Emre Can Acikgoz
Current Agents Fail to Leverage World Model as Tool for Foresight
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Agents built on vision-language models increasingly face tasks that demand anticipating future states rather than relying on short-horizon reasoning. Generative world models offer a promising remedy: agents could use them as external simulators to foresee outcomes before acting. This paper empirically examines whether current agents can leverage such world models as tools to enhance their cognition. Across diverse agentic and visual question answering tasks, we observe that some agents rarely invoke simulation (fewer than 1%), frequently misuse predicted rollouts (approximately 15%), and often exhibit inconsistent or even degraded performance (up to 5%) when simulation is available or enforced. Attribution analysis further indicates that the primary bottleneck lies in the agents' capacity to decide when to simulate, how to interpret predicted outcomes, and how to integrate foresight into downstream reasoning. These findings underscore the need for mechanisms that foster calibrated, strategic interaction with world models, paving the way toward more reliable anticipatory cognition in future agent systems.
SpeakRL: Synergizing Reasoning, Speaking, and Acting in Language Models with Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025
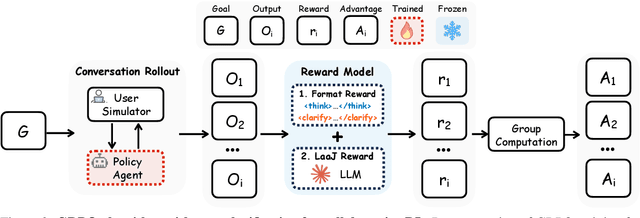
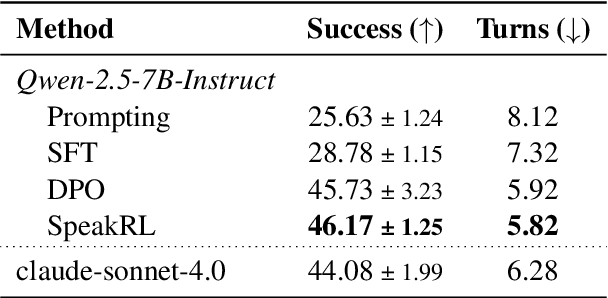
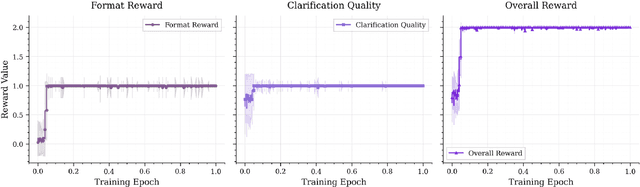
Abstract:Effective human-agent collaboration is increasingly prevalent in real-world applications. Current trends in such collaborations are predominantly unidirectional, with users providing instructions or posing questions to agents, where agents respond directly without seeking necessary clarifications or confirmations. However, the evolving capabilities of these agents require more proactive engagement, where agents should dynamically participate in conversations to clarify user intents, resolve ambiguities, and adapt to changing circumstances. Existing prior work under-utilize the conversational capabilities of language models (LMs), thereby optimizing agents as better followers rather than effective speakers. In this work, we introduce SpeakRL, a reinforcement learning (RL) method that enhances agents' conversational capabilities by rewarding proactive interactions with users, such as asking right clarification questions when necessary. To support this, we curate SpeakER, a synthetic dataset that includes diverse scenarios from task-oriented dialogues, where tasks are resolved through interactive clarification questions. We present a systematic analysis of reward design for conversational proactivity and propose a principled reward formulation for teaching agents to balance asking with acting. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our approach achieves a 20.14% absolute improvement in task completion over base models without increasing conversation turns even surpassing even much larger proprietary models, demonstrating the promise of clarification-centric user-agent interactions.
MAC: A Multi-Agent Framework for Interactive User Clarification in Multi-turn Conversations
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Conversational agents often encounter ambiguous user requests, requiring an effective clarification to successfully complete tasks. While recent advancements in real-world applications favor multi-agent architectures to manage complex conversational scenarios efficiently, ambiguity resolution remains a critical and underexplored challenge--particularly due to the difficulty of determining which agent should initiate a clarification and how agents should coordinate their actions when faced with uncertain or incomplete user input. The fundamental questions of when to interrupt a user and how to formulate the optimal clarification query within the most optimal multi-agent settings remain open. In this paper, we propose MAC (Multi-Agent Clarification), an interactive multi-agent framework specifically optimized to resolve user ambiguities by strategically managing clarification dialogues. We first introduce a novel taxonomy categorizing user ambiguities to systematically guide clarification strategies. Then, we present MAC that autonomously coordinates multiple agents to interact synergistically with users. Empirical evaluations on MultiWOZ 2.4 demonstrate that enabling clarification at both levels increases task success rate 7.8\% (54.5 to 62.3) and reduces the average number of dialogue turns (6.53 to 4.86) by eliciting all required user information up front and minimizing repetition. Our findings highlight the importance of active user interaction and role-aware clarification for more reliable human-agent communication.
Self-Improving LLM Agents at Test-Time
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:One paradigm of language model (LM) fine-tuning relies on creating large training datasets, under the assumption that high quantity and diversity will enable models to generalize to novel tasks after post-training. In practice, gathering large sets of data is inefficient, and training on them is prohibitively expensive; worse, there is no guarantee that the resulting model will handle complex scenarios or generalize better. Moreover, existing techniques rarely assess whether a training sample provides novel information or is redundant with the knowledge already acquired by the model, resulting in unnecessary costs. In this work, we explore a new test-time self-improvement method to create more effective and generalizable agentic LMs on-the-fly. The proposed algorithm can be summarized in three steps: (i) first it identifies the samples that model struggles with (self-awareness), (ii) then generates similar examples from detected uncertain samples (self-data augmentation), and (iii) uses these newly generated samples at test-time fine-tuning (self-improvement). We study two variants of this approach: Test-Time Self-Improvement (TT-SI), where the same model generates additional training examples from its own uncertain cases and then learns from them, and contrast this approach with Test-Time Distillation (TT-D), where a stronger model generates similar examples for uncertain cases, enabling student to adapt using distilled supervision. Empirical evaluations across different agent benchmarks demonstrate that TT-SI improves the performance with +5.48% absolute accuracy gain on average across all benchmarks and surpasses other standard learning methods, yet using 68x less training samples. Our findings highlight the promise of TT-SI, demonstrating the potential of self-improvement algorithms at test-time as a new paradigm for building more capable agents toward self-evolution.
PIPA: A Unified Evaluation Protocol for Diagnosing Interactive Planning Agents
May 02, 2025


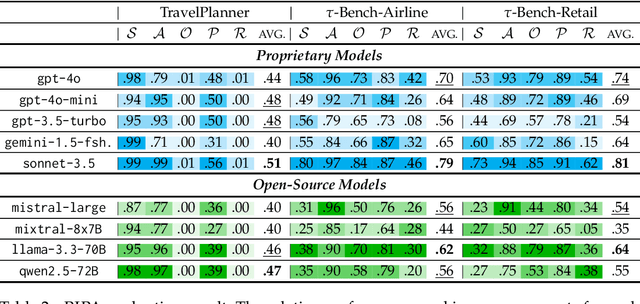
Abstract:The growing capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in instruction-following and context-understanding lead to the era of agents with numerous applications. Among these, task planning agents have become especially prominent in realistic scenarios involving complex internal pipelines, such as context understanding, tool management, and response generation. However, existing benchmarks predominantly evaluate agent performance based on task completion as a proxy for overall effectiveness. We hypothesize that merely improving task completion is misaligned with maximizing user satisfaction, as users interact with the entire agentic process and not only the end result. To address this gap, we propose PIPA, a unified evaluation protocol that conceptualizes the behavioral process of interactive task planning agents within a partially observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP) paradigm. The proposed protocol offers a comprehensive assessment of agent performance through a set of atomic evaluation criteria, allowing researchers and practitioners to diagnose specific strengths and weaknesses within the agent's decision-making pipeline. Our analyses show that agents excel in different behavioral stages, with user satisfaction shaped by both outcomes and intermediate behaviors. We also highlight future directions, including systems that leverage multiple agents and the limitations of user simulators in task planning.
TD-EVAL: Revisiting Task-Oriented Dialogue Evaluation by Combining Turn-Level Precision with Dialogue-Level Comparisons
Apr 28, 2025



Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems are experiencing a revolution driven by Large Language Models (LLMs), yet the evaluation methodologies for these systems remain insufficient for their growing sophistication. While traditional automatic metrics effectively assessed earlier modular systems, they focus solely on the dialogue level and cannot detect critical intermediate errors that can arise during user-agent interactions. In this paper, we introduce TD-EVAL (Turn and Dialogue-level Evaluation), a two-step evaluation framework that unifies fine-grained turn-level analysis with holistic dialogue-level comparisons. At turn level, we evaluate each response along three TOD-specific dimensions: conversation cohesion, backend knowledge consistency, and policy compliance. Meanwhile, we design TOD Agent Arena that uses pairwise comparisons to provide a measure of dialogue-level quality. Through experiments on MultiWOZ 2.4 and {\tau}-Bench, we demonstrate that TD-EVAL effectively identifies the conversational errors that conventional metrics miss. Furthermore, TD-EVAL exhibits better alignment with human judgments than traditional and LLM-based metrics. These findings demonstrate that TD-EVAL introduces a new paradigm for TOD system evaluation, efficiently assessing both turn and system levels with a plug-and-play framework for future research.
ToolRL: Reward is All Tool Learning Needs
Apr 16, 2025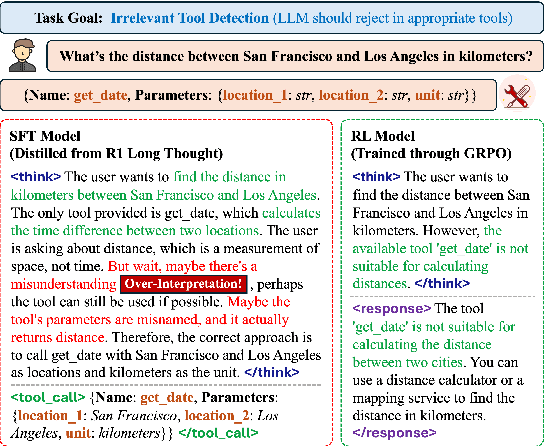
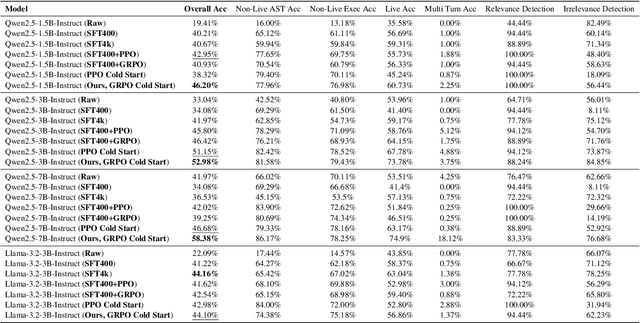
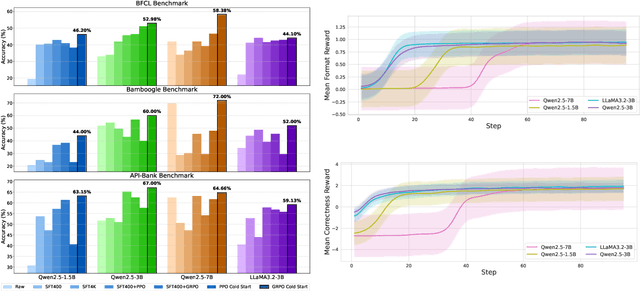
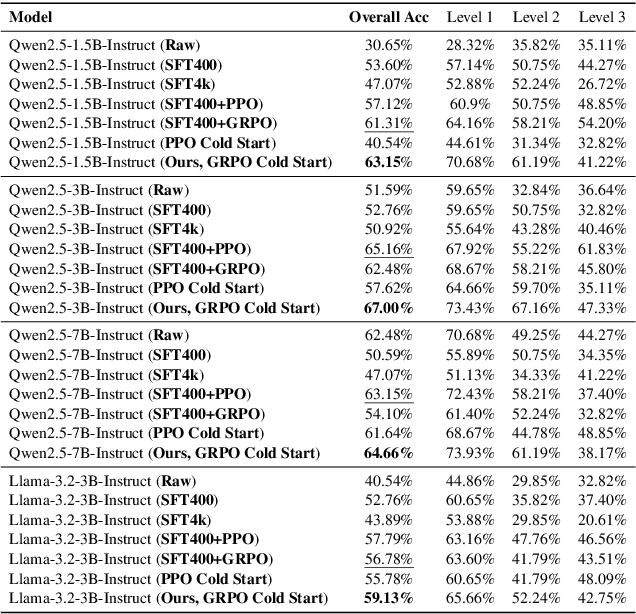
Abstract:Current Large Language Models (LLMs) often undergo supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to acquire tool use capabilities. However, SFT struggles to generalize to unfamiliar or complex tool use scenarios. Recent advancements in reinforcement learning (RL), particularly with R1-like models, have demonstrated promising reasoning and generalization abilities. Yet, reward design for tool use presents unique challenges: multiple tools may be invoked with diverse parameters, and coarse-grained reward signals, such as answer matching, fail to offer the finegrained feedback required for effective learning. In this work, we present the first comprehensive study on reward design for tool selection and application tasks within the RL paradigm. We systematically explore a wide range of reward strategies, analyzing their types, scales, granularity, and temporal dynamics. Building on these insights, we propose a principled reward design tailored for tool use tasks and apply it to train LLMs using Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Empirical evaluations across diverse benchmarks demonstrate that our approach yields robust, scalable, and stable training, achieving a 17% improvement over base models and a 15% gain over SFT models. These results highlight the critical role of thoughtful reward design in enhancing the tool use capabilities and generalization performance of LLMs. All the codes are released to facilitate future research.
SMART: Self-Aware Agent for Tool Overuse Mitigation
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:Current Large Language Model (LLM) agents demonstrate strong reasoning and tool use capabilities, but often lack self-awareness, failing to balance these approaches effectively. This imbalance leads to Tool Overuse, where models unnecessarily rely on external tools for tasks solvable with parametric knowledge, increasing computational overhead. Inspired by human metacognition, we introduce SMART (Strategic Model-Aware Reasoning with Tools), a paradigm that enhances an agent's self-awareness to optimize task handling and reduce tool overuse. To support this paradigm, we introduce SMART-ER, a dataset spanning three domains, where reasoning alternates between parametric knowledge and tool-dependent steps, with each step enriched by rationales explaining when tools are necessary. Through supervised training, we develop SMARTAgent, a family of models that dynamically balance parametric knowledge and tool use. Evaluations show that SMARTAgent reduces tool use by 24% while improving performance by over 37%, enabling 7B-scale models to match its 70B counterpart and GPT-4o. Additionally, SMARTAgent generalizes to out-of-distribution test data like GSM8K and MINTQA, maintaining accuracy with just one-fifth the tool calls. These highlight the potential of strategic tool use to enhance reasoning, mitigate overuse, and bridge the gap between model size and performance, advancing intelligent and resource-efficient agent designs.
Can a Single Model Master Both Multi-turn Conversations and Tool Use? CALM: A Unified Conversational Agentic Language Model
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) with API-calling capabilities enabled building effective Language Agents (LA), while also revolutionizing the conventional task-oriented dialogue (TOD) paradigm. However, current approaches face a critical dilemma: TOD systems are often trained on a limited set of target APIs, requiring new data to maintain their quality when interfacing with new services, while LAs are not trained to maintain user intent over multi-turn conversations. Because both robust multi-turn management and advanced function calling are crucial for effective conversational agents, we evaluate these skills on three popular benchmarks: MultiWOZ 2.4 (TOD), BFCL V3 (LA), and API-Bank (LA), and our analyses reveal that specialized approaches excel in one domain but underperform in the other. To bridge this chasm, we introduce CALM (Conversational Agentic Language Model), a unified approach that integrates both conversational and agentic capabilities. We created CALM-IT, a carefully constructed multi-task dataset that interleave multi-turn ReAct reasoning with complex API usage. Using CALM-IT, we train three models CALM 8B, CALM 70B, and CALM 405B, which outperform top domain-specific models, including GPT-4o, across all three benchmarks.
ReSpAct: Harmonizing Reasoning, Speaking, and Acting Towards Building Large Language Model-Based Conversational AI Agents
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents have been increasingly used to interact with external environments (e.g., games, APIs, etc.) and solve tasks. However, current frameworks do not enable these agents to work with users and interact with them to align on the details of their tasks and reach user-defined goals; instead, in ambiguous situations, these agents may make decisions based on assumptions. This work introduces ReSpAct (Reason, Speak, and Act), a novel framework that synergistically combines the essential skills for building task-oriented "conversational" agents. ReSpAct addresses this need for agents, expanding on the ReAct approach. The ReSpAct framework enables agents to interpret user instructions, reason about complex tasks, execute appropriate actions, and engage in dynamic dialogue to seek guidance, clarify ambiguities, understand user preferences, resolve problems, and use the intermediate feedback and responses of users to update their plans. We evaluated ReSpAct in environments supporting user interaction, such as task-oriented dialogue (MultiWOZ) and interactive decision-making (AlfWorld, WebShop). ReSpAct is flexible enough to incorporate dynamic user feedback and addresses prevalent issues like error propagation and agents getting stuck in reasoning loops. This results in more interpretable, human-like task-solving trajectories than relying solely on reasoning traces. In two interactive decision-making benchmarks, AlfWorld and WebShop, ReSpAct outperform the strong reasoning-only method ReAct by an absolute success rate of 6% and 4%, respectively. In the task-oriented dialogue benchmark MultiWOZ, ReSpAct improved Inform and Success scores by 5.5% and 3%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge