Lars Pennig
Regress, Don't Guess -- A Regression-like Loss on Number Tokens for Language Models
Nov 04, 2024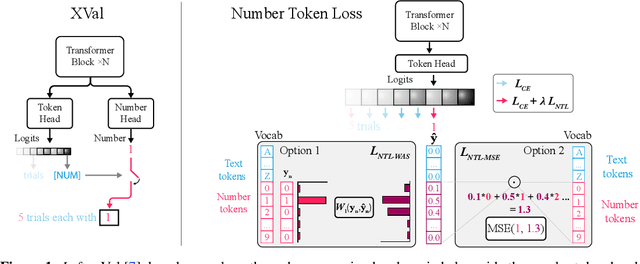
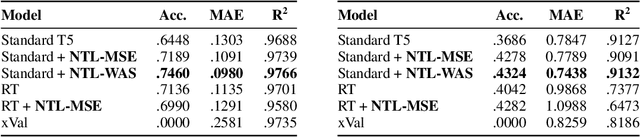
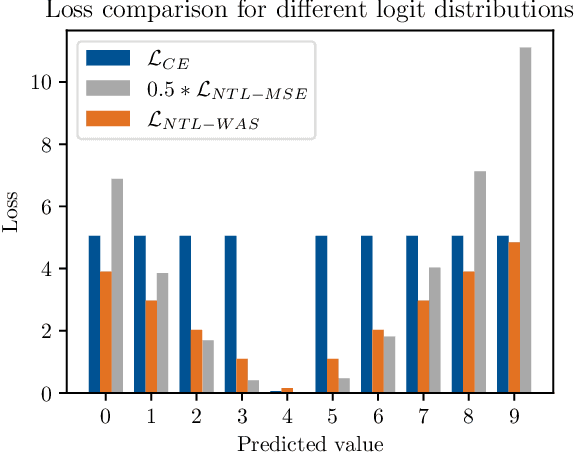
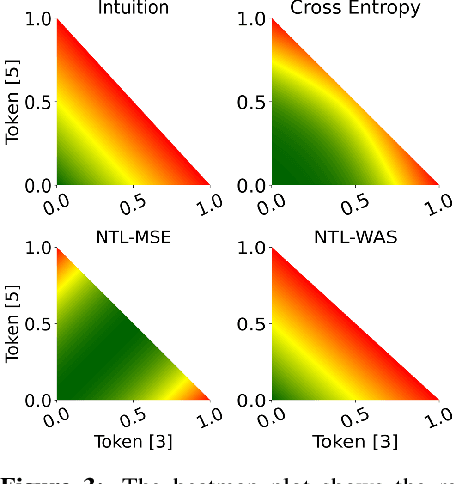
Abstract:While language models have exceptional capabilities at text generation, they lack a natural inductive bias for emitting numbers and thus struggle in tasks involving reasoning over quantities, especially arithmetics. This has particular relevance in scientific datasets where combinations of text and numerical data are abundant. One fundamental limitation is the nature of the CE loss, which assumes a nominal (categorical) scale and thus cannot convey proximity between generated number tokens. As a remedy, we here present two versions of a number token loss. The first is based on an $L_p$ loss between the ground truth token value and the weighted sum of the predicted class probabilities. The second loss minimizes the Wasserstein-1 distance between the distribution of the predicted output probabilities and the ground truth distribution. These regression-like losses can easily be added to any language model and extend the CE objective during training. We compare the proposed schemes on a mathematics dataset against existing tokenization, encoding, and decoding schemes for improving number representation in language models. Our results reveal a significant improvement in numerical accuracy when equipping a standard T5 model with the proposed loss schemes.
Contrastive Pretraining for Visual Concept Explanations of Socioeconomic Outcomes
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:Predicting socioeconomic indicators from satellite imagery with deep learning has become an increasingly popular research direction. Post-hoc concept-based explanations can be an important step towards broader adoption of these models in policy-making as they enable the interpretation of socioeconomic outcomes based on visual concepts that are intuitive to humans. In this paper, we study the interplay between representation learning using an additional task-specific contrastive loss and post-hoc concept explainability for socioeconomic studies. Our results on two different geographical locations and tasks indicate that the task-specific pretraining imposes a continuous ordering of the latent space embeddings according to the socioeconomic outcomes. This improves the model's interpretability as it enables the latent space of the model to associate urban concepts with continuous intervals of socioeconomic outcomes. Further, we illustrate how analyzing the model's conceptual sensitivity for the intervals of socioeconomic outcomes can shed light on new insights for urban studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge