Chang Tan
Multi-query Vehicle Re-identification: Viewpoint-conditioned Network, Unified Dataset and New Metric
May 25, 2023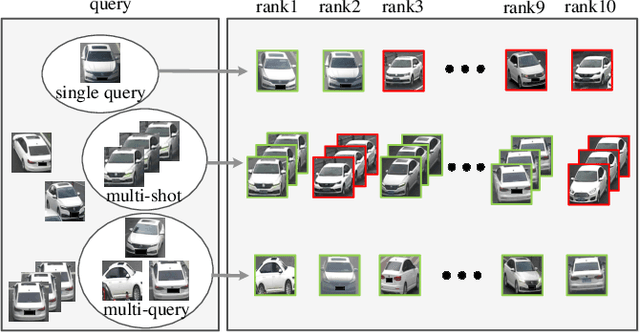
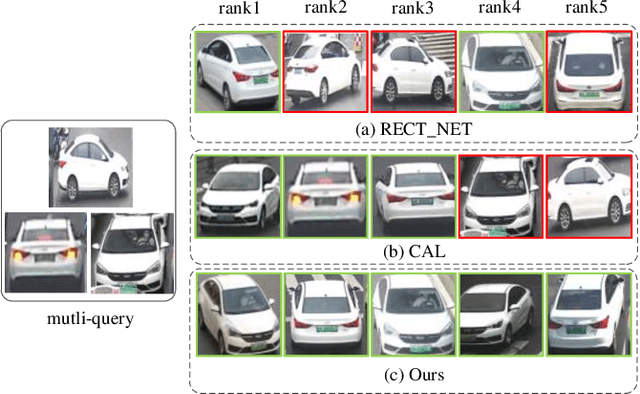
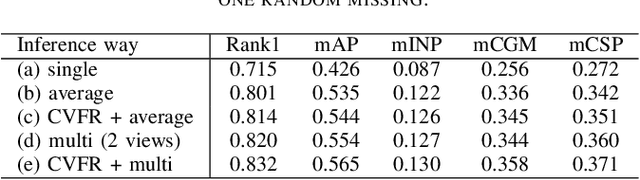
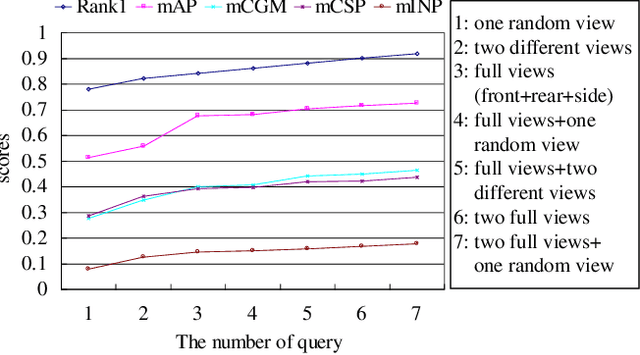
Abstract:Existing vehicle re-identification methods mainly rely on the single query, which has limited information for vehicle representation and thus significantly hinders the performance of vehicle Re-ID in complicated surveillance networks. In this paper, we propose a more realistic and easily accessible task, called multi-query vehicle Re-ID, which leverages multiple queries to overcome viewpoint limitation of single one. Based on this task, we make three major contributions. First, we design a novel viewpoint-conditioned network (VCNet), which adaptively combines the complementary information from different vehicle viewpoints, for multi-query vehicle Re-ID. Moreover, to deal with the problem of missing vehicle viewpoints, we propose a cross-view feature recovery module which recovers the features of the missing viewpoints by learnt the correlation between the features of available and missing viewpoints. Second, we create a unified benchmark dataset, taken by 6142 cameras from a real-life transportation surveillance system, with comprehensive viewpoints and large number of crossed scenes of each vehicle for multi-query vehicle Re-ID evaluation. Finally, we design a new evaluation metric, called mean cross-scene precision (mCSP), which measures the ability of cross-scene recognition by suppressing the positive samples with similar viewpoints from same camera. Comprehensive experiments validate the superiority of the proposed method against other methods, as well as the effectiveness of the designed metric in the evaluation of multi-query vehicle Re-ID.
Disentangled Generation Network for Enlarged License Plate Recognition and A Unified Dataset
Jun 02, 2022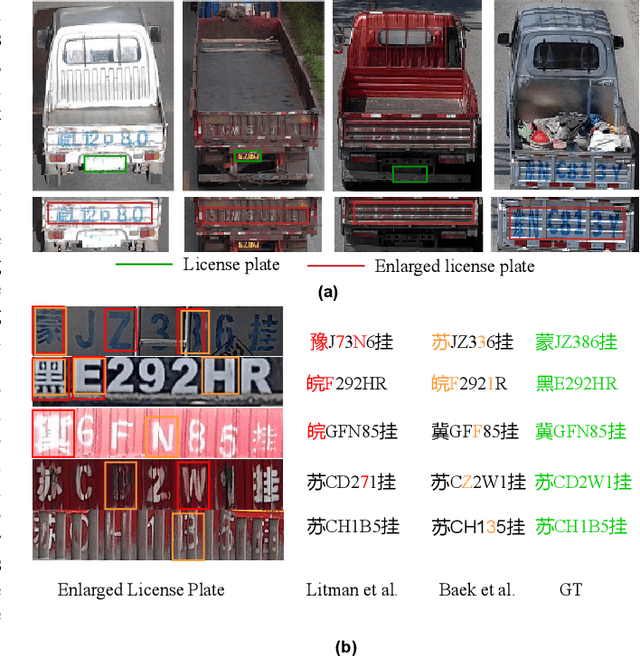
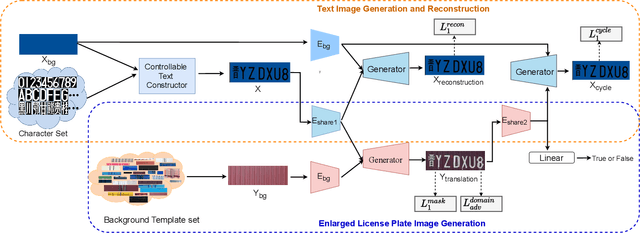
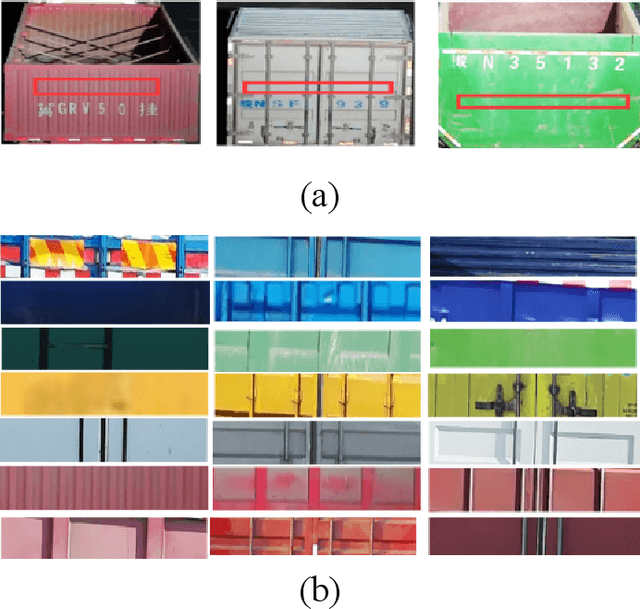
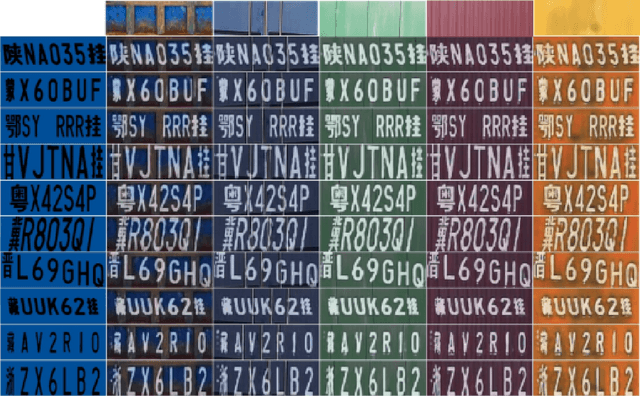
Abstract:License plate recognition plays a critical role in many practical applications, but license plates of large vehicles are difficult to be recognized due to the factors of low resolution, contamination, low illumination, and occlusion, to name a few. To overcome the above factors, the transportation management department generally introduces the enlarged license plate behind the rear of a vehicle. However, enlarged license plates have high diversity as they are non-standard in position, size, and style. Furthermore, the background regions contain a variety of noisy information which greatly disturbs the recognition of license plate characters. Existing works have not studied this challenging problem. In this work, we first address the enlarged license plate recognition problem and contribute a dataset containing 9342 images, which cover most of the challenges of real scenes. However, the created data are still insufficient to train deep methods of enlarged license plate recognition, and building large-scale training data is very time-consuming and high labor cost. To handle this problem, we propose a novel task-level disentanglement generation framework based on the Disentangled Generation Network (DGNet), which disentangles the generation into the text generation and background generation in an end-to-end manner to effectively ensure diversity and integrity, for robust enlarged license plate recognition. Extensive experiments on the created dataset are conducted, and we demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach in three representative text recognition frameworks.
Learning to Help Emergency Vehicles Arrive Faster: A Cooperative Vehicle-Road Scheduling Approach
Feb 20, 2022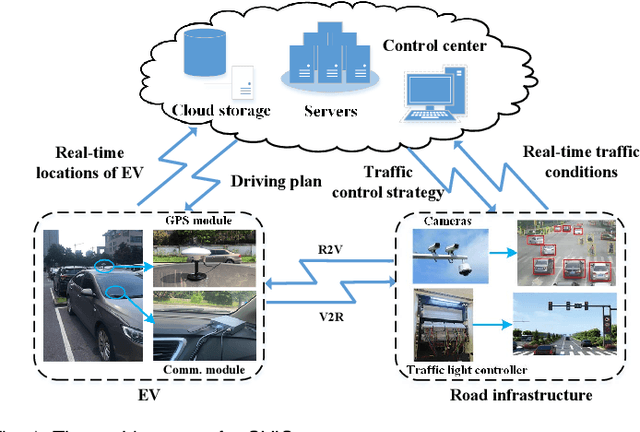
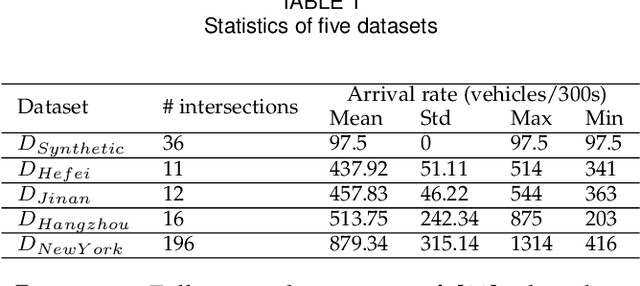
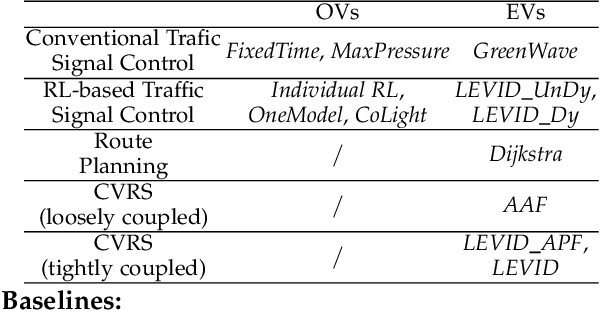
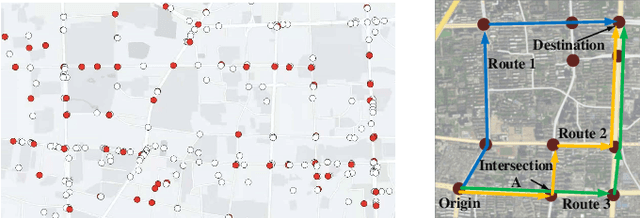
Abstract:The ever-increasing heavy traffic congestion potentially impedes the accessibility of emergency vehicles (EVs), resulting in detrimental impacts on critical services and even safety of people's lives. Hence, it is significant to propose an efficient scheduling approach to help EVs arrive faster. Existing vehicle-centric scheduling approaches aim to recommend the optimal paths for EVs based on the current traffic status while the road-centric scheduling approaches aim to improve the traffic condition and assign a higher priority for EVs to pass an intersection. With the intuition that real-time vehicle-road information interaction and strategy coordination can bring more benefits, we propose LEVID, a LEarning-based cooperative VehIcle-roaD scheduling approach including a real-time route planning module and a collaborative traffic signal control module, which interact with each other and make decisions iteratively. The real-time route planning module adapts the artificial potential field method to address the real-time changes of traffic signals and avoid falling into a local optimum. The collaborative traffic signal control module leverages a graph attention reinforcement learning framework to extract the latent features of different intersections and abstract their interplay to learn cooperative policies. Extensive experiments based on multiple real-world datasets show that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines.
Exploiting Bi-directional Global Transition Patterns and Personal Preferences for Missing POI Category Identification
Dec 31, 2021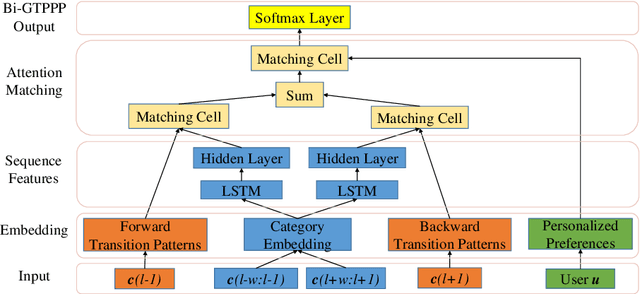
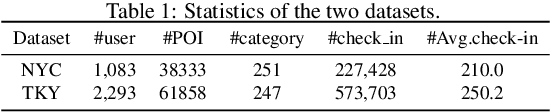
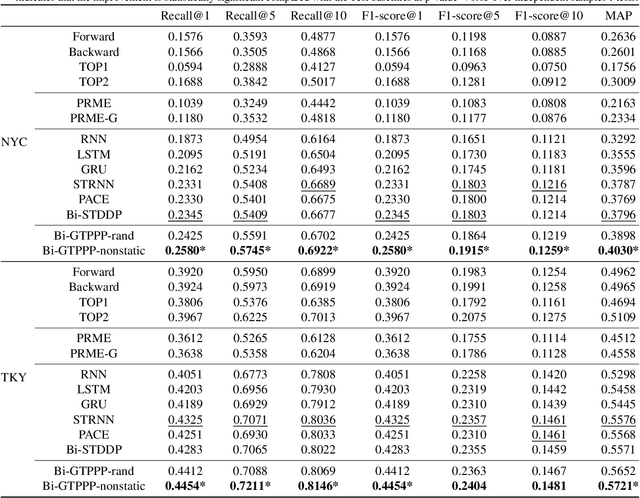
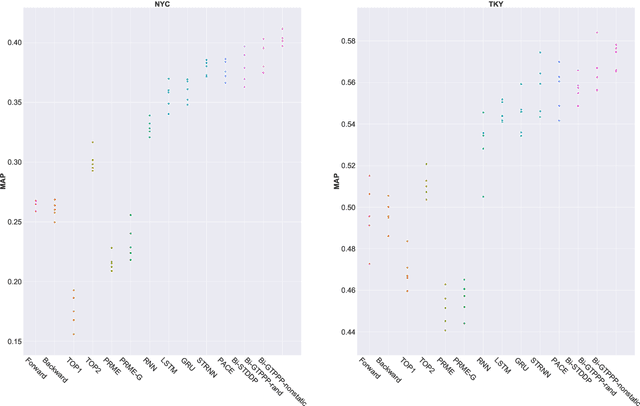
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the increasing popularity of Location-based Social Network (LBSN) services, which provides unparalleled opportunities to build personalized Point-of-Interest (POI) recommender systems. Existing POI recommendation and location prediction tasks utilize past information for future recommendation or prediction from a single direction perspective, while the missing POI category identification task needs to utilize the check-in information both before and after the missing category. Therefore, a long-standing challenge is how to effectively identify the missing POI categories at any time in the real-world check-in data of mobile users. To this end, in this paper, we propose a novel neural network approach to identify the missing POI categories by integrating both bi-directional global non-personal transition patterns and personal preferences of users. Specifically, we delicately design an attention matching cell to model how well the check-in category information matches their non-personal transition patterns and personal preferences. Finally, we evaluate our model on two real-world datasets, which clearly validate its effectiveness compared with the state-of-the-art baselines. Furthermore, our model can be naturally extended to address next POI category recommendation and prediction tasks with competitive performance.
STMARL: A Spatio-Temporal Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Approach for Traffic Light Control
Aug 28, 2019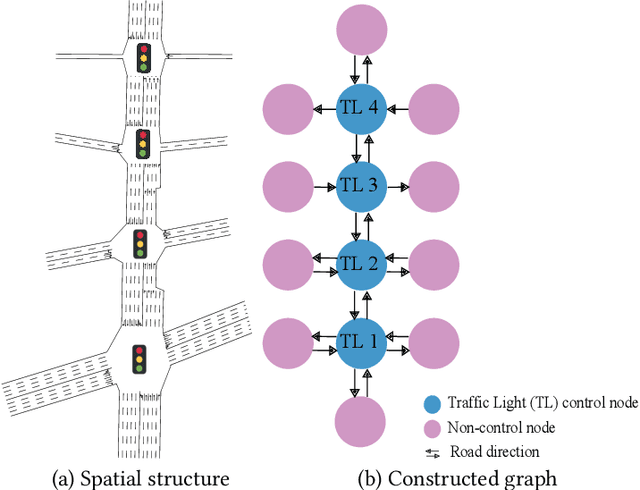
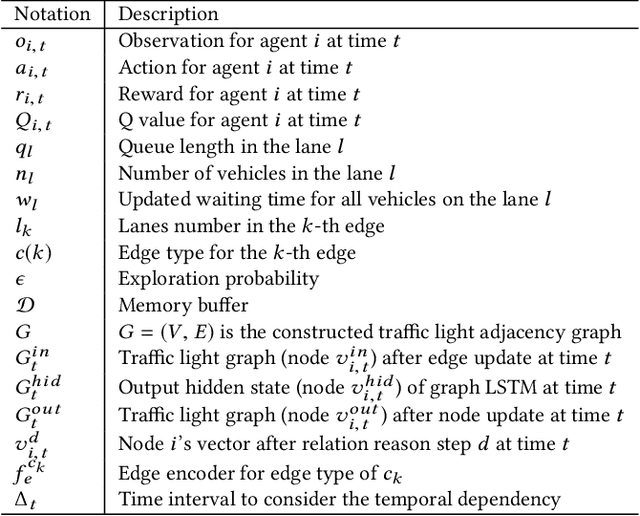

Abstract:The development of intelligent traffic light control systems is essential for smart transportation management. While some efforts have been made to optimize the use of individual traffic lights in an isolated way, related studies have largely ignored the fact that the use of multi-intersection traffic lights is spatially influenced and there is a temporal dependency of historical traffic status for current traffic light control. To that end, in this paper, we propose a novel SpatioTemporal Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (STMARL) framework for effectively capturing the spatio-temporal dependency of multiple related traffic lights and control these traffic lights in a coordinating way. Specifically, we first construct the traffic light adjacency graph based on the spatial structure among traffic lights. Then, historical traffic records will be integrated with current traffic status via Recurrent Neural Network structure. Moreover, based on the temporally-dependent traffic information, we design a Graph Neural Network based model to represent relationships among multiple traffic lights, and the decision for each traffic light will be made in a distributed way by the deep Q-learning method. Finally, the experimental results on both synthetic and real-world data have demonstrated the effectiveness of our STMARL framework, which also provides an insightful understanding of the influence mechanism among multi-intersection traffic lights.
Optimized Cost per Click in Taobao Display Advertising
Nov 01, 2018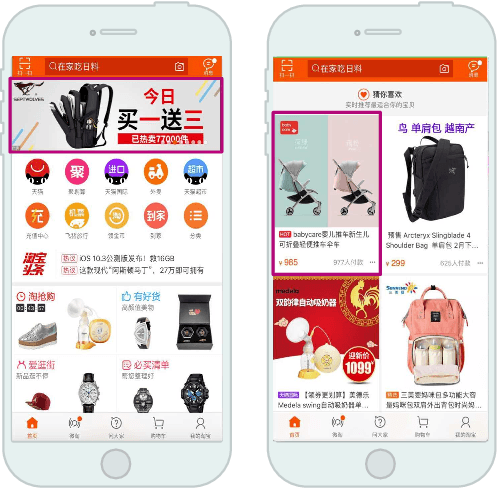
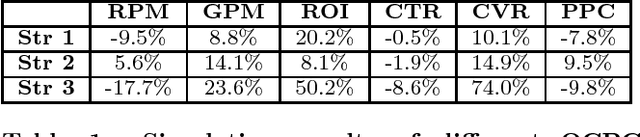


Abstract:Taobao, as the largest online retail platform in the world, provides billions of online display advertising impressions for millions of advertisers every day. For commercial purposes, the advertisers bid for specific spots and target crowds to compete for business traffic. The platform chooses the most suitable ads to display in tens of milliseconds. Common pricing methods include cost per mille (CPM) and cost per click (CPC). Traditional advertising systems target certain traits of users and ad placements with fixed bids, essentially regarded as coarse-grained matching of bid and traffic quality. However, the fixed bids set by the advertisers competing for different quality requests cannot fully optimize the advertisers' key requirements. Moreover, the platform has to be responsible for the business revenue and user experience. Thus, we proposed a bid optimizing strategy called optimized cost per click (OCPC) which automatically adjusts the bid to achieve finer matching of bid and traffic quality of page view (PV) request granularity. Our approach optimizes advertisers' demands, platform business revenue and user experience and as a whole improves traffic allocation efficiency. We have validated our approach in Taobao display advertising system in production. The online A/B test shows our algorithm yields substantially better results than previous fixed bid manner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge