Yanan Wang
SpatialV2A: Visual-Guided High-fidelity Spatial Audio Generation
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:While video-to-audio generation has achieved remarkable progress in semantic and temporal alignment, most existing studies focus solely on these aspects, paying limited attention to the spatial perception and immersive quality of the synthesized audio. This limitation stems largely from current models' reliance on mono audio datasets, which lack the binaural spatial information needed to learn visual-to-spatial audio mappings. To address this gap, we introduce two key contributions: we construct BinauralVGGSound, the first large-scale video-binaural audio dataset designed to support spatially aware video-to-audio generation; and we propose a end-to-end spatial audio generation framework guided by visual cues, which explicitly models spatial features. Our framework incorporates a visual-guided audio spatialization module that ensures the generated audio exhibits realistic spatial attributes and layered spatial depth while maintaining semantic and temporal alignment. Experiments show that our approach substantially outperforms state-of-the-art models in spatial fidelity and delivers a more immersive auditory experience, without sacrificing temporal or semantic consistency. All datasets, code, and model checkpoints will be publicly released to facilitate future research.
Learning Audio-Visual Embeddings with Inferred Latent Interaction Graphs
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Learning robust audio-visual embeddings requires bringing genuinely related audio and visual signals together while filtering out incidental co-occurrences - background noise, unrelated elements, or unannotated events. Most contrastive and triplet-loss methods use sparse annotated labels per clip and treat any co-occurrence as semantic similarity. For example, a video labeled "train" might also contain motorcycle audio and visual, because "motorcycle" is not the chosen annotation; standard methods treat these co-occurrences as negatives to true motorcycle anchors elsewhere, creating false negatives and missing true cross-modal dependencies. We propose a framework that leverages soft-label predictions and inferred latent interactions to address these issues: (1) Audio-Visual Semantic Alignment Loss (AV-SAL) trains a teacher network to produce aligned soft-label distributions across modalities, assigning nonzero probability to co-occurring but unannotated events and enriching the supervision signal. (2) Inferred Latent Interaction Graph (ILI) applies the GRaSP algorithm to teacher soft labels to infer a sparse, directed dependency graph among classes. This graph highlights directional dependencies (e.g., "Train (visual)" -> "Motorcycle (audio)") that expose likely semantic or conditional relationships between classes; these are interpreted as estimated dependency patterns. (3) Latent Interaction Regularizer (LIR): A student network is trained with both metric loss and a regularizer guided by the ILI graph, pulling together embeddings of dependency-linked but unlabeled pairs in proportion to their soft-label probabilities. Experiments on AVE and VEGAS benchmarks show consistent improvements in mean average precision (mAP), demonstrating that integrating inferred latent interactions into embedding learning enhances robustness and semantic coherence.
DirectSwap: Mask-Free Cross-Identity Training and Benchmarking for Expression-Consistent Video Head Swapping
Dec 10, 2025
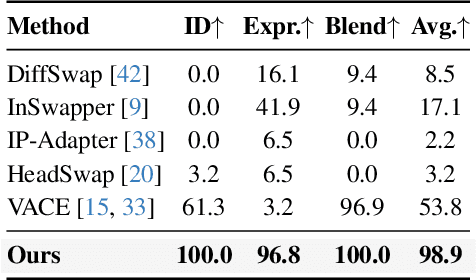
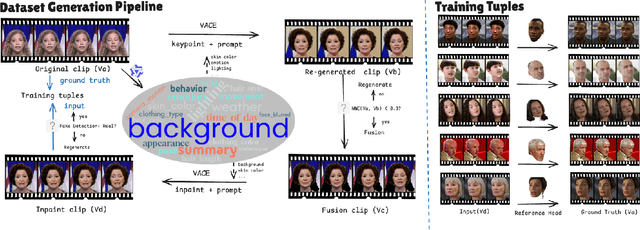
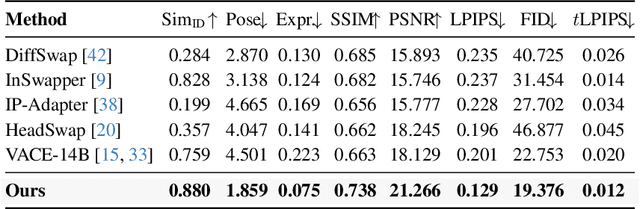
Abstract:Video head swapping aims to replace the entire head of a video subject, including facial identity, head shape, and hairstyle, with that of a reference image, while preserving the target body, background, and motion dynamics. Due to the lack of ground-truth paired swapping data, prior methods typically train on cross-frame pairs of the same person within a video and rely on mask-based inpainting to mitigate identity leakage. Beyond potential boundary artifacts, this paradigm struggles to recover essential cues occluded by the mask, such as facial pose, expressions, and motion dynamics. To address these issues, we prompt a video editing model to synthesize new heads for existing videos as fake swapping inputs, while maintaining frame-synchronized facial poses and expressions. This yields HeadSwapBench, the first cross-identity paired dataset for video head swapping, which supports both training (\TrainNum{} videos) and benchmarking (\TestNum{} videos) with genuine outputs. Leveraging this paired supervision, we propose DirectSwap, a mask-free, direct video head-swapping framework that extends an image U-Net into a video diffusion model with a motion module and conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce the Motion- and Expression-Aware Reconstruction (MEAR) loss, which reweights the diffusion loss per pixel using frame-difference magnitudes and facial-landmark proximity, thereby enhancing cross-frame coherence in motion and expressions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DirectSwap achieves state-of-the-art visual quality, identity fidelity, and motion and expression consistency across diverse in-the-wild video scenes. We will release the source code and the HeadSwapBench dataset to facilitate future research.
RCPU: Rotation-Constrained Error Compensation for Structured Pruning of a Large Language Model
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we propose a rotation-constrained compensation method to address the errors introduced by structured pruning of large language models (LLMs). LLMs are trained on massive datasets and accumulate rich semantic knowledge in their representation space. In contrast, pruning is typically carried out with only a small amount of calibration data, which makes output mismatches unavoidable. Although direct least-squares fitting can reduce such errors, it tends to overfit to the limited calibration set, destructively modifying pretrained weights. To overcome this difficulty, we update the pruned parameters under a rotation constraint. This constrained update preserves the geometry of output representations (i.e., norms and inner products) and simultaneously re-aligns the pruned subspace with the original outputs. Furthermore, in rotation-constrained compensation, removing components that strongly contribute to the principal directions of the output makes error recovery difficult. Since input dimensions with large variance strongly affect these principal directions, we design a variance-aware importance score that ensures such dimensions are preferentially kept in the pruned model. By combining this scoring rule with rotation-constrained updates, the proposed method effectively compensates errors while retaining the components likely to be more important in a geometry-preserving manner. In the experiments, we apply the proposed method to LLaMA-7B and evaluate it on WikiText-2 and multiple language understanding benchmarks. The results demonstrate consistently better perplexity and task accuracy compared with existing baselines.
MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning: Datasets, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Outlook
Sep 17, 2025
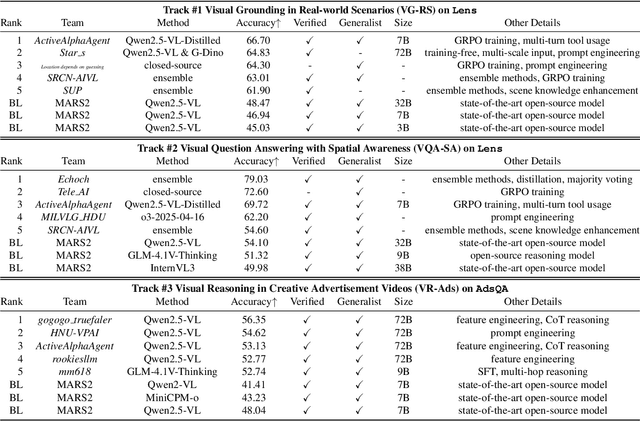

Abstract:This paper reviews the MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning. We aim to bring together different approaches in multimodal machine learning and LLMs via a large benchmark. We hope it better allows researchers to follow the state-of-the-art in this very dynamic area. Meanwhile, a growing number of testbeds have boosted the evolution of general-purpose large language models. Thus, this year's MARS2 focuses on real-world and specialized scenarios to broaden the multimodal reasoning applications of MLLMs. Our organizing team released two tailored datasets Lens and AdsQA as test sets, which support general reasoning in 12 daily scenarios and domain-specific reasoning in advertisement videos, respectively. We evaluated 40+ baselines that include both generalist MLLMs and task-specific models, and opened up three competition tracks, i.e., Visual Grounding in Real-world Scenarios (VG-RS), Visual Question Answering with Spatial Awareness (VQA-SA), and Visual Reasoning in Creative Advertisement Videos (VR-Ads). Finally, 76 teams from the renowned academic and industrial institutions have registered and 40+ valid submissions (out of 1200+) have been included in our ranking lists. Our datasets, code sets (40+ baselines and 15+ participants' methods), and rankings are publicly available on the MARS2 workshop website and our GitHub organization page https://github.com/mars2workshop/, where our updates and announcements of upcoming events will be continuously provided.
Strawberry Robotic Operation Interface: An Open-Source Device for Collecting Dexterous Manipulation Data in Robotic Strawberry Farming
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:The strawberry farming is labor-intensive, particularly in tasks requiring dexterous manipulation such as picking occluded strawberries. To address this challenge, we present the Strawberry Robotic Operation Interface (SROI), an open-source device designed for collecting dexterous manipulation data in robotic strawberry farming. The SROI features a handheld unit with a modular end effector, a stereo robotic camera, enabling the easy collection of demonstration data in field environments. A data post-processing pipeline is introduced to extract spatial trajectories and gripper states from the collected data. Additionally, we release an open-source dataset of strawberry picking demonstrations to facilitate research in dexterous robotic manipulation. The SROI represents a step toward automating complex strawberry farming tasks, reducing reliance on manual labor.
Learn from Foundation Model: Fruit Detection Model without Manual Annotation
Nov 25, 2024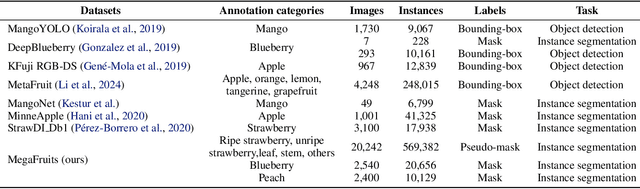
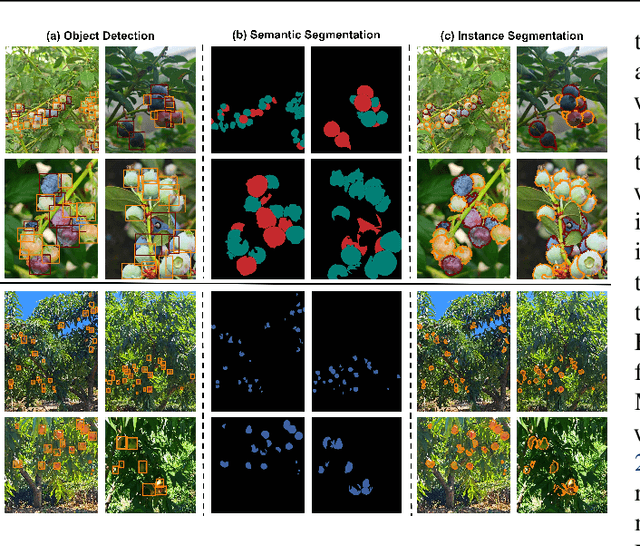
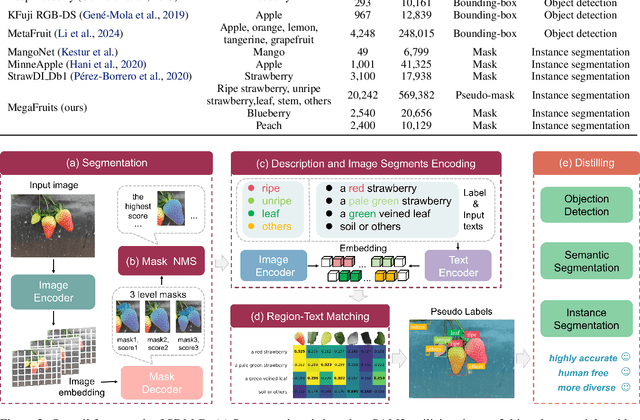
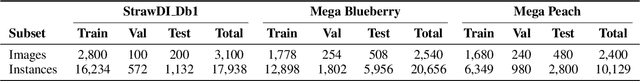

Abstract:Recent breakthroughs in large foundation models have enabled the possibility of transferring knowledge pre-trained on vast datasets to domains with limited data availability. Agriculture is one of the domains that lacks sufficient data. This study proposes a framework to train effective, domain-specific, small models from foundation models without manual annotation. Our approach begins with SDM (Segmentation-Description-Matching), a stage that leverages two foundation models: SAM2 (Segment Anything in Images and Videos) for segmentation and OpenCLIP (Open Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining) for zero-shot open-vocabulary classification. In the second stage, a novel knowledge distillation mechanism is utilized to distill compact, edge-deployable models from SDM, enhancing both inference speed and perception accuracy. The complete method, termed SDM-D (Segmentation-Description-Matching-Distilling), demonstrates strong performance across various fruit detection tasks object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation) without manual annotation. It nearly matches the performance of models trained with abundant labels. Notably, SDM-D outperforms open-set detection methods such as Grounding SAM and YOLO-World on all tested fruit detection datasets. Additionally, we introduce MegaFruits, a comprehensive fruit segmentation dataset encompassing over 25,000 images, and all code and datasets are made publicly available at https://github.com/AgRoboticsResearch/SDM-D.git.
TTT4Rec: A Test-Time Training Approach for Rapid Adaption in Sequential Recommendation
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:Sequential recommendation tasks, which aim to predict the next item a user will interact with, typically rely on models trained solely on historical data. However, in real-world scenarios, user behavior can fluctuate in the long interaction sequences, and training data may be limited to model this dynamics. To address this, Test-Time Training (TTT) offers a novel approach by using self-supervised learning during inference to dynamically update model parameters. This allows the model to adapt to new user interactions in real-time, leading to more accurate recommendations. In this paper, we propose TTT4Rec, a sequential recommendation framework that integrates TTT to better capture dynamic user behavior. By continuously updating model parameters during inference, TTT4Rec is particularly effective in scenarios where user interaction sequences are long, training data is limited, or user behavior is highly variable. We evaluate TTT4Rec on three widely-used recommendation datasets, demonstrating that it achieves performance on par with or exceeding state-of-the-art models. The codes are available at https://github.com/ZhaoqiZachYang/TTT4Rec.
Multi-object event graph representation learning for Video Question Answering
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Video question answering (VideoQA) is a task to predict the correct answer to questions posed about a given video. The system must comprehend spatial and temporal relationships among objects extracted from videos to perform causal and temporal reasoning. While prior works have focused on modeling individual object movements using transformer-based methods, they falter when capturing complex scenarios involving multiple objects (e.g., "a boy is throwing a ball in a hoop"). We propose a contrastive language event graph representation learning method called CLanG to address this limitation. Aiming to capture event representations associated with multiple objects, our method employs a multi-layer GNN-cluster module for adversarial graph representation learning, enabling contrastive learning between the question text and its relevant multi-object event graph. Our method outperforms a strong baseline, achieving up to 2.2% higher accuracy on two challenging VideoQA datasets, NExT-QA and TGIF-QA-R. In particular, it is 2.8% better than baselines in handling causal and temporal questions, highlighting its strength in reasoning multiple object-based events.
Top-down Activity Representation Learning for Video Question Answering
Sep 12, 2024Abstract:Capturing complex hierarchical human activities, from atomic actions (e.g., picking up one present, moving to the sofa, unwrapping the present) to contextual events (e.g., celebrating Christmas) is crucial for achieving high-performance video question answering (VideoQA). Recent works have expanded multimodal models (e.g., CLIP, LLaVA) to process continuous video sequences, enhancing the model's temporal reasoning capabilities. However, these approaches often fail to capture contextual events that can be decomposed into multiple atomic actions non-continuously distributed over relatively long-term sequences. In this paper, to leverage the spatial visual context representation capability of the CLIP model for obtaining non-continuous visual representations in terms of contextual events in videos, we convert long-term video sequences into a spatial image domain and finetune the multimodal model LLaVA for the VideoQA task. Our approach achieves competitive performance on the STAR task, in particular, with a 78.4% accuracy score, exceeding the current state-of-the-art score by 2.8 points on the NExTQA task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge