Charlie Deck
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Open-Ended Learning Leads to Generally Capable Agents
Jul 31, 2021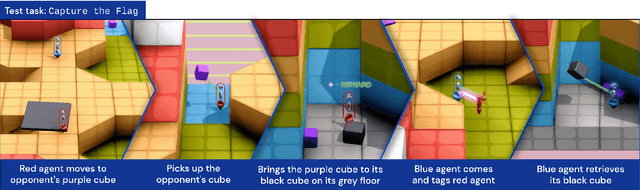
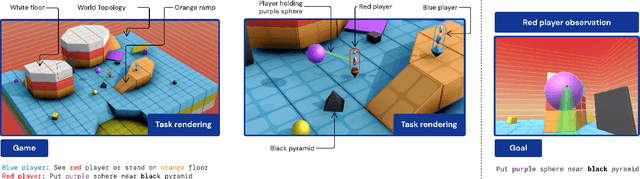
Abstract:In this work we create agents that can perform well beyond a single, individual task, that exhibit much wider generalisation of behaviour to a massive, rich space of challenges. We define a universe of tasks within an environment domain and demonstrate the ability to train agents that are generally capable across this vast space and beyond. The environment is natively multi-agent, spanning the continuum of competitive, cooperative, and independent games, which are situated within procedurally generated physical 3D worlds. The resulting space is exceptionally diverse in terms of the challenges posed to agents, and as such, even measuring the learning progress of an agent is an open research problem. We propose an iterative notion of improvement between successive generations of agents, rather than seeking to maximise a singular objective, allowing us to quantify progress despite tasks being incomparable in terms of achievable rewards. We show that through constructing an open-ended learning process, which dynamically changes the training task distributions and training objectives such that the agent never stops learning, we achieve consistent learning of new behaviours. The resulting agent is able to score reward in every one of our humanly solvable evaluation levels, with behaviour generalising to many held-out points in the universe of tasks. Examples of this zero-shot generalisation include good performance on Hide and Seek, Capture the Flag, and Tag. Through analysis and hand-authored probe tasks we characterise the behaviour of our agent, and find interesting emergent heuristic behaviours such as trial-and-error experimentation, simple tool use, option switching, and cooperation. Finally, we demonstrate that the general capabilities of this agent could unlock larger scale transfer of behaviour through cheap finetuning.
Alchemy: A structured task distribution for meta-reinforcement learning
Feb 04, 2021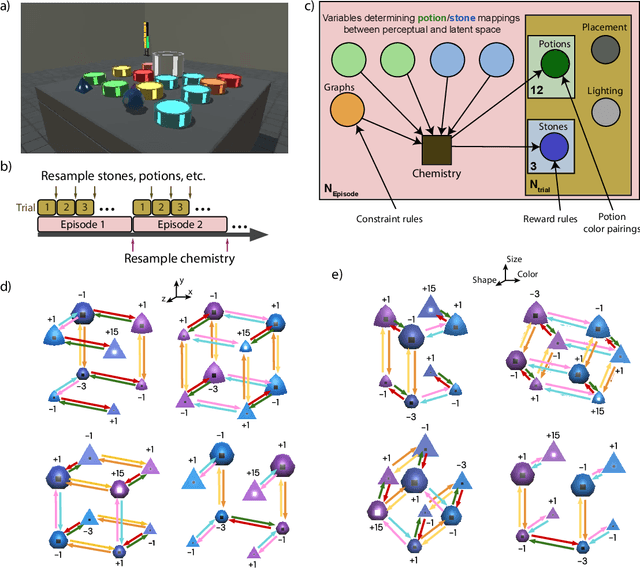
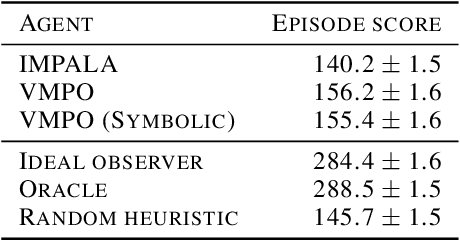
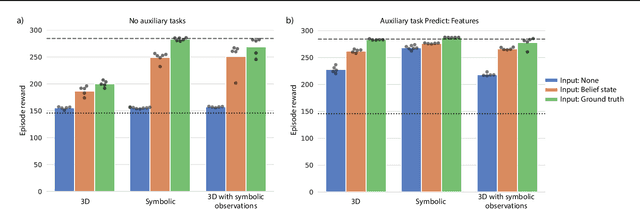
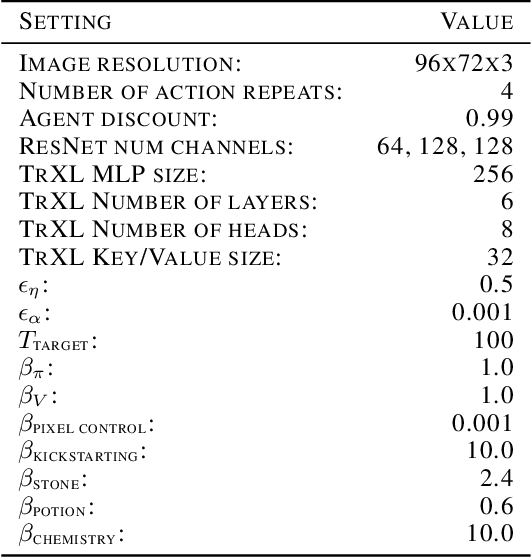
Abstract:There has been rapidly growing interest in meta-learning as a method for increasing the flexibility and sample efficiency of reinforcement learning. One problem in this area of research, however, has been a scarcity of adequate benchmark tasks. In general, the structure underlying past benchmarks has either been too simple to be inherently interesting, or too ill-defined to support principled analysis. In the present work, we introduce a new benchmark for meta-RL research, which combines structural richness with structural transparency. Alchemy is a 3D video game, implemented in Unity, which involves a latent causal structure that is resampled procedurally from episode to episode, affording structure learning, online inference, hypothesis testing and action sequencing based on abstract domain knowledge. We evaluate a pair of powerful RL agents on Alchemy and present an in-depth analysis of one of these agents. Results clearly indicate a frank and specific failure of meta-learning, providing validation for Alchemy as a challenging benchmark for meta-RL. Concurrent with this report, we are releasing Alchemy as public resource, together with a suite of analysis tools and sample agent trajectories.
Generalization of Reinforcement Learners with Working and Episodic Memory
Oct 29, 2019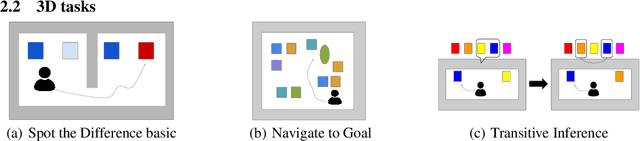
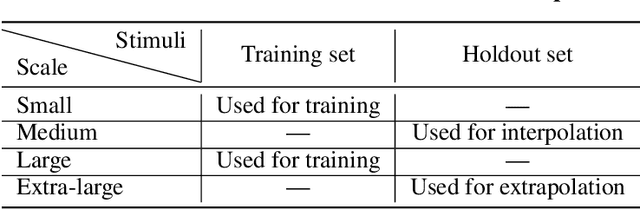
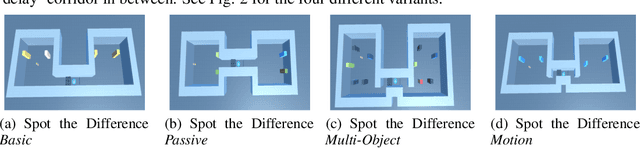
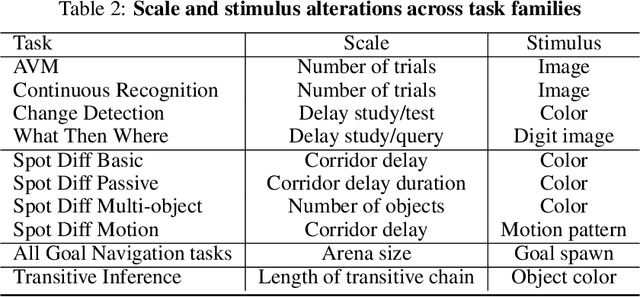
Abstract:Memory is an important aspect of intelligence and plays a role in many deep reinforcement learning models. However, little progress has been made in understanding when specific memory systems help more than others and how well they generalize. The field also has yet to see a prevalent consistent and rigorous approach for evaluating agent performance on holdout data. In this paper, we aim to develop a comprehensive methodology to test different kinds of memory in an agent and assess how well the agent can apply what it learns in training to a holdout set that differs from the training set along dimensions that we suggest are relevant for evaluating memory-specific generalization. To that end, we first construct a diverse set of memory tasks that allow us to evaluate test-time generalization across multiple dimensions. Second, we develop and perform multiple ablations on an agent architecture that combines multiple memory systems, observe its baseline models, and investigate its performance against the task suite.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge