Di Sun
VP-MEL: Visual Prompts Guided Multimodal Entity Linking
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal Entity Linking (MEL) is extensively utilized in the domains of information retrieval. However, existing MEL methods typically utilize mention words as mentions for retrieval. This results in a significant dependence of MEL on mention words, thereby constraining its capacity to effectively leverage information from both images and text. In situations where mention words are absent, MEL methods struggle to leverage image-text pairs for entity linking. To solve these issues, we introduce a Visual Prompts guided Multimodal Entity Linking (VP-MEL) task. VP-MEL directly marks specific regions within the image. These markers are referred to as visual prompts in VP-MEL. Without mention words, VP-MEL aims to utilize marked image-text pairs to align visual prompts with specific entities in the knowledge bases. A new dataset for the VP-MEL task, VPWiki, is proposed in this paper. Moreover, we propose a framework named FBMEL, which enhances the significance of visual prompts and fully leverages the information in image-text pairs. Experimental results on the VPWiki dataset demonstrate that FBMEL outperforms baseline methods across multiple benchmarks for the VP-MEL task.
VisAidMath: Benchmarking Visual-Aided Mathematical Reasoning
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Although previous research on large language models (LLMs) and large multi-modal models (LMMs) has systematically explored mathematical problem-solving (MPS) within visual contexts, the analysis of how these models process visual information during problem-solving remains insufficient. To address this gap, we present VisAidMath, a benchmark for evaluating the MPS process related to visual information. We follow a rigorous data curation pipeline involving both automated processes and manual annotations to ensure data quality and reliability. Consequently, this benchmark includes 1,200 challenging problems from various mathematical branches, vision-aid formulations, and difficulty levels, collected from diverse sources such as textbooks, examination papers, and Olympiad problems. Based on the proposed benchmark, we conduct comprehensive evaluations on ten mainstream LLMs and LMMs, highlighting deficiencies in the visual-aided reasoning process. For example, GPT-4V only achieves 45.33% accuracy in the visual-aided reasoning task, even with a drop of 2 points when provided with golden visual aids. In-depth analysis reveals that the main cause of deficiencies lies in hallucination regarding the implicit visual reasoning process, shedding light on future research directions in the visual-aided MPS process.
Sewer Image Super-Resolution with Depth Priors and Its Lightweight Network
Jul 27, 2024



Abstract:The Quick-view (QV) technique serves as a primary method for detecting defects within sewerage systems. However, the effectiveness of QV is impeded by the limited visual range of its hardware, resulting in suboptimal image quality for distant portions of the sewer network. Image super-resolution is an effective way to improve image quality and has been applied in a variety of scenes. However, research on super-resolution for sewer images remains considerably unexplored. In response, this study leverages the inherent depth relationships present within QV images and introduces a novel Depth-guided, Reference-based Super-Resolution framework denoted as DSRNet. It comprises two core components: a depth extraction module and a depth information matching module (DMM). DSRNet utilizes the adjacent frames of the low-resolution image as reference images and helps them recover texture information based on the correlation. By combining these modules, the integration of depth priors significantly enhances both visual quality and performance benchmarks. Besides, in pursuit of computational efficiency and compactness, our paper introduces a super-resolution knowledge distillation model based on an attention mechanism. This mechanism facilitates the acquisition of feature similarity between a more complex teacher model and a streamlined student model, the latter being a lightweight version of DSRNet. Experimental results demonstrate that DSRNet significantly improves PSNR and SSIM compared with other methods. This study also conducts experiments on sewer defect semantic segmentation, object detection, and classification on the Pipe dataset and Sewer-ML dataset. Experiments show that the method can improve the performance of low-resolution sewer images in these tasks.
Advancing Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition via LLM-Based Reformulation and Box-Based Segmentation
Jun 11, 2024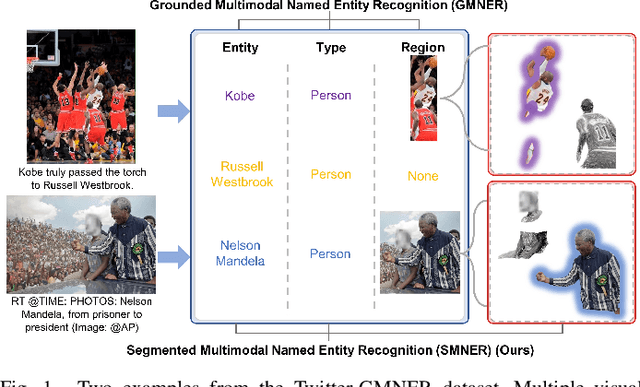
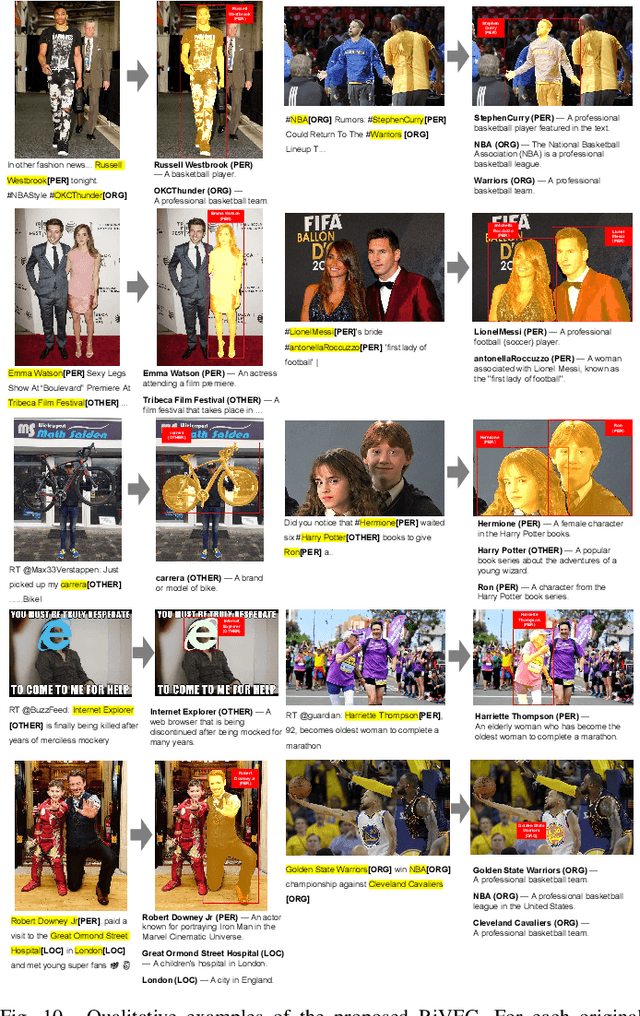
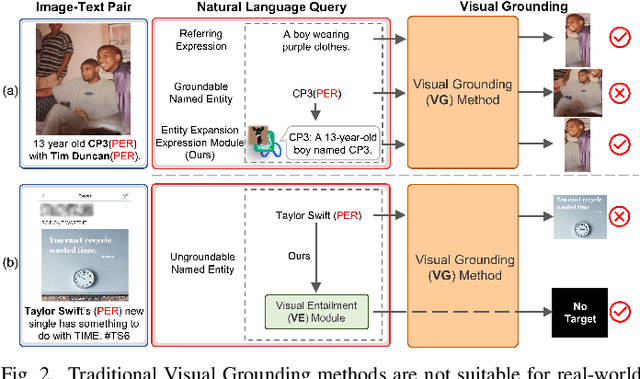
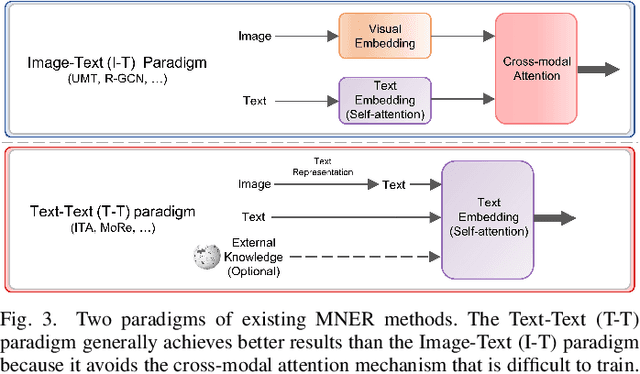
Abstract:Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) task aims to identify named entities, entity types and their corresponding visual regions. GMNER task exhibits two challenging attributes: 1) The tenuous correlation between images and text on social media contributes to a notable proportion of named entities being ungroundable. 2) There exists a distinction between coarse-grained noun phrases used in similar tasks (e.g., phrase localization) and fine-grained named entities. In this paper, we propose RiVEG, a unified framework that reformulates GMNER into a joint MNER-VE-VG task by leveraging large language models (LLMs) as connecting bridges. This reformulation brings two benefits: 1) It enables us to optimize the MNER module for optimal MNER performance and eliminates the need to pre-extract region features using object detection methods, thus naturally addressing the two major limitations of existing GMNER methods. 2) The introduction of Entity Expansion Expression module and Visual Entailment (VE) module unifies Visual Grounding (VG) and Entity Grounding (EG). This endows the proposed framework with unlimited data and model scalability. Furthermore, to address the potential ambiguity stemming from the coarse-grained bounding box output in GMNER, we further construct the new Segmented Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (SMNER) task and corresponding Twitter-SMNER dataset aimed at generating fine-grained segmentation masks, and experimentally demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of using box prompt-based Segment Anything Model (SAM) to empower any GMNER model with the ability to accomplish the SMNER task. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RiVEG significantly outperforms SoTA methods on four datasets across the MNER, GMNER, and SMNER tasks.
LOGO: Video Text Spotting with Language Collaboration and Glyph Perception Model
May 29, 2024Abstract:Video text spotting aims to simultaneously localize, recognize and track text instances in videos. To address the limited recognition capability of end-to-end methods, tracking the zero-shot results of state-of-the-art image text spotters directly can achieve impressive performance. However, owing to the domain gap between different datasets, these methods usually obtain limited tracking trajectories on extreme dataset. Fine-tuning transformer-based text spotters on specific datasets could yield performance enhancements, albeit at the expense of considerable training resources. In this paper, we propose a Language Collaboration and Glyph Perception Model, termed LOGO to enhance the performance of conventional text spotters through the integration of a synergy module. To achieve this goal, a language synergy classifier (LSC) is designed to explicitly discern text instances from background noise in the recognition stage. Specially, the language synergy classifier can output text content or background code based on the legibility of text regions, thus computing language scores. Subsequently, fusion scores are computed by taking the average of detection scores and language scores, and are utilized to re-score the detection results before tracking. By the re-scoring mechanism, the proposed LSC facilitates the detection of low-resolution text instances while filtering out text-like regions. Besides, the glyph supervision and visual position mixture module are proposed to enhance the recognition accuracy of noisy text regions, and acquire more discriminative tracking features, respectively. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
LLMs as Bridges: Reformulating Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition
Feb 17, 2024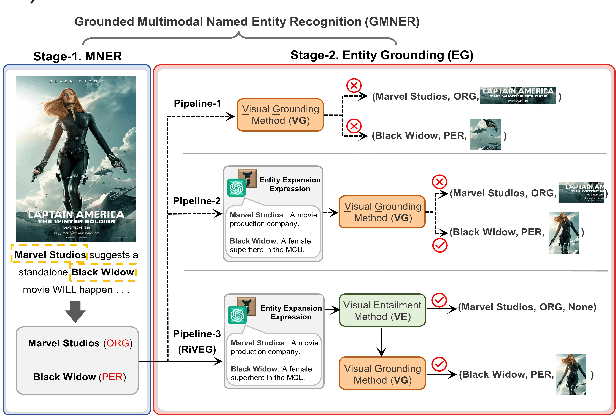
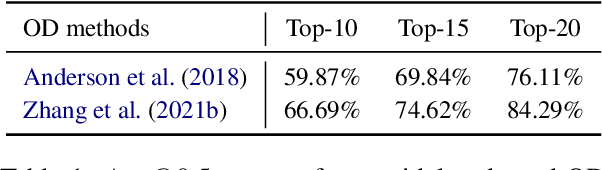
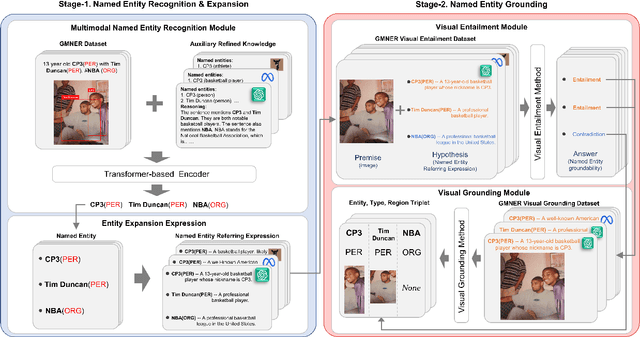

Abstract:Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) is a nascent multimodal task that aims to identify named entities, entity types and their corresponding visual regions. GMNER task exhibits two challenging properties: 1) The weak correlation between image-text pairs in social media results in a significant portion of named entities being ungroundable. 2) There exists a distinction between coarse-grained referring expressions commonly used in similar tasks (e.g., phrase localization, referring expression comprehension) and fine-grained named entities. In this paper, we propose RiVEG, a unified framework that reformulates GMNER into a joint MNER-VE-VG task by leveraging large language models (LLMs) as a connecting bridge. This reformulation brings two benefits: 1) It maintains the optimal MNER performance and eliminates the need for employing object detection methods to pre-extract regional features, thereby naturally addressing two major limitations of existing GMNER methods. 2) The introduction of entity expansion expression and Visual Entailment (VE) Module unifies Visual Grounding (VG) and Entity Grounding (EG). It enables RiVEG to effortlessly inherit the Visual Entailment and Visual Grounding capabilities of any current or prospective multimodal pretraining models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RiVEG outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the existing GMNER dataset and achieves absolute leads of 10.65%, 6.21%, and 8.83% in all three subtasks.
Experimental Investigation on the Friction-induced Vibration with Periodic Characteristics in a Running-in Process under Lubrication
Nov 24, 2021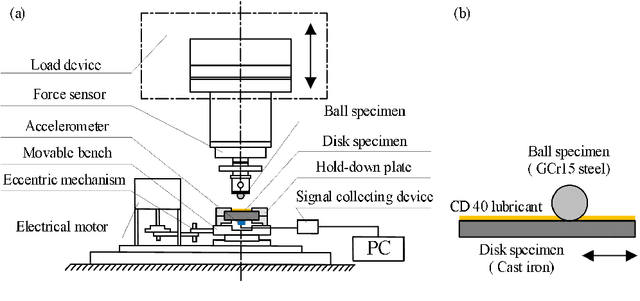
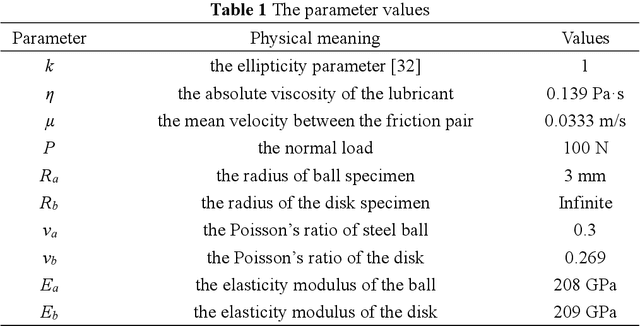
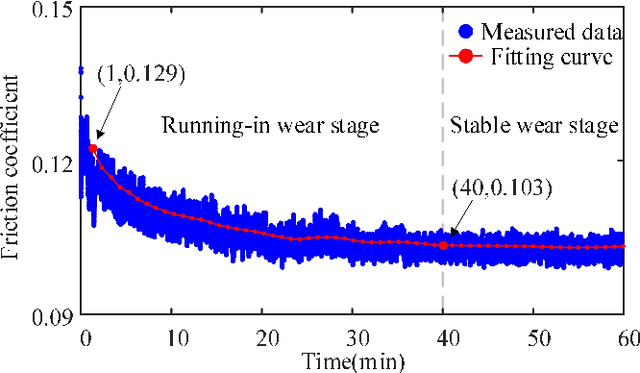
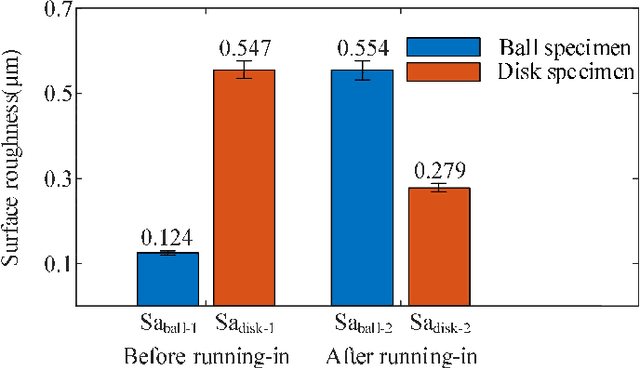
Abstract:This paper investigated the friction-induced vibration (FIV) behavior under the running-in process with oil lubrication. The FIV signal with periodic characteristics under lubrication was identified with the help of the squeal signal induced in an oil-free wear experiment and then extracted by the harmonic wavelet packet transform (HWPT). The variation of the FIV signal from running-in wear stage to steady wear stage was studied by its root mean square (RMS) values. The result indicates that the time-frequency characteristics of the FIV signals evolve with the wear process and can reflect the wear stages of the friction pairs. The RMS evolvement of the FIV signal is in the same trend to the composite surface roughness and demonstrates that the friction pair goes through the running-in wear stage and the steady wear stage. Therefore, the FIV signal with periodic characteristics can describe the evolvement of the running-in process and distinguish the running-in wear stage and the stable wear stage of the friction pair.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge