Dinesh Raghu
A Library of LLM Intrinsics for Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 16, 2025
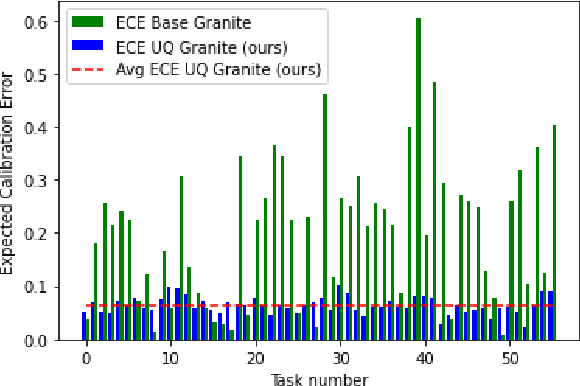
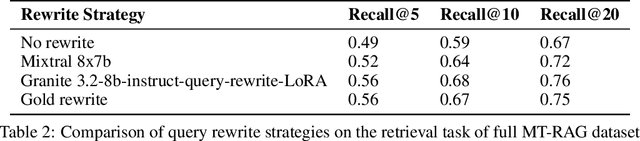
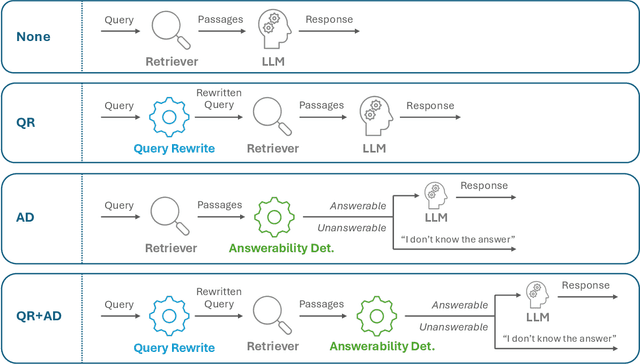
Abstract:In the developer community for large language models (LLMs), there is not yet a clean pattern analogous to a software library, to support very large scale collaboration. Even for the commonplace use case of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), it is not currently possible to write a RAG application against a well-defined set of APIs that are agreed upon by different LLM providers. Inspired by the idea of compiler intrinsics, we propose some elements of such a concept through introducing a library of LLM Intrinsics for RAG. An LLM intrinsic is defined as a capability that can be invoked through a well-defined API that is reasonably stable and independent of how the LLM intrinsic itself is implemented. The intrinsics in our library are released as LoRA adapters on HuggingFace, and through a software interface with clear structured input/output characteristics on top of vLLM as an inference platform, accompanied in both places with documentation and code. This article describes the intended usage, training details, and evaluations for each intrinsic, as well as compositions of multiple intrinsics.
Selective Self-to-Supervised Fine-Tuning for Generalization in Large Language Models
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) on specific datasets is a common practice to improve performance on target tasks. However, this performance gain often leads to overfitting, where the model becomes too specialized in either the task or the characteristics of the training data, resulting in a loss of generalization. This paper introduces Selective Self-to-Supervised Fine-Tuning (S3FT), a fine-tuning approach that achieves better performance than the standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) while improving generalization. S3FT leverages the existence of multiple valid responses to a query. By utilizing the model's correct responses, S3FT reduces model specialization during the fine-tuning stage. S3FT first identifies the correct model responses from the training set by deploying an appropriate judge. Then, it fine-tunes the model using the correct model responses and the gold response (or its paraphrase) for the remaining samples. The effectiveness of S3FT is demonstrated through experiments on mathematical reasoning, Python programming and reading comprehension tasks. The results show that standard SFT can lead to an average performance drop of up to $4.4$ on multiple benchmarks, such as MMLU and TruthfulQA. In contrast, S3FT reduces this drop by half, i.e. $2.5$, indicating better generalization capabilities than SFT while performing significantly better on the fine-tuning tasks.
Systematic Knowledge Injection into Large Language Models via Diverse Augmentation for Domain-Specific RAG
Feb 12, 2025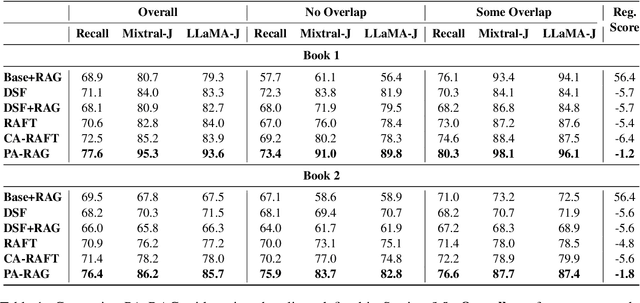
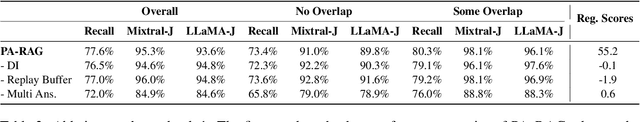
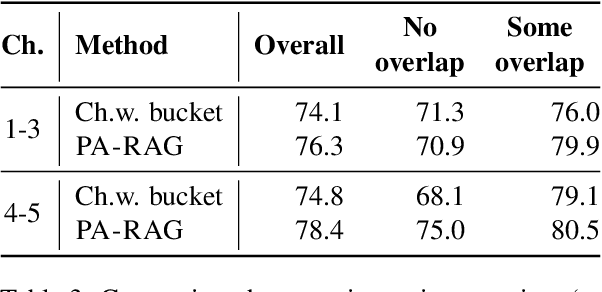
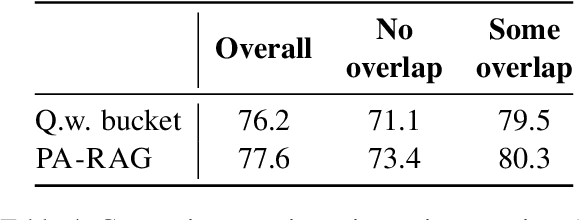
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a prominent method for incorporating domain knowledge into Large Language Models (LLMs). While RAG enhances response relevance by incorporating retrieved domain knowledge in the context, retrieval errors can still lead to hallucinations and incorrect answers. To recover from retriever failures, domain knowledge is injected by fine-tuning the model to generate the correct response, even in the case of retrieval errors. However, we observe that without systematic knowledge augmentation, fine-tuned LLMs may memorize new information but still fail to extract relevant domain knowledge, leading to poor performance. In this work, we present a novel framework that significantly enhances the fine-tuning process by augmenting the training data in two ways -- context augmentation and knowledge paraphrasing. In context augmentation, we create multiple training samples for a given QA pair by varying the relevance of the retrieved information, teaching the model when to ignore and when to rely on retrieved content. In knowledge paraphrasing, we fine-tune with multiple answers to the same question, enabling LLMs to better internalize specialized knowledge. To mitigate catastrophic forgetting due to fine-tuning, we add a domain-specific identifier to a question and also utilize a replay buffer containing general QA pairs. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our method over existing techniques, achieving up to 10\% relative gain in token-level recall while preserving the LLM's generalization capabilities.
MediTOD: An English Dialogue Dataset for Medical History Taking with Comprehensive Annotations
Oct 18, 2024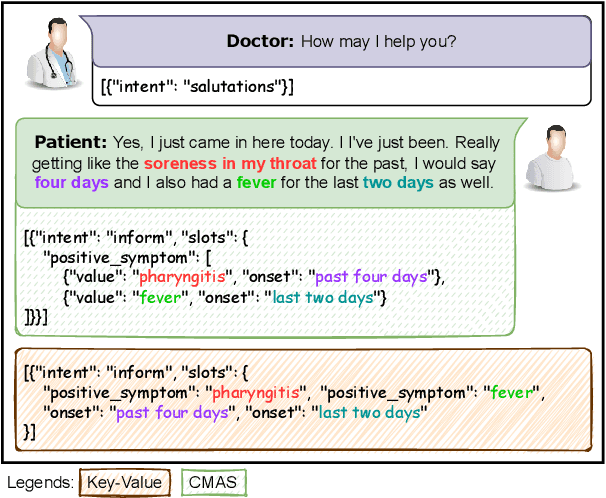
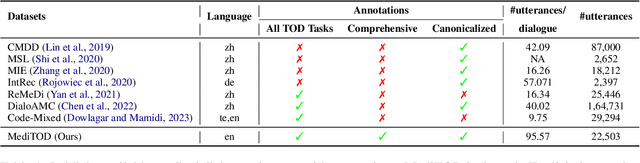
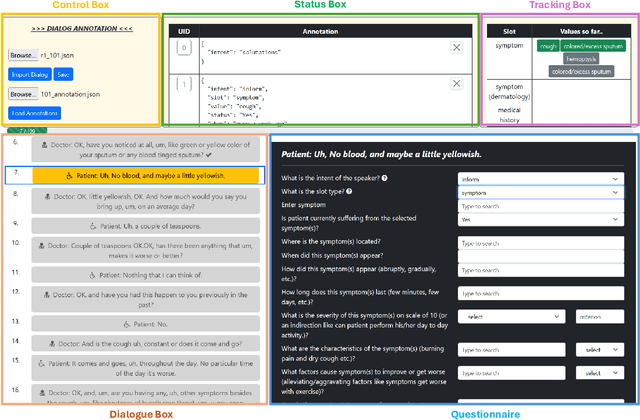

Abstract:Medical task-oriented dialogue systems can assist doctors by collecting patient medical history, aiding in diagnosis, or guiding treatment selection, thereby reducing doctor burnout and expanding access to medical services. However, doctor-patient dialogue datasets are not readily available, primarily due to privacy regulations. Moreover, existing datasets lack comprehensive annotations involving medical slots and their different attributes, such as symptoms and their onset, progression, and severity. These comprehensive annotations are crucial for accurate diagnosis. Finally, most existing datasets are non-English, limiting their utility for the larger research community. In response, we introduce MediTOD, a new dataset of doctor-patient dialogues in English for the medical history-taking task. Collaborating with doctors, we devise a questionnaire-based labeling scheme tailored to the medical domain. Then, medical professionals create the dataset with high-quality comprehensive annotations, capturing medical slots and their attributes. We establish benchmarks in supervised and few-shot settings on MediTOD for natural language understanding, policy learning, and natural language generation subtasks, evaluating models from both TOD and biomedical domains. We make MediTOD publicly available for future research.
Selective Self-Rehearsal: A Fine-Tuning Approach to Improve Generalization in Large Language Models
Sep 07, 2024
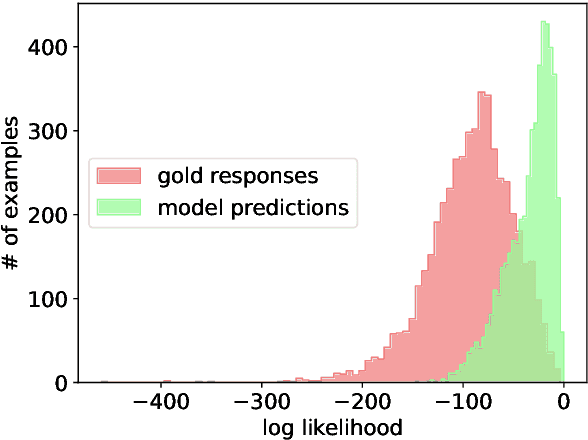
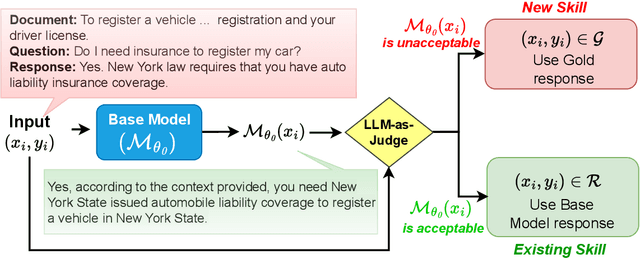
Abstract:Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) on specific datasets is a common practice to improve performance on target tasks. However, this performance gain often leads to overfitting, where the model becomes too specialized in either the task or the characteristics of the training data, resulting in a loss of generalization. This paper introduces Selective Self-Rehearsal (SSR), a fine-tuning approach that achieves performance comparable to the standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) while improving generalization. SSR leverages the fact that there can be multiple valid responses to a query. By utilizing the model's correct responses, SSR reduces model specialization during the fine-tuning stage. SSR first identifies the correct model responses from the training set by deploying an appropriate LLM as a judge. Then, it fine-tunes the model using the correct model responses and the gold response for the remaining samples. The effectiveness of SSR is demonstrated through experiments on the task of identifying unanswerable queries across various datasets. The results show that standard SFT can lead to an average performance drop of up to $16.7\%$ on multiple benchmarks, such as MMLU and TruthfulQA. In contrast, SSR results in close to $2\%$ drop on average, indicating better generalization capabilities compared to standard SFT.
Granite-Function Calling Model: Introducing Function Calling Abilities via Multi-task Learning of Granular Tasks
Jun 27, 2024


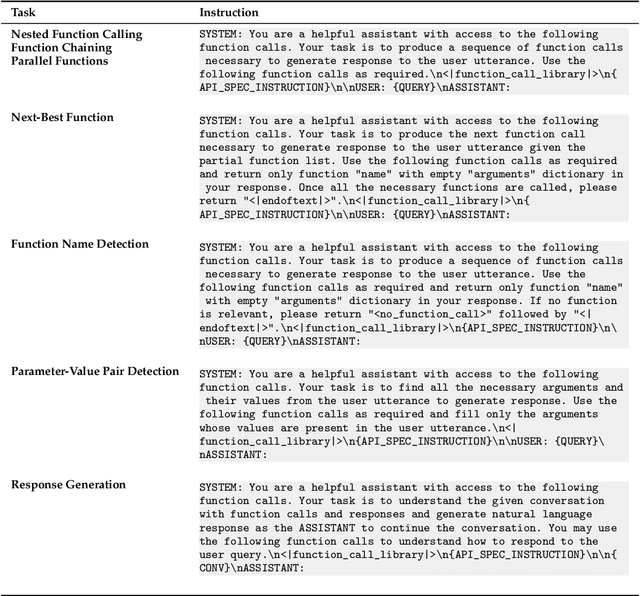
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently shown tremendous promise in serving as the backbone to agentic systems, as demonstrated by their performance in multi-faceted, challenging benchmarks like SWE-Bench and Agent-Bench. However, to realize the true potential of LLMs as autonomous agents, they must learn to identify, call, and interact with external tools and application program interfaces (APIs) to complete complex tasks. These tasks together are termed function calling. Endowing LLMs with function calling abilities leads to a myriad of advantages, such as access to current and domain-specific information in databases and knowledge sources, and the ability to outsource tasks that can be reliably performed by tools, e.g., a Python interpreter or calculator. While there has been significant progress in function calling with LLMs, there is still a dearth of open models that perform on par with proprietary LLMs like GPT, Claude, and Gemini. Therefore, in this work, we introduce the GRANITE-20B-FUNCTIONCALLING model under an Apache 2.0 license. The model is trained using a multi-task training approach on seven fundamental tasks encompassed in function calling, those being Nested Function Calling, Function Chaining, Parallel Functions, Function Name Detection, Parameter-Value Pair Detection, Next-Best Function, and Response Generation. We present a comprehensive evaluation on multiple out-of-domain datasets comparing GRANITE-20B-FUNCTIONCALLING to more than 15 other best proprietary and open models. GRANITE-20B-FUNCTIONCALLING provides the best performance among all open models on the Berkeley Function Calling Leaderboard and fourth overall. As a result of the diverse tasks and datasets used for training our model, we show that GRANITE-20B-FUNCTIONCALLING has better generalizability on multiple tasks in seven different evaluation datasets.
Synergizing In-context Learning with Hints for End-to-end Task-oriented Dialog Systems
May 24, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLM) based end-to-end task-oriented dialog (TOD) systems built using few-shot (in-context) learning perform better than supervised models only when the train data is limited. This is due to the inherent ability of LLMs to learn any task with just a few demonstrations. As the number of train dialogs increases, supervised SoTA models surpass in-context learning LLMs as they learn to better align with the style of the system responses in the training data, which LLMs struggle to mimic. In response, we propose SyncTOD, which synergizes LLMs with useful hints about the task for improved alignment. At a high level, SyncTOD trains auxiliary models to provide these hints and select exemplars for the in-context prompts. With ChatGPT, SyncTOD achieves superior performance compared to LLM-based baselines and SoTA models in low-data settings, while retaining competitive performance in full-data settings
Few shot chain-of-thought driven reasoning to prompt LLMs for open ended medical question answering
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:Large Language models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in transforming healthcare by automating tasks such as clinical documentation, information retrieval, and decision support. In this aspect, carefully engineered prompts have emerged as a powerful tool for using LLMs for medical scenarios, e.g., patient clinical scenarios. In this paper, we propose a modified version of the MedQA-USMLE dataset, which is subjective, to mimic real-life clinical scenarios. We explore the Chain of Thought (CoT) reasoning based on subjective response generation for the modified MedQA-USMLE dataset with appropriate LM-driven forward reasoning for correct responses to the medical questions. Keeping in mind the importance of response verification in the medical setting, we utilize a reward training mechanism whereby the language model also provides an appropriate verified response for a particular response to a clinical question. In this regard, we also include human-in-the-loop for different evaluation aspects. We develop better in-contrast learning strategies by modifying the 5-shot-codex-CoT-prompt from arXiv:2207.08143 for the subjective MedQA dataset and developing our incremental-reasoning prompt. Our evaluations show that the incremental reasoning prompt performs better than the modified codex prompt in certain scenarios. We also show that greedy decoding with the incremental reasoning method performs better than other strategies, such as prompt chaining and eliminative reasoning.
BRAIn: Bayesian Reward-conditioned Amortized Inference for natural language generation from feedback
Feb 04, 2024



Abstract:Following the success of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) for Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), new techniques such as Sequence Likelihood Calibration (SLiC) and Direct Policy Optimization (DPO) have been proposed that are offline in nature and use rewards in an indirect manner. These techniques, in particular DPO, have recently become the tools of choice for LLM alignment due to their scalability and performance. However, they leave behind important features of the PPO approach. Methods such as SLiC or RRHF make use of the Reward Model (RM) only for ranking/preference, losing fine-grained information and ignoring the parametric form of the RM (eg., Bradley-Terry, Plackett-Luce), while methods such as DPO do not use even a separate reward model. In this work, we propose a novel approach, named BRAIn, that re-introduces the RM as part of a distribution matching approach.BRAIn considers the LLM distribution conditioned on the assumption of output goodness and applies Bayes theorem to derive an intractable posterior distribution where the RM is explicitly represented. BRAIn then distills this posterior into an amortized inference network through self-normalized importance sampling, leading to a scalable offline algorithm that significantly outperforms prior art in summarization and AntropicHH tasks. BRAIn also has interesting connections to PPO and DPO for specific RM choices.
DKAF: KB Arbitration for Learning Task-Oriented Dialog Systems with Dialog-KB Inconsistencies
May 26, 2023



Abstract:Task-oriented dialog (TOD) agents often ground their responses on external knowledge bases (KBs). These KBs can be dynamic and may be updated frequently. Existing approaches for learning TOD agents assume the KB snapshot contemporary to each individual dialog is available during training. However, in real-world scenarios, only the latest KB snapshot is available during training and as a result, the train dialogs may contain facts conflicting with the latest KB. These dialog-KB inconsistencies in the training data may potentially confuse the TOD agent learning algorithm. In this work, we define the novel problem of learning a TOD agent with dialog-KB inconsistencies in the training data. We propose a Dialog-KB Arbitration Framework (DKAF) which reduces the dialog-KB inconsistencies by predicting the contemporary KB snapshot for each train dialog. These predicted KB snapshots are then used for training downstream TOD agents. As there are no existing datasets with dialog-KB inconsistencies, we systematically introduce inconsistencies in two publicly available dialog datasets. We show that TOD agents trained with DKAF perform better than existing baselines on both these datasets
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge