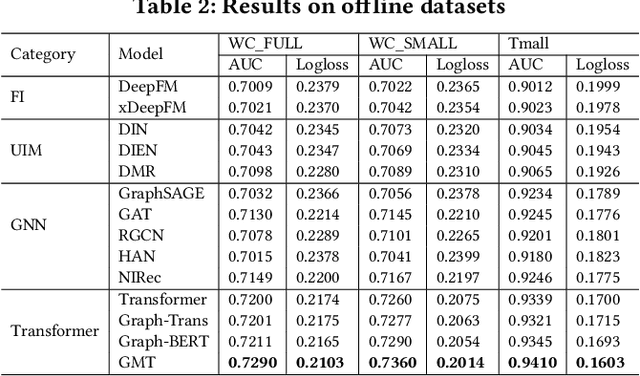
Abstract:Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction, is an essential component of online advertising. The mainstream techniques mostly focus on feature interaction or user interest modeling, which rely on users' directly interacted items. The performance of these methods are usally impeded by inactive behaviours and system's exposure, incurring that the features extracted do not contain enough information to represent all potential interests. For this sake, we propose Neighbor-Interaction based CTR prediction, which put this task into a Heterogeneous Information Network (HIN) setting, then involves local neighborhood of the target user-item pair in the HIN to predict their linkage. In order to enhance the representation of the local neighbourhood, we consider four types of topological interaction among the nodes, and propose a novel Graph-masked Transformer architecture to effectively incorporates both feature and topological information. We conduct comprehensive experiments on two real world datasets and the experimental results show that our proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art CTR models significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge