Chenwei Xu
Yifan
LLM-based Text Simplification and its Effect on User Comprehension and Cognitive Load
May 04, 2025Abstract:Information on the web, such as scientific publications and Wikipedia, often surpasses users' reading level. To help address this, we used a self-refinement approach to develop a LLM capability for minimally lossy text simplification. To validate our approach, we conducted a randomized study involving 4563 participants and 31 texts spanning 6 broad subject areas: PubMed (biomedical scientific articles), biology, law, finance, literature/philosophy, and aerospace/computer science. Participants were randomized to viewing original or simplified texts in a subject area, and answered multiple-choice questions (MCQs) that tested their comprehension of the text. The participants were also asked to provide qualitative feedback such as task difficulty. Our results indicate that participants who read the simplified text answered more MCQs correctly than their counterparts who read the original text (3.9% absolute increase, p<0.05). This gain was most striking with PubMed (14.6%), while more moderate gains were observed for finance (5.5%), aerospace/computer science (3.8%) domains, and legal (3.5%). Notably, the results were robust to whether participants could refer back to the text while answering MCQs. The absolute accuracy decreased by up to ~9% for both original and simplified setups where participants could not refer back to the text, but the ~4% overall improvement persisted. Finally, participants' self-reported perceived ease based on a simplified NASA Task Load Index was greater for those who read the simplified text (absolute change on a 5-point scale 0.33, p<0.05). This randomized study, involving an order of magnitude more participants than prior works, demonstrates the potential of LLMs to make complex information easier to understand. Our work aims to enable a broader audience to better learn and make use of expert knowledge available on the web, improving information accessibility.
Adaptive Batch Size Schedules for Distributed Training of Language Models with Data and Model Parallelism
Dec 30, 2024
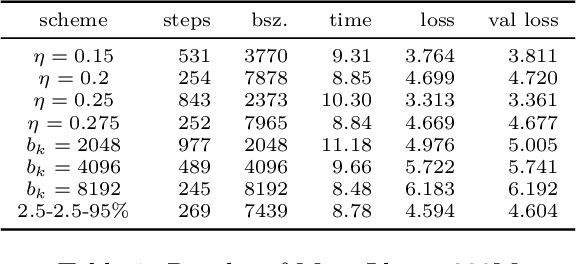

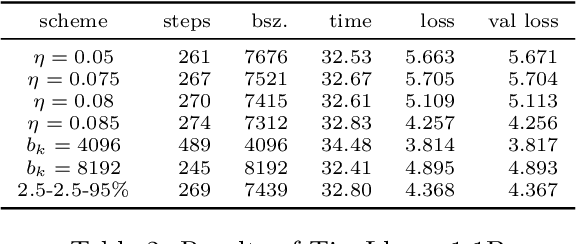
Abstract:An appropriate choice of batch sizes in large-scale model training is crucial, yet it involves an intrinsic yet inevitable dilemma: large-batch training improves training efficiency in terms of memory utilization, while generalization performance often deteriorates due to small amounts of gradient noise. Despite this dilemma, the common practice of choosing batch sizes in language model training often prioritizes training efficiency -- employing either constant large sizes with data parallelism or implementing batch size warmup schedules. However, such batch size schedule designs remain heuristic and often fail to adapt to training dynamics, presenting the challenge of designing adaptive batch size schedules. Given the abundance of available datasets and the data-hungry nature of language models, data parallelism has become an indispensable distributed training paradigm, enabling the use of larger batch sizes for gradient computation. However, vanilla data parallelism requires replicas of model parameters, gradients, and optimizer states at each worker, which prohibits training larger models with billions of parameters. To optimize memory usage, more advanced parallelism strategies must be employed. In this work, we propose general-purpose and theoretically principled adaptive batch size schedules compatible with data parallelism and model parallelism. We develop a practical implementation with PyTorch Fully Sharded Data Parallel, facilitating the pretraining of language models of different sizes. We empirically demonstrate that our proposed approaches outperform constant batch sizes and heuristic batch size warmup schedules in the pretraining of models in the Llama family, with particular focus on smaller models with up to 3 billion parameters. We also establish theoretical convergence guarantees for such adaptive batch size schedules with Adam for general smooth nonconvex objectives.
AlignAb: Pareto-Optimal Energy Alignment for Designing Nature-Like Antibodies
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:We present a three-stage framework for training deep learning models specializing in antibody sequence-structure co-design. We first pre-train a language model using millions of antibody sequence data. Then, we employ the learned representations to guide the training of a diffusion model for joint optimization over both sequence and structure of antibodies. During the final alignment stage, we optimize the model to favor antibodies with low repulsion and high attraction to the antigen binding site, enhancing the rationality and functionality of the designs. To mitigate conflicting energy preferences, we extend AbDPO (Antibody Direct Preference Optimization) to guide the model towards Pareto optimality under multiple energy-based alignment objectives. Furthermore, we adopt an iterative learning paradigm with temperature scaling, enabling the model to benefit from diverse online datasets without requiring additional data. In practice, our proposed methods achieve high stability and efficiency in producing a better Pareto front of antibody designs compared to top samples generated by baselines and previous alignment techniques. Through extensive experiments, we showcase the superior performance of our methods in generating nature-like antibodies with high binding affinity consistently.
Communication-Efficient Adaptive Batch Size Strategies for Distributed Local Gradient Methods
Jun 20, 2024



Abstract:Modern deep neural networks often require distributed training with many workers due to their large size. As worker numbers increase, communication overheads become the main bottleneck in data-parallel minibatch stochastic gradient methods with per-iteration gradient synchronization. Local gradient methods like Local SGD reduce communication by only syncing after several local steps. Despite understanding their convergence in i.i.d. and heterogeneous settings and knowing the importance of batch sizes for efficiency and generalization, optimal local batch sizes are difficult to determine. We introduce adaptive batch size strategies for local gradient methods that increase batch sizes adaptively to reduce minibatch gradient variance. We provide convergence guarantees under homogeneous data conditions and support our claims with image classification experiments, demonstrating the effectiveness of our strategies in training and generalization.
BiSHop: Bi-Directional Cellular Learning for Tabular Data with Generalized Sparse Modern Hopfield Model
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:We introduce the \textbf{B}i-Directional \textbf{S}parse \textbf{Hop}field Network (\textbf{BiSHop}), a novel end-to-end framework for deep tabular learning. BiSHop handles the two major challenges of deep tabular learning: non-rotationally invariant data structure and feature sparsity in tabular data. Our key motivation comes from the recent established connection between associative memory and attention mechanisms. Consequently, BiSHop uses a dual-component approach, sequentially processing data both column-wise and row-wise through two interconnected directional learning modules. Computationally, these modules house layers of generalized sparse modern Hopfield layers, a sparse extension of the modern Hopfield model with adaptable sparsity. Methodologically, BiSHop facilitates multi-scale representation learning, capturing both intra-feature and inter-feature interactions, with adaptive sparsity at each scale. Empirically, through experiments on diverse real-world datasets, we demonstrate that BiSHop surpasses current SOTA methods with significantly less HPO runs, marking it a robust solution for deep tabular learning.
SMUTF: Schema Matching Using Generative Tags and Hybrid Features
Feb 06, 2024



Abstract:We introduce SMUTF, a unique approach for large-scale tabular data schema matching (SM), which assumes that supervised learning does not affect performance in open-domain tasks, thereby enabling effective cross-domain matching. This system uniquely combines rule-based feature engineering, pre-trained language models, and generative large language models. In an innovative adaptation inspired by the Humanitarian Exchange Language, we deploy 'generative tags' for each data column, enhancing the effectiveness of SM. SMUTF exhibits extensive versatility, working seamlessly with any pre-existing pre-trained embeddings, classification methods, and generative models. Recognizing the lack of extensive, publicly available datasets for SM, we have created and open-sourced the HDXSM dataset from the public humanitarian data. We believe this to be the most exhaustive SM dataset currently available. In evaluations across various public datasets and the novel HDXSM dataset, SMUTF demonstrated exceptional performance, surpassing existing state-of-the-art models in terms of accuracy and efficiency, and} improving the F1 score by 11.84% and the AUC of ROC by 5.08%.
Beyond PID Controllers: PPO with Neuralized PID Policy for Proton Beam Intensity Control in Mu2e
Dec 28, 2023
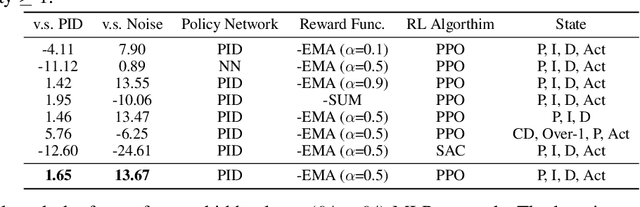
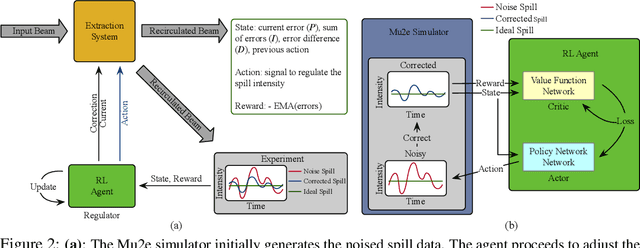

Abstract:We introduce a novel Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm aimed at addressing the challenge of maintaining a uniform proton beam intensity delivery in the Muon to Electron Conversion Experiment (Mu2e) at Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab). Our primary objective is to regulate the spill process to ensure a consistent intensity profile, with the ultimate goal of creating an automated controller capable of providing real-time feedback and calibration of the Spill Regulation System (SRS) parameters on a millisecond timescale. We treat the Mu2e accelerator system as a Markov Decision Process suitable for Reinforcement Learning (RL), utilizing PPO to reduce bias and enhance training stability. A key innovation in our approach is the integration of a neuralized Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller into the policy function, resulting in a significant improvement in the Spill Duty Factor (SDF) by 13.6%, surpassing the performance of the current PID controller baseline by an additional 1.6%. This paper presents the preliminary offline results based on a differentiable simulator of the Mu2e accelerator. It paves the groundwork for real-time implementations and applications, representing a crucial step towards automated proton beam intensity control for the Mu2e experiment.
On Sparse Modern Hopfield Model
Sep 22, 2023Abstract:We introduce the sparse modern Hopfield model as a sparse extension of the modern Hopfield model. Like its dense counterpart, the sparse modern Hopfield model equips a memory-retrieval dynamics whose one-step approximation corresponds to the sparse attention mechanism. Theoretically, our key contribution is a principled derivation of a closed-form sparse Hopfield energy using the convex conjugate of the sparse entropic regularizer. Building upon this, we derive the sparse memory retrieval dynamics from the sparse energy function and show its one-step approximation is equivalent to the sparse-structured attention. Importantly, we provide a sparsity-dependent memory retrieval error bound which is provably tighter than its dense analog. The conditions for the benefits of sparsity to arise are therefore identified and discussed. In addition, we show that the sparse modern Hopfield model maintains the robust theoretical properties of its dense counterpart, including rapid fixed point convergence and exponential memory capacity. Empirically, we use both synthetic and real-world datasets to demonstrate that the sparse Hopfield model outperforms its dense counterpart in many situations.
Feature Programming for Multivariate Time Series Prediction
Jun 09, 2023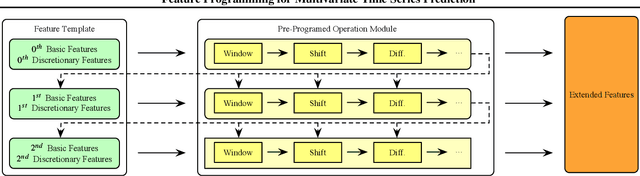
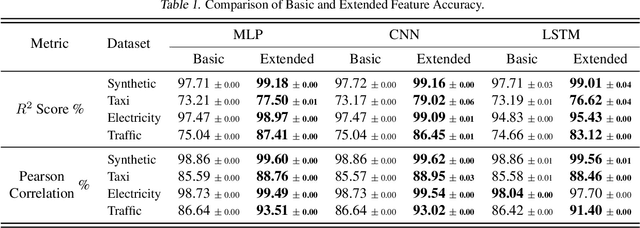
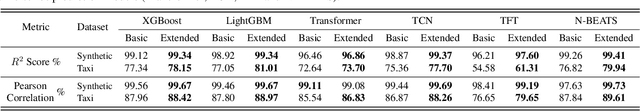
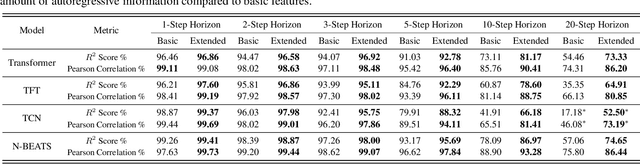
Abstract:We introduce the concept of programmable feature engineering for time series modeling and propose a feature programming framework. This framework generates large amounts of predictive features for noisy multivariate time series while allowing users to incorporate their inductive bias with minimal effort. The key motivation of our framework is to view any multivariate time series as a cumulative sum of fine-grained trajectory increments, with each increment governed by a novel spin-gas dynamical Ising model. This fine-grained perspective motivates the development of a parsimonious set of operators that summarize multivariate time series in an abstract fashion, serving as the foundation for large-scale automated feature engineering. Numerically, we validate the efficacy of our method on several synthetic and real-world noisy time series datasets.
Person-job fit estimation from candidate profile and related recruitment history with co-attention neural networks
Jun 18, 2022
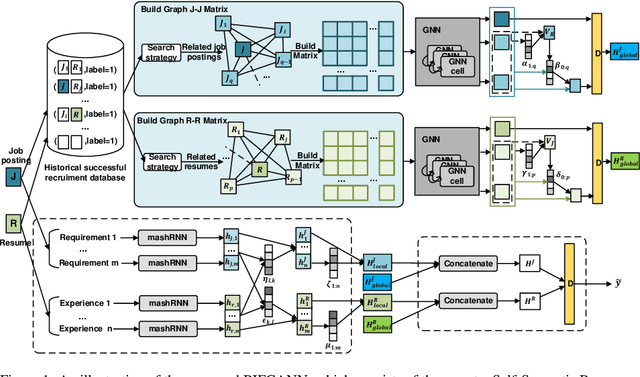
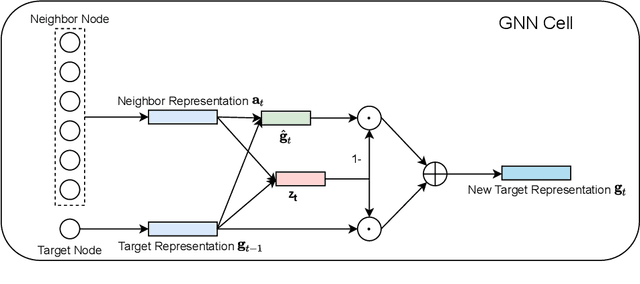
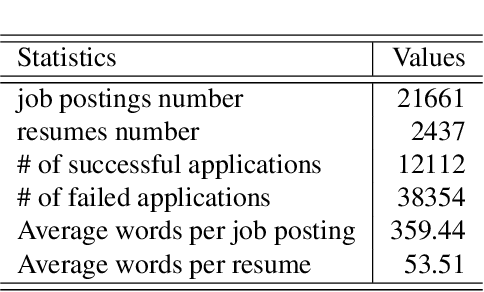
Abstract:Existing online recruitment platforms depend on automatic ways of conducting the person-job fit, whose goal is matching appropriate job seekers with job positions. Intuitively, the previous successful recruitment records contain important information, which should be helpful for the current person-job fit. Existing studies on person-job fit, however, mainly focus on calculating the similarity between the candidate resumes and the job postings on the basis of their contents, without taking the recruiters' experience (i.e., historical successful recruitment records) into consideration. In this paper, we propose a novel neural network approach for person-job fit, which estimates person-job fit from candidate profile and related recruitment history with co-attention neural networks (named PJFCANN). Specifically, given a target resume-job post pair, PJFCANN generates local semantic representations through co-attention neural networks and global experience representations via graph neural networks. The final matching degree is calculated by combining these two representations. In this way, the historical successful recruitment records are introduced to enrich the features of resumes and job postings and strengthen the current matching process. Extensive experiments conducted on a large-scale recruitment dataset verify the effectiveness of PJFCANN compared with several state-of-the-art baselines. The codes are released at: https://github.com/CCIIPLab/PJFCANN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge