Dianbing Xi
PFAvatar: Pose-Fusion 3D Personalized Avatar Reconstruction from Real-World Outfit-of-the-Day Photos
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:We propose PFAvatar (Pose-Fusion Avatar), a new method that reconstructs high-quality 3D avatars from Outfit of the Day(OOTD) photos, which exhibit diverse poses, occlusions, and complex backgrounds. Our method consists of two stages: (1) fine-tuning a pose-aware diffusion model from few-shot OOTD examples and (2) distilling a 3D avatar represented by a neural radiance field (NeRF). In the first stage, unlike previous methods that segment images into assets (e.g., garments, accessories) for 3D assembly, which is prone to inconsistency, we avoid decomposition and directly model the full-body appearance. By integrating a pre-trained ControlNet for pose estimation and a novel Condition Prior Preservation Loss (CPPL), our method enables end-to-end learning of fine details while mitigating language drift in few-shot training. Our method completes personalization in just 5 minutes, achieving a 48x speed-up compared to previous approaches. In the second stage, we introduce a NeRF-based avatar representation optimized by canonical SMPL-X space sampling and Multi-Resolution 3D-SDS. Compared to mesh-based representations that suffer from resolution-dependent discretization and erroneous occluded geometry, our continuous radiance field can preserve high-frequency textures (e.g., hair) and handle occlusions correctly through transmittance. Experiments demonstrate that PFAvatar outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of reconstruction fidelity, detail preservation, and robustness to occlusions/truncations, advancing practical 3D avatar generation from real-world OOTD albums. In addition, the reconstructed 3D avatar supports downstream applications such as virtual try-on, animation, and human video reenactment, further demonstrating the versatility and practical value of our approach.
OmniVDiff: Omni Controllable Video Diffusion for Generation and Understanding
Apr 15, 2025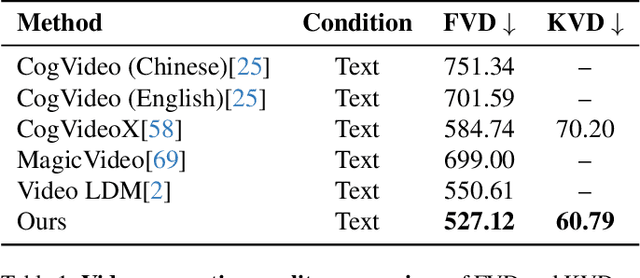
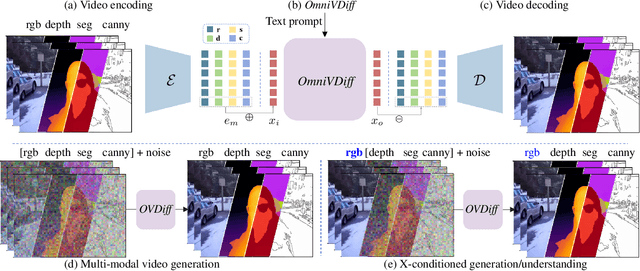
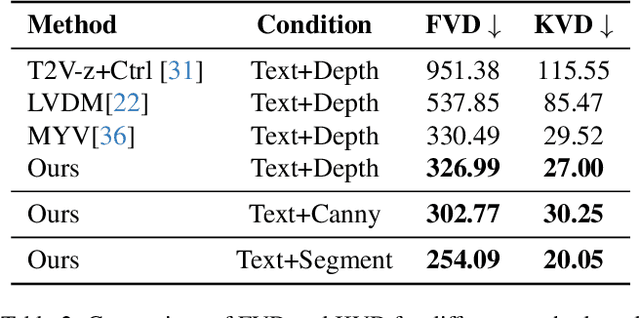

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel framework for controllable video diffusion, OmniVDiff, aiming to synthesize and comprehend multiple video visual content in a single diffusion model. To achieve this, OmniVDiff treats all video visual modalities in the color space to learn a joint distribution, while employing an adaptive control strategy that dynamically adjusts the role of each visual modality during the diffusion process, either as a generation modality or a conditioning modality. This allows flexible manipulation of each modality's role, enabling support for a wide range of tasks. Consequently, our model supports three key functionalities: (1) Text-conditioned video generation: multi-modal visual video sequences (i.e., rgb, depth, canny, segmentaion) are generated based on the text conditions in one diffusion process; (2) Video understanding: OmniVDiff can estimate the depth, canny map, and semantic segmentation across the input rgb frames while ensuring coherence with the rgb input; and (3) X-conditioned video generation: OmniVDiff generates videos conditioned on fine-grained attributes (e.g., depth maps or segmentation maps). By integrating these diverse tasks into a unified video diffusion framework, OmniVDiff enhances the flexibility and scalability for controllable video diffusion, making it an effective tool for a variety of downstream applications, such as video-to-video translation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, highlighting its potential for various video-related applications.
SGW-based Multi-Task Learning in Vision Tasks
Oct 03, 2024Abstract:Multi-task-learning(MTL) is a multi-target optimization task. Neural networks try to realize each target using a shared interpretative space within MTL. However, as the scale of datasets expands and the complexity of tasks increases, knowledge sharing becomes increasingly challenging. In this paper, we first re-examine previous cross-attention MTL methods from the perspective of noise. We theoretically analyze this issue and identify it as a flaw in the cross-attention mechanism. To address this issue, we propose an information bottleneck knowledge extraction module (KEM). This module aims to reduce inter-task interference by constraining the flow of information, thereby reducing computational complexity. Furthermore, we have employed neural collapse to stabilize the knowledge-selection process. That is, before input to KEM, we projected the features into ETF space. This mapping makes our method more robust. We implemented and conducted comparative experiments with this method on multiple datasets. The results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing methods in multi-task learning.
MIRReS: Multi-bounce Inverse Rendering using Reservoir Sampling
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:We present MIRReS, a novel two-stage inverse rendering framework that jointly reconstructs and optimizes the explicit geometry, material, and lighting from multi-view images. Unlike previous methods that rely on implicit irradiance fields or simplified path tracing algorithms, our method extracts an explicit geometry (triangular mesh) in stage one, and introduces a more realistic physically-based inverse rendering model that utilizes multi-bounce path tracing and Monte Carlo integration. By leveraging multi-bounce path tracing, our method effectively estimates indirect illumination, including self-shadowing and internal reflections, which improves the intrinsic decomposition of shape, material, and lighting. Moreover, we incorporate reservoir sampling into our framework to address the noise in Monte Carlo integration, enhancing convergence and facilitating gradient-based optimization with low sample counts. Through qualitative and quantitative evaluation of several scenarios, especially in challenging scenarios with complex shadows, we demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on decomposition results. Additionally, our optimized explicit geometry enables applications such as scene editing, relighting, and material editing with modern graphics engines or CAD software. The source code is available at https://brabbitdousha.github.io/MIRReS/
I$^2$-SDF: Intrinsic Indoor Scene Reconstruction and Editing via Raytracing in Neural SDFs
Mar 29, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we present I$^2$-SDF, a new method for intrinsic indoor scene reconstruction and editing using differentiable Monte Carlo raytracing on neural signed distance fields (SDFs). Our holistic neural SDF-based framework jointly recovers the underlying shapes, incident radiance and materials from multi-view images. We introduce a novel bubble loss for fine-grained small objects and error-guided adaptive sampling scheme to largely improve the reconstruction quality on large-scale indoor scenes. Further, we propose to decompose the neural radiance field into spatially-varying material of the scene as a neural field through surface-based, differentiable Monte Carlo raytracing and emitter semantic segmentations, which enables physically based and photorealistic scene relighting and editing applications. Through a number of qualitative and quantitative experiments, we demonstrate the superior quality of our method on indoor scene reconstruction, novel view synthesis, and scene editing compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
Learning-based Inverse Rendering of Complex Indoor Scenes with Differentiable Monte Carlo Raytracing
Nov 06, 2022



Abstract:Indoor scenes typically exhibit complex, spatially-varying appearance from global illumination, making inverse rendering a challenging ill-posed problem. This work presents an end-to-end, learning-based inverse rendering framework incorporating differentiable Monte Carlo raytracing with importance sampling. The framework takes a single image as input to jointly recover the underlying geometry, spatially-varying lighting, and photorealistic materials. Specifically, we introduce a physically-based differentiable rendering layer with screen-space ray tracing, resulting in more realistic specular reflections that match the input photo. In addition, we create a large-scale, photorealistic indoor scene dataset with significantly richer details like complex furniture and dedicated decorations. Further, we design a novel out-of-view lighting network with uncertainty-aware refinement leveraging hypernetwork-based neural radiance fields to predict lighting outside the view of the input photo. Through extensive evaluations on common benchmark datasets, we demonstrate superior inverse rendering quality of our method compared to state-of-the-art baselines, enabling various applications such as complex object insertion and material editing with high fidelity. Code and data will be made available at \url{https://jingsenzhu.github.io/invrend}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge