Dario Oliveira
Steve
i-WiViG: Interpretable Window Vision GNN
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models based on graph neural networks have emerged as a popular approach for solving computer vision problems. They encode the image into a graph structure and can be beneficial for efficiently capturing the long-range dependencies typically present in remote sensing imagery. However, an important drawback of these methods is their black-box nature which may hamper their wider usage in critical applications. In this work, we tackle the self-interpretability of the graph-based vision models by proposing our Interpretable Window Vision GNN (i-WiViG) approach, which provides explanations by automatically identifying the relevant subgraphs for the model prediction. This is achieved with window-based image graph processing that constrains the node receptive field to a local image region and by using a self-interpretable graph bottleneck that ranks the importance of the long-range relations between the image regions. We evaluate our approach to remote sensing classification and regression tasks, showing it achieves competitive performance while providing inherent and faithful explanations through the identified relations. Further, the quantitative evaluation reveals that our model reduces the infidelity of post-hoc explanations compared to other Vision GNN models, without sacrificing explanation sparsity.
Contrastive Pretraining for Visual Concept Explanations of Socioeconomic Outcomes
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Predicting socioeconomic indicators from satellite imagery with deep learning has become an increasingly popular research direction. Post-hoc concept-based explanations can be an important step towards broader adoption of these models in policy-making as they enable the interpretation of socioeconomic outcomes based on visual concepts that are intuitive to humans. In this paper, we study the interplay between representation learning using an additional task-specific contrastive loss and post-hoc concept explainability for socioeconomic studies. Our results on two different geographical locations and tasks indicate that the task-specific pretraining imposes a continuous ordering of the latent space embeddings according to the socioeconomic outcomes. This improves the model's interpretability as it enables the latent space of the model to associate urban concepts with continuous intervals of socioeconomic outcomes. Further, we illustrate how analyzing the model's conceptual sensitivity for the intervals of socioeconomic outcomes can shed light on new insights for urban studies.
Opening the Black-Box: A Systematic Review on Explainable AI in Remote Sensing
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:In recent years, black-box machine learning approaches have become a dominant modeling paradigm for knowledge extraction in Remote Sensing. Despite the potential benefits of uncovering the inner workings of these models with explainable AI, a comprehensive overview summarizing the used explainable AI methods and their objectives, findings, and challenges in Remote Sensing applications is still missing. In this paper, we address this issue by performing a systematic review to identify the key trends of how explainable AI is used in Remote Sensing and shed light on novel explainable AI approaches and emerging directions that tackle specific Remote Sensing challenges. We also reveal the common patterns of explanation interpretation, discuss the extracted scientific insights in Remote Sensing, and reflect on the approaches used for explainable AI methods evaluation. Our review provides a complete summary of the state-of-the-art in the field. Further, we give a detailed outlook on the challenges and promising research directions, representing a basis for novel methodological development and a useful starting point for new researchers in the field of explainable AI in Remote Sensing.
Foundation Models for Generalist Geospatial Artificial Intelligence
Nov 08, 2023Abstract:Significant progress in the development of highly adaptable and reusable Artificial Intelligence (AI) models is expected to have a significant impact on Earth science and remote sensing. Foundation models are pre-trained on large unlabeled datasets through self-supervision, and then fine-tuned for various downstream tasks with small labeled datasets. This paper introduces a first-of-a-kind framework for the efficient pre-training and fine-tuning of foundational models on extensive geospatial data. We have utilized this framework to create Prithvi, a transformer-based geospatial foundational model pre-trained on more than 1TB of multispectral satellite imagery from the Harmonized Landsat-Sentinel 2 (HLS) dataset. Our study demonstrates the efficacy of our framework in successfully fine-tuning Prithvi to a range of Earth observation tasks that have not been tackled by previous work on foundation models involving multi-temporal cloud gap imputation, flood mapping, wildfire scar segmentation, and multi-temporal crop segmentation. Our experiments show that the pre-trained model accelerates the fine-tuning process compared to leveraging randomly initialized weights. In addition, pre-trained Prithvi compares well against the state-of-the-art, e.g., outperforming a conditional GAN model in multi-temporal cloud imputation by up to 5pp (or 5.7%) in the structural similarity index. Finally, due to the limited availability of labeled data in the field of Earth observation, we gradually reduce the quantity of available labeled data for refining the model to evaluate data efficiency and demonstrate that data can be decreased significantly without affecting the model's accuracy. The pre-trained 100 million parameter model and corresponding fine-tuning workflows have been released publicly as open source contributions to the global Earth sciences community through Hugging Face.
A modular framework for extreme weather generation
Feb 05, 2021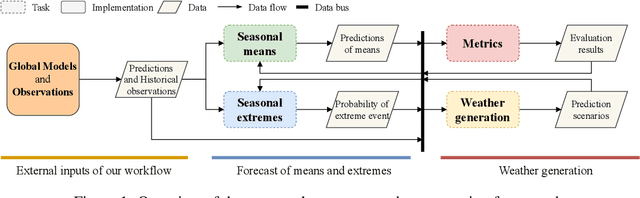
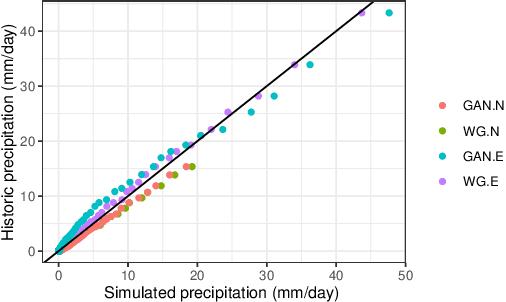
Abstract:Extreme weather events have an enormous impact on society and are expected to become more frequent and severe with climate change. In this context, resilience planning becomes crucial for risk mitigation and coping with these extreme events. Machine learning techniques can play a critical role in resilience planning through the generation of realistic extreme weather event scenarios that can be used to evaluate possible mitigation actions. This paper proposes a modular framework that relies on interchangeable components to produce extreme weather event scenarios. We discuss possible alternatives for each of the components and show initial results comparing two approaches on the task of generating precipitation scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge